Product Description
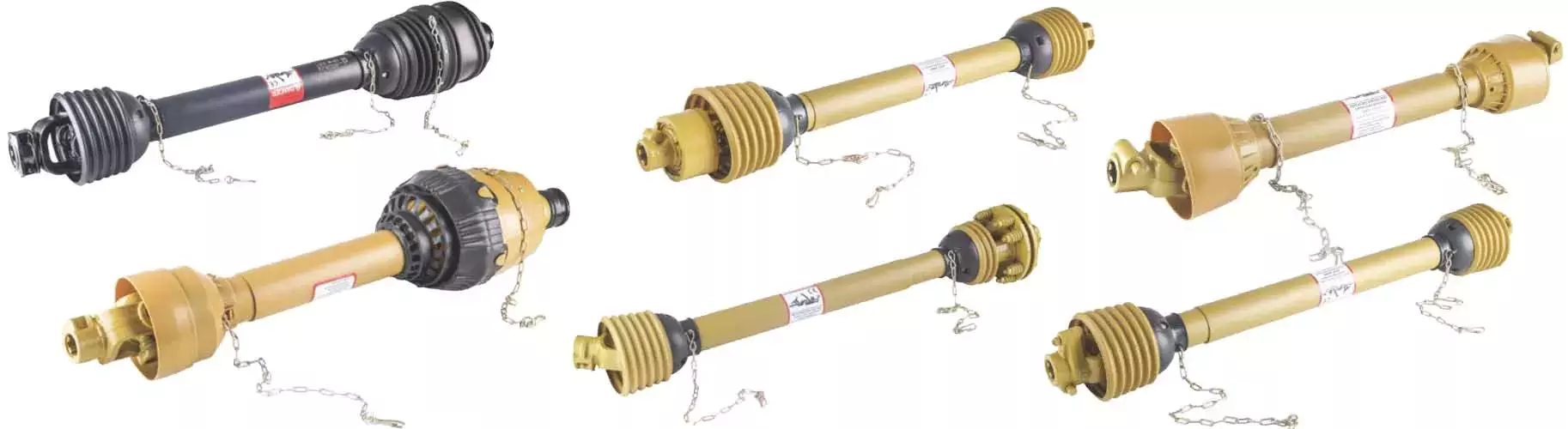
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
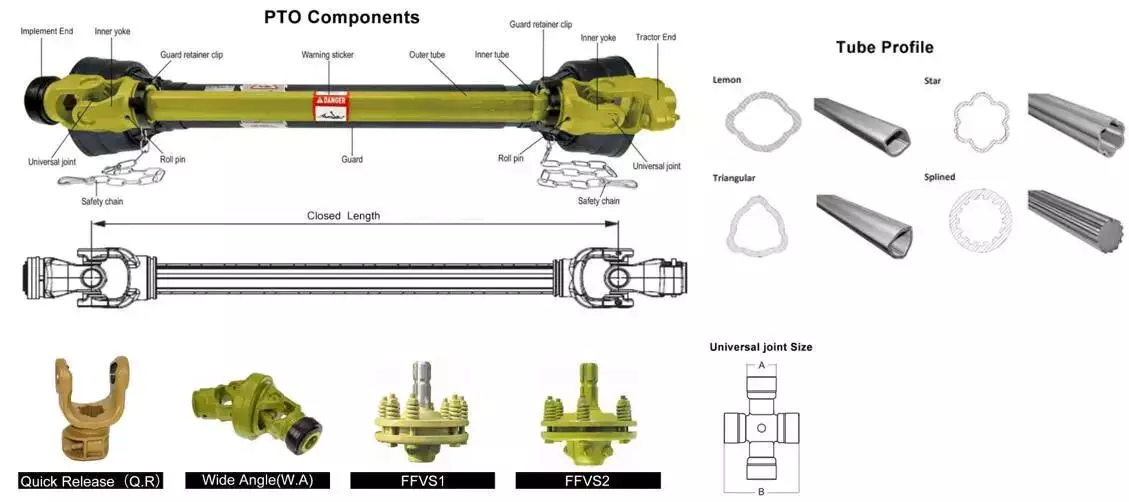
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
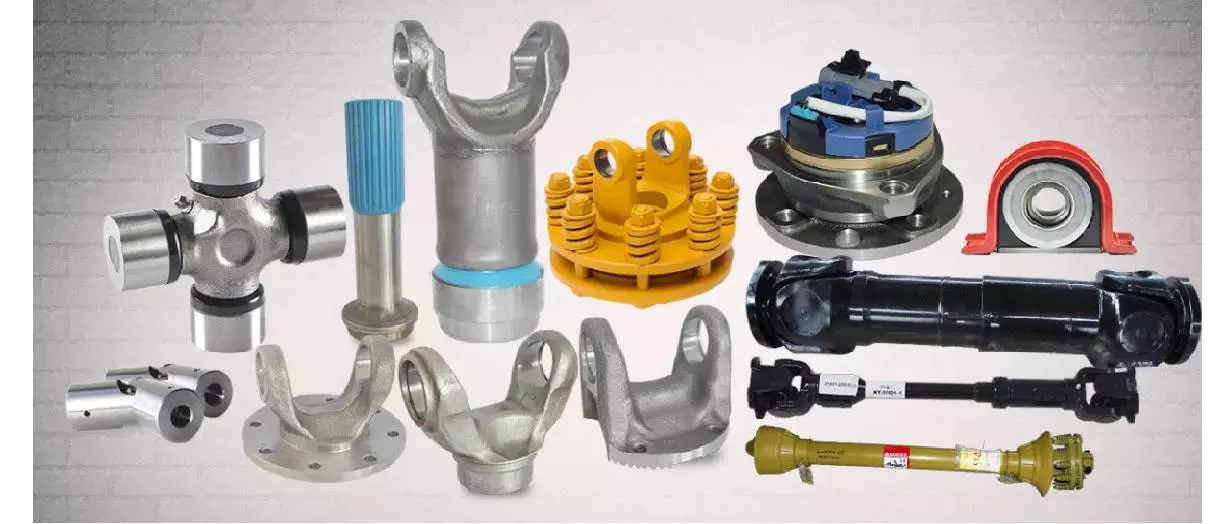
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.

What Safety Precautions Should Be Followed When Working with Rear Drive Shafts?
Working with rear drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage to the vehicle or surrounding components. Here are detailed safety precautions that should be followed when working with rear drive shafts:
1. Wear Protective Gear:
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with rear drive shafts. This includes safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from debris, gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges or moving parts, and sturdy footwear to provide foot protection in case of accidents or dropped tools.
2. Ensure Vehicle Stability:
Prioritize vehicle stability when working with rear drive shafts. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. If necessary, use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling. Additionally, if you are raising the vehicle using a jack or lift, ensure that it is securely supported with jack stands or appropriate lift points to prevent accidental movement or collapse.
3. Disconnect the Battery:
Before beginning any work on the rear drive shaft, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This precaution helps prevent accidental engagement of the starter motor or other electrical components, reducing the risk of injury or damage during the maintenance or replacement process.
4. Release Tension on the Drivetrain:
Release tension on the drivetrain components before removing the rear drive shaft. If applicable, release tension on the parking brake, shift the transmission into neutral, and engage the wheel chocks. This step helps prevent unexpected movement of the vehicle or drivetrain components while working on the drive shaft.
5. Secure the Drive Shaft:
Prior to removing the rear drive shaft, ensure it is securely supported and immobilized. Use a drive shaft support fixture or a transmission jack to hold the drive shaft in place. This prevents the drive shaft from falling or causing injury when it is disconnected from the transmission or differential.
6. Mark Alignment Points:
Before disconnecting the rear drive shaft, mark alignment points on the drive shaft and the surrounding components. This will help ensure proper reinstallation and alignment during assembly. Marking the orientation of the drive shaft also aids in identifying any imbalance or misalignment issues that may arise during reinstallation.
7. Use Proper Tools and Techniques:
Always use the appropriate tools and techniques when working with rear drive shafts. Use socket wrenches, torque wrenches, and other specialized tools designed for drive shaft removal and installation. Avoid using improper tools or excessive force, as this can lead to damage or personal injury. Follow manufacturer guidelines and service manuals for specific procedures and torque specifications.
8. Handle with Care:
Handle the rear drive shaft with care to avoid unnecessary damage or injury. Avoid dropping or striking the drive shaft against hard surfaces, as this can cause dents, bends, or other structural damage. Additionally, be cautious of sharp edges or splines on the drive shaft that can cause cuts or abrasions. Always handle the drive shaft by gripping secure areas and wearing appropriate gloves for added protection.
9. Inspect for Damage and Wear:
Before reinstalling or replacing the rear drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, dents, corrosion, or loose components. Also, inspect the U-joints or CV joints for excessive play, rust, or damaged seals. If any issues are detected, it is advisable to replace the damaged parts or the entire drive shaft to ensure safe and reliable operation.
10. Follow Proper Reinstallation Procedures:
When reinstalling the rear drive shaft, follow proper procedures to ensure correct alignment and engagement with the transmission output shaft and differential input flange. Use the alignment marks made during disassembly as a guide. Tighten all fasteners to the recommended torque specifications, and ensure that all retaining clips or bolts are properly secured.
11. Test for Proper Functioning:
After completing the rear drive shaft work, conduct a thorough test to ensure proper functioning. Check for any abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks during vehicle operation. If any issues are observed, reinspect the drive shaft installation and address the problem promptly.
12. Consult Professional Assistance if Needed:
If you are uncertain about any aspect of working with rear drive shafts or encounter difficulties during the process, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician or automotive service center. Theycan provide the necessary expertise and ensure the work is carried out safely and correctly.
By following these safety precautions when working with rear drive shafts, you can help protect yourself, prevent damage to the vehicle, and maintain a safe working environment. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution throughout the entire process.
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-04-13
China manufacturer Pto Drive Shaft Driveline Cardan Power Take off Parts Adapter Tractor Spline Universal Joint Flexible Front Rear Drive Automatic Shaft Plastic Concrete Mixer
Product Description
PTO drive shaft driveline cardan power take off parts adapter tractor spline Universal joint flexible front rear drive shaft plastic concrete mixer
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Followed When Working with Rear Drive Shafts?
Working with rear drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage to the vehicle or surrounding components. Here are detailed safety precautions that should be followed when working with rear drive shafts:
1. Wear Protective Gear:
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with rear drive shafts. This includes safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from debris, gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges or moving parts, and sturdy footwear to provide foot protection in case of accidents or dropped tools.
2. Ensure Vehicle Stability:
Prioritize vehicle stability when working with rear drive shafts. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. If necessary, use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling. Additionally, if you are raising the vehicle using a jack or lift, ensure that it is securely supported with jack stands or appropriate lift points to prevent accidental movement or collapse.
3. Disconnect the Battery:
Before beginning any work on the rear drive shaft, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This precaution helps prevent accidental engagement of the starter motor or other electrical components, reducing the risk of injury or damage during the maintenance or replacement process.
4. Release Tension on the Drivetrain:
Release tension on the drivetrain components before removing the rear drive shaft. If applicable, release tension on the parking brake, shift the transmission into neutral, and engage the wheel chocks. This step helps prevent unexpected movement of the vehicle or drivetrain components while working on the drive shaft.
5. Secure the Drive Shaft:
Prior to removing the rear drive shaft, ensure it is securely supported and immobilized. Use a drive shaft support fixture or a transmission jack to hold the drive shaft in place. This prevents the drive shaft from falling or causing injury when it is disconnected from the transmission or differential.
6. Mark Alignment Points:
Before disconnecting the rear drive shaft, mark alignment points on the drive shaft and the surrounding components. This will help ensure proper reinstallation and alignment during assembly. Marking the orientation of the drive shaft also aids in identifying any imbalance or misalignment issues that may arise during reinstallation.
7. Use Proper Tools and Techniques:
Always use the appropriate tools and techniques when working with rear drive shafts. Use socket wrenches, torque wrenches, and other specialized tools designed for drive shaft removal and installation. Avoid using improper tools or excessive force, as this can lead to damage or personal injury. Follow manufacturer guidelines and service manuals for specific procedures and torque specifications.
8. Handle with Care:
Handle the rear drive shaft with care to avoid unnecessary damage or injury. Avoid dropping or striking the drive shaft against hard surfaces, as this can cause dents, bends, or other structural damage. Additionally, be cautious of sharp edges or splines on the drive shaft that can cause cuts or abrasions. Always handle the drive shaft by gripping secure areas and wearing appropriate gloves for added protection.
9. Inspect for Damage and Wear:
Before reinstalling or replacing the rear drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, dents, corrosion, or loose components. Also, inspect the U-joints or CV joints for excessive play, rust, or damaged seals. If any issues are detected, it is advisable to replace the damaged parts or the entire drive shaft to ensure safe and reliable operation.
10. Follow Proper Reinstallation Procedures:
When reinstalling the rear drive shaft, follow proper procedures to ensure correct alignment and engagement with the transmission output shaft and differential input flange. Use the alignment marks made during disassembly as a guide. Tighten all fasteners to the recommended torque specifications, and ensure that all retaining clips or bolts are properly secured.
11. Test for Proper Functioning:
After completing the rear drive shaft work, conduct a thorough test to ensure proper functioning. Check for any abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks during vehicle operation. If any issues are observed, reinspect the drive shaft installation and address the problem promptly.
12. Consult Professional Assistance if Needed:
If you are uncertain about any aspect of working with rear drive shafts or encounter difficulties during the process, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician or automotive service center. Theycan provide the necessary expertise and ensure the work is carried out safely and correctly.
By following these safety precautions when working with rear drive shafts, you can help protect yourself, prevent damage to the vehicle, and maintain a safe working environment. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution throughout the entire process.

What Is a Rear Drive Shaft and How Does It Contribute to Vehicle Propulsion?
A rear drive shaft is a component of a vehicle’s drivetrain system that connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s propulsion. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a rear drive shaft is and how it contributes to vehicle propulsion:
1. Drivetrain Connection:
The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. It is typically a tubular shaft that rotates at high speeds to transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels.
When the engine generates power, it is transmitted through the transmission or transfer case, which determines the appropriate gear ratio. The rear drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes power to the rear wheels.
2. Torque Transmission:
The primary function of the rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine to the rear wheels. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for propelling the vehicle forward.
As the engine produces torque, it is transferred to the transmission or transfer case. From there, the torque is sent through the rear drive shaft to the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque and sends it to the rear wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle.
3. Power Distribution:
The rear drive shaft plays a critical role in distributing power evenly between the rear wheels. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft ensures that power is distributed to both wheels, enabling balanced propulsion.
By transmitting torque from the engine to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to both rear wheels based on traction conditions. This power distribution ensures that both wheels contribute to vehicle propulsion and provides stability and control during acceleration and cornering.
4. Suspension Movement Compensation:
Another important function of the rear drive shaft is to compensate for the movement of the suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move up and down independently to absorb bumps, uneven road surfaces, and other disturbances.
As the suspension moves, the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential changes. The rear drive shaft accommodates this movement by expanding or contracting its length, allowing the rear wheels to move vertically while maintaining a continuous torque transmission.
5. Drive System Efficiency:
An efficiently operating rear drive shaft contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s drivetrain system. By effectively transmitting torque from the engine to the rear wheels, it minimizes power losses and ensures optimal power delivery.
Efficiency in power transmission reduces energy waste and maximizes the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. A well-maintained rear drive shaft with proper lubrication and alignment helps minimize friction and mechanical losses, maximizing the effectiveness of the drivetrain system.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft is a crucial component for engaging the front wheels for propulsion. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which then distributes power to the front and rear differentials.
By transmitting torque to the transfer case, the rear drive shaft enables four-wheel drive capability, allowing the vehicle to engage all four wheels for enhanced traction and off-road performance.
In summary, a rear drive shaft is a key component in a vehicle’s drivetrain system. It serves as a drivetrain connection, transmits torque from the engine to the rear wheels, distributes power between the rear wheels, compensates for suspension movement, enhances drive system efficiency, and facilitates four-wheel drive capability. By fulfilling these functions, the rear drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s propulsion, stability, and overall performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-12
China wholesaler Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Accommodate Variations in Length and Connection Methods?
Rear drive shafts are designed to accommodate variations in length and connection methods to ensure proper fitment and functionality in different vehicle configurations. These variations arise due to differences in vehicle size, drivetrain layout, suspension geometry, and other factors. Rear drive shafts employ several mechanisms and design considerations to adapt to these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods:
1. Telescoping Design:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate a telescoping design that allows for length adjustments. Telescoping drive shafts consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other, enabling changes in length. This design is beneficial when vehicles have adjustable suspension systems or when there is a need to accommodate variations in the distance between the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. By adjusting the telescoping sections, rear drive shafts can be extended or retracted to match the required length, ensuring proper alignment and engagement of the drivetrain components.
2. Slip Yokes:
Slip yokes are commonly used in rear drive shafts to allow for axial movement and compensate for changes in length. A slip yoke is a splined component that connects the drive shaft to the transmission output shaft. It is designed to slide in and out of the drive shaft, allowing for length adjustments. As the suspension moves or the rear axle travels up and down, the slip yoke accommodates the changes in distance between the transmission and the rear axle, maintaining constant engagement and power transfer. Slip yokes are often used in conjunction with telescoping drive shafts to provide a wider range of length adjustability.
3. Universal Joints (U-Joints) and Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Rear drive shafts utilize different types of joints, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate variations in connection methods. U-joints are commonly used in rear drive shafts and allow for angular movement between two shafts. They can handle misalignment and changes in operating angles, making them suitable for applications where the rear axle and transmission output shaft are not perfectly aligned. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in applications that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer, such as in vehicles with independent rear suspension. CV joints accommodate variations in length and allow for a wider range of articulation angles while maintaining a constant velocity of the drive shaft.
4. Flange Connections and Bolt Patterns:
Rear drive shafts feature flange connections at each end to facilitate attachment to the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. The flanges are designed with specific bolt patterns that correspond to the mating surfaces on the transmission and axle. These bolt patterns ensure proper alignment and secure attachment of the drive shaft to the drivetrain components. The bolt patterns may vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer, drivetrain configuration, and specific model. By accommodating different flange connections and bolt patterns, rear drive shafts can be compatible with a wide range of vehicles and drivetrain layouts.
5. Customization and Engineering:
In some cases, rear drive shafts may require customization and engineering to accommodate specific variations in length and connection methods. Vehicle manufacturers, aftermarket suppliers, and drivetrain specialists have the expertise to design and manufacture custom drive shafts to meet unique requirements. This may involve fabricating drive shafts with specific lengths, spline counts, or joint configurations that are not readily available in standard off-the-shelf options. Customization allows for precise adaptation of rear drive shafts to fit vehicles with non-standard drivetrain configurations or to address specific challenges posed by unique suspension setups or vehicle modifications.
In summary, rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods through telescoping designs, slip yokes, universal joints (U-joints), constant velocity (CV) joints, flange connections, bolt patterns, and customization. These features and design considerations ensure proper fitment, alignment, and engagement of the rear drive shaft in different vehicle configurations. By incorporating these mechanisms, rear drive shafts provide the flexibility and adaptability necessary to accommodate variations in length and connection methods, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse drivetrain layouts.
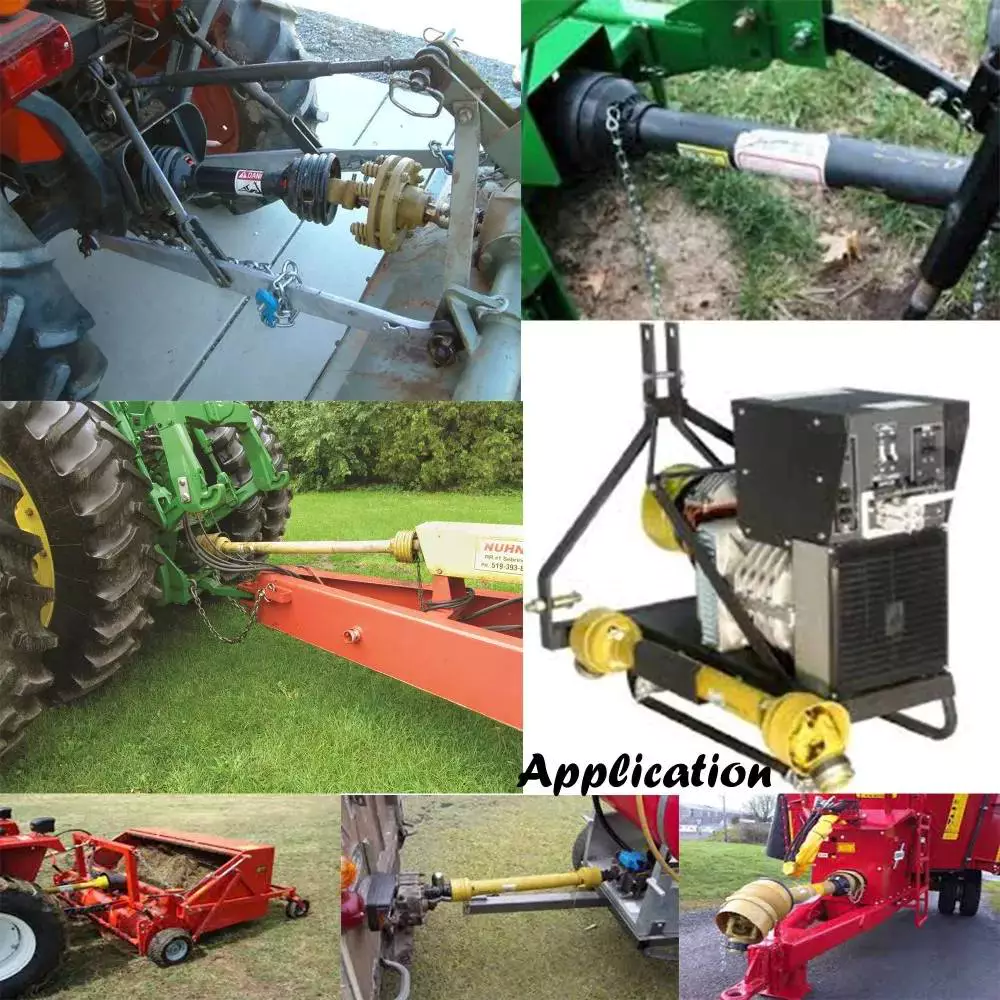

Can You Provide Real-World Examples of Vehicles Where Rear Drive Shafts Are Crucial?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in various types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) systems. Here are real-world examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial:
1. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Many sports cars and high-performance vehicles rely on rear-wheel drive configurations for their dynamic handling and performance characteristics. Rear drive shafts are crucial components in these vehicles as they transfer power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient acceleration and delivering torque for precise handling. Examples of sports cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Corvette, Porsche 911, Ford Mustang, and BMW M3.
2. Pickup Trucks and SUVs:
Pickup trucks and SUVs often employ rear-wheel drive or 4WD systems for their towing and off-road capabilities. Rear drive shafts are essential in these vehicles as they transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power distribution to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved traction and towing capacity. Examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial in the pickup truck and SUV segment include the Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado, Toyota Tacoma, and Jeep Wrangler.
3. Commercial Vehicles and Vans:
Many commercial vehicles and vans utilize rear-wheel drive for their cargo-carrying capacity and towing capabilities. Rear drive shafts are critical in these vehicles as they transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient propulsion and load-carrying capabilities. Examples of commercial vehicles and vans where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter, Ford Transit, Chevrolet Express, and Ram ProMaster.
4. Muscle Cars and Classic Cars:
Muscle cars and classic cars often feature rear-wheel drive configurations, and rear drive shafts are essential components in these vehicles. They transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels, providing the iconic rear-wheel drive performance and driving experience typically associated with these vehicles. Examples of muscle cars and classic cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Camaro, Ford Mustang, Dodge Challenger, and Chevrolet Chevelle.
5. Off-Road and 4×4 Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles and 4×4 vehicles rely on rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles often have a transfer case that distributes power to both the front and rear axles. Rear drive shafts play a critical role in transmitting torque from the transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power delivery to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved off-road traction and maneuverability. Examples of off-road and 4×4 vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Jeep Wrangler, Land Rover Defender, Toyota Land Cruiser, and Ford Bronco.
6. Luxury and Executive Vehicles:
Many luxury and executive vehicles feature rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive configurations, where rear drive shafts are essential components. Rear drive shafts transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or rear axle, providing power distribution to the rear wheels. These vehicles prioritize comfort, performance, and refined driving experiences. Examples of luxury and executive vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz S-Class, BMW 7 Series, Audi A8, and Lexus LS.
In summary, rear drive shafts are crucial in a wide range of vehicles, including sports cars, pickup trucks, SUVs, commercial vehicles, muscle cars, off-road vehicles, and luxury vehicles. They play a vital role in power transmission, torque delivery, and overall performance, enabling efficient acceleration, traction, and handling. Rear drive shafts are integral components in these vehicles, contributing to their specific characteristics and capabilities.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Impact the Performance and Drivability of Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. As a crucial component of the drivetrain system, the rear drive shaft affects various aspects of a vehicle’s operation, including power delivery, handling, stability, and overall driving experience. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts impact the performance and drivability of vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts play a vital role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, the rear drive shaft transfers this rotational force to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and vehicle movement. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the rear drive shaft directly impact a vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Traction and Stability:
The distribution of power between the rear wheels, controlled by the rear drive shaft and the rear differential, significantly affects a vehicle’s traction and stability. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to each rear wheel based on traction conditions.
Proper power distribution between the rear wheels ensures balanced traction, reducing the likelihood of wheel slippage or loss of control. This enhances the vehicle’s stability, especially during acceleration, cornering, or driving on uneven or slippery surfaces.
3. Handling and Cornering:
Rear drive shafts influence a vehicle’s handling and cornering capabilities. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, the rear drive shaft connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, resulting in a weight distribution biased towards the rear of the vehicle.
This weight distribution, combined with the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels, contributes to better traction and stability during cornering. RWD vehicles typically exhibit a more balanced and predictable handling characteristic, allowing drivers to maintain better control and confidence while navigating turns.
4. Suspension Compatibility:
Rear drive shafts also need to be compatible with a vehicle’s suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move independently, absorbing bumps, road irregularities, and other disturbances for a smoother ride.
The rear drive shaft must accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension without affecting power transmission. It achieves this by incorporating flexible joints or splines that allow the drive shaft to expand or contract in length as the suspension moves. This compatibility ensures that the rear drive shaft does not hinder the suspension’s ability to absorb shocks and maintain tire contact with the road surface.
5. Drivetrain Efficiency:
The efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain system is influenced by the performance of the rear drive shaft. A well-designed and properly maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels and optimizing overall drivetrain efficiency.
Efficient power transmission through the rear drive shaft contributes to improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy waste, and enhanced performance. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and alignment, ensures that the rear drive shaft operates smoothly and maximizes its contribution to drivetrain efficiency.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enabling four-wheel drive capability. The rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
By facilitating power distribution to all four wheels, rear drive shafts enhance the vehicle’s off-road performance, traction, and stability. Four-wheel drive capability allows the vehicle to tackle challenging terrain, slippery conditions, or uneven surfaces with improved control and maneuverability.
In summary, rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. They affect power transmission, traction, stability, handling, suspension compatibility, drivetrain efficiency, and enable four-wheel drive capability. By understanding and optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of rear drive shafts, manufacturers and drivers can enhance a vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and driving experience.


editor by CX 2024-04-11
China high quality Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.

Are There Any Emerging Trends in Rear Drive Shaft Technology, Such as Lightweight Materials?
Rear drive shaft technology has been evolving over the years, and there are indeed emerging trends, including the use of lightweight materials, that are shaping the development of rear drive shafts. These trends aim to improve overall vehicle efficiency, performance, and reliability. Here are some notable emerging trends in rear drive shaft technology:
1. Lightweight Materials:
One significant trend in rear drive shaft technology is the utilization of lightweight materials. Traditional rear drive shafts have been predominantly made of steel due to its strength and durability. However, advancements in materials engineering have introduced lightweight alternatives such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and composite materials. These lightweight materials offer comparable or even superior strength while significantly reducing the weight of the drive shaft. By reducing weight, the overall vehicle weight is decreased, leading to improved fuel efficiency, handling, and performance.
2. Composite Drive Shafts:
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), are gaining popularity in rear drive shaft construction. Composite drive shafts offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent torsional rigidity, and improved damping characteristics compared to traditional steel drive shafts. The use of composites allows for weight reduction while maintaining the necessary structural integrity and performance requirements. Composite drive shafts also exhibit better resistance to corrosion and fatigue, increasing their durability and lifespan.
3. Advanced Manufacturing Techniques:
Advancements in manufacturing techniques have also impacted rear drive shaft technology. Techniques such as automated filament winding and resin transfer molding enable the production of complex shapes and optimized designs for drive shafts. These advanced manufacturing processes allow for precise control over the fiber orientation and resin distribution in composite drive shafts, resulting in enhanced strength, stiffness, and overall performance.
4. Integration of Sensors:
Another emerging trend is the integration of sensors within rear drive shafts. By incorporating sensors, such as strain gauges or torque sensors, into the drive shafts, manufacturers can monitor various parameters, including torque transmission, vibrations, and temperature. This data can be utilized for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimizing vehicle performance. Sensor integration enables early detection of potential issues, improving reliability and reducing the risk of drive shaft failures.
5. Adaptive Drive Shaft Systems:
Some manufacturers are developing adaptive drive shaft systems that can actively adjust torsional stiffness based on driving conditions. These systems utilize technologies like electromagnetic clutches or hydraulic mechanisms to vary the stiffness of the drive shaft. By adapting to different driving situations, such as cornering, acceleration, or off-road conditions, adaptive drive shaft systems can optimize power delivery, improve traction, and enhance vehicle stability.
6. Electric Drive Shafts:
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, electric drive shafts are becoming a notable trend. In these vehicles, electric motors are often integrated into the drivetrain, eliminating the need for a traditional mechanical drive shaft. Instead, electric drive shafts transmit torque from the electric motor to the wheels using electrical power. Electric drive shafts offer efficient power transmission, precise control, and the potential for regenerative braking, contributing to the overall performance and energy efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles.
7. Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Manufacturers are also focusing on reducing noise and vibration levels associated with rear drive shafts. Advanced design techniques, improved material damping properties, and precision manufacturing contribute to minimizing unwanted vibrations and noise transmission to the vehicle’s cabin. By reducing noise and vibration, occupants experience improved comfort and a quieter driving experience.
In summary, emerging trends in rear drive shaft technology include the use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum and composites, advanced manufacturing techniques, sensor integration, adaptive drive shaft systems, electric drive shafts, and efforts to reduce noise and vibrations. These trends aim to enhance vehicle efficiency, performance, durability, and overall driving experience.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Impact the Performance and Drivability of Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. As a crucial component of the drivetrain system, the rear drive shaft affects various aspects of a vehicle’s operation, including power delivery, handling, stability, and overall driving experience. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts impact the performance and drivability of vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts play a vital role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, the rear drive shaft transfers this rotational force to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and vehicle movement. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the rear drive shaft directly impact a vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Traction and Stability:
The distribution of power between the rear wheels, controlled by the rear drive shaft and the rear differential, significantly affects a vehicle’s traction and stability. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to each rear wheel based on traction conditions.
Proper power distribution between the rear wheels ensures balanced traction, reducing the likelihood of wheel slippage or loss of control. This enhances the vehicle’s stability, especially during acceleration, cornering, or driving on uneven or slippery surfaces.
3. Handling and Cornering:
Rear drive shafts influence a vehicle’s handling and cornering capabilities. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, the rear drive shaft connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, resulting in a weight distribution biased towards the rear of the vehicle.
This weight distribution, combined with the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels, contributes to better traction and stability during cornering. RWD vehicles typically exhibit a more balanced and predictable handling characteristic, allowing drivers to maintain better control and confidence while navigating turns.
4. Suspension Compatibility:
Rear drive shafts also need to be compatible with a vehicle’s suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move independently, absorbing bumps, road irregularities, and other disturbances for a smoother ride.
The rear drive shaft must accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension without affecting power transmission. It achieves this by incorporating flexible joints or splines that allow the drive shaft to expand or contract in length as the suspension moves. This compatibility ensures that the rear drive shaft does not hinder the suspension’s ability to absorb shocks and maintain tire contact with the road surface.
5. Drivetrain Efficiency:
The efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain system is influenced by the performance of the rear drive shaft. A well-designed and properly maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels and optimizing overall drivetrain efficiency.
Efficient power transmission through the rear drive shaft contributes to improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy waste, and enhanced performance. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and alignment, ensures that the rear drive shaft operates smoothly and maximizes its contribution to drivetrain efficiency.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enabling four-wheel drive capability. The rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
By facilitating power distribution to all four wheels, rear drive shafts enhance the vehicle’s off-road performance, traction, and stability. Four-wheel drive capability allows the vehicle to tackle challenging terrain, slippery conditions, or uneven surfaces with improved control and maneuverability.
In summary, rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. They affect power transmission, traction, stability, handling, suspension compatibility, drivetrain efficiency, and enable four-wheel drive capability. By understanding and optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of rear drive shafts, manufacturers and drivers can enhance a vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and driving experience.


editor by CX 2024-04-09
China OEM Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What Maintenance Practices Are Essential for Prolonging the Lifespan of Rear Drive Shafts?
Maintaining rear drive shafts is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. By following proper maintenance practices, you can prolong the lifespan of rear drive shafts and prevent premature failures. Here are the key maintenance practices that are essential for maximizing the lifespan of rear drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is crucial for identifying any early signs of wear, damage, or misalignment in the rear drive shaft. Inspect the drive shaft for any visible cracks, dents, or corrosion. Pay attention to the condition of the universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, as they are prone to wear. Look for excessive play or looseness in the joints, and check for leaks or torn boots that could allow dirt and moisture to enter. Regular inspections help catch potential issues before they escalate and cause significant damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of the drive shaft’s u-joints or CV joints is critical for reducing friction, preventing wear, and maintaining smooth operation. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the recommended lubricant and interval for greasing the joints. Use high-quality lubricants that are compatible with the specific joint type and follow the correct greasing procedure. Insufficient lubrication can lead to accelerated wear and premature failure of the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the joints’ condition during the greasing process to ensure they are adequately lubricated and in good working order.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Keep the rear drive shaft properly balanced and aligned to prevent vibrations and excessive stress on the drivetrain components. If you notice vibrations, especially at higher speeds, have the drive shaft’s balance checked by a professional. Imbalances can occur due to the accumulation of dirt or debris, damaged balancing weights, or wear on the drive shaft. Similarly, if you experience driveline vibrations or notice uneven tire wear, it may indicate misalignment. Have the drive shaft alignment checked and adjusted as necessary. Proper balancing and alignment contribute to a smoother and more reliable operation, minimizing wear on the drive shaft.
4. Protection from Moisture and Contaminants:
Rear drive shafts are susceptible to moisture, dirt, and other contaminants that can lead to corrosion, accelerated wear, and joint failure. Avoid driving through deep water or muddy conditions that can submerge or coat the drive shaft with corrosive substances. If the drive shaft becomes wet or dirty, clean it promptly using a gentle stream of water and mild soap, and ensure it is thoroughly dried. Applying a protective coating or lubricant to exposed surfaces can help prevent corrosion. Additionally, inspect and replace damaged or torn joint boots to prevent dirt and moisture from entering and causing damage.
5. Proper Torque and Fastener Inspection:
Ensure that all fasteners, such as bolts and nuts, are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to vibrations, misalignment, and damage to the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the fasteners for any signs of loosening or damage and tighten them as necessary. During maintenance or repairs that involve removing the drive shaft, ensure that the fasteners are properly reinstalled and torqued to the recommended specifications. Following the correct torque values and fastener inspection practices helps maintain the integrity and safety of the rear drive shaft.
6. Professional Maintenance and Repairs:
While some maintenance tasks can be performed by vehicle owners, certain maintenance and repair procedures are best left to professionals with specialized knowledge and equipment. If you encounter significant issues, such as severe wear, damaged joints, or suspected balance or alignment problems, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or drivetrain specialist. They can conduct thorough inspections, provide accurate diagnoses, and perform the necessary repairs or replacements to ensure the rear drive shaft’s longevity and proper functioning.
7. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to your vehicle’s rear drive shaft. Manufacturers provide valuable information regarding maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, inspection procedures, and other important considerations. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that you follow the best practices and requirements specified for your particular drive shaft model, contributing to its prolonged lifespan.
In summary, regular inspection, proper lubrication, balancing and alignment, protection from moisture and contaminants, proper torque and fastener inspection, professional maintenance and repairs when necessary, and following manufacturer guidelines are essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of rear drive shafts. By implementing these practices, you can enhance the reliability, durability, and performanceof the rear drive shaft, ultimately extending its lifespan and reducing the risk of unexpected failures or costly repairs.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Contribute to the Overall Performance of Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in the overall performance of rear-wheel-drive (RWD) vehicles. They are responsible for transferring torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, which then distributes power to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to the overall performance of RWD vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing for propulsion and forward motion. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission or transfer case to the rear drive shaft. The drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes the power to the rear wheels. The efficiency and effectiveness of this power transmission process directly impact the acceleration, speed, and overall performance of the vehicle.
2. Torque Delivery:
Rear drive shafts ensure efficient torque delivery to the rear wheels, enabling traction and propulsion. By connecting the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, the drive shaft transfers torque generated by the engine to the wheels. The rear wheels receive this torque, allowing them to grip the road surface and propel the vehicle forward. The ability of the rear drive shaft to effectively deliver torque contributes to improved acceleration, responsiveness, and overall performance of RWD vehicles.
3. Weight Distribution:
Rear drive shafts contribute to the proper weight distribution in RWD vehicles. Since the engine is typically positioned at the front of the vehicle, the rear drive shaft helps balance the weight distribution by transferring power to the rear wheels. This balanced weight distribution enhances overall stability, handling, and cornering capabilities. It allows for better control of the vehicle and helps optimize the performance during various driving conditions.
4. Handling and Stability:
Rear drive shafts significantly influence the handling and stability of RWD vehicles. By delivering torque to the rear wheels, the drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s rear-wheel traction. This configuration provides better weight transfer during acceleration, which improves traction and reduces the chances of wheel spin. The rear drive shaft also aids in maintaining stability during cornering by helping to distribute the vehicle’s weight more evenly. RWD vehicles are known for their balanced and predictable handling characteristics, and the rear drive shaft plays a vital role in achieving these attributes.
5. Performance in Various Conditions:
Rear drive shafts impact the performance of RWD vehicles in different driving conditions. In dry or high-grip situations, the rear-wheel traction provided by the drive shaft enables quick acceleration and efficient power delivery. RWD vehicles often exhibit superior handling characteristics in these conditions due to the balanced weight distribution and the rear drive shaft’s ability to transfer torque effectively. However, in low-traction conditions such as rain, snow, or off-road situations, RWD vehicles may require additional driver skill and careful throttle control to maintain traction and stability.
6. Customization and Performance Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can be customized or upgraded to enhance the performance of RWD vehicles. For example, performance-oriented drive shafts made from lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can reduce rotational mass, improving overall vehicle agility and responsiveness. Upgraded drive shafts with strengthened components can handle increased torque and power outputs in high-performance applications. Customization and upgrades to the rear drive shaft allow vehicle owners to tailor the performance characteristics to their specific needs and preferences.
7. Maintenance and Service:
Regular maintenance and service of rear drive shafts are essential for maintaining optimal performance. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and addressing any issues such as worn U-joints or CV joints can prevent driveline vibrations, reduce power losses, and ensure smooth torque transmission. Proper maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the rear drive shaft, allowing it to continue supporting the overall performance of the RWD vehicle.
In summary, rear drive shafts are integral to the overall performance of RWD vehicles. They facilitate power transmission, torque delivery, and weight distribution, contributing to acceleration, traction, handling, and stability. The rear drive shaft’s ability to efficiently transfer torque to the rear wheels is key to the performance characteristics of RWD vehicles. Through customization, upgrades, and regular maintenance, rear drive shafts can be optimized to further enhance the performance of RWD vehicles in various driving conditions and applications.

What Benefits Do Properly Functioning Rear Drive Shafts Offer for Vehicle Dynamics?
A properly functioning rear drive shaft offers several benefits for vehicle dynamics. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power, distributing torque, and maintaining stability, which directly impact the performance and handling characteristics of a vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that properly functioning rear drive shafts offer for vehicle dynamics:
1. Power Delivery:
A properly functioning rear drive shaft ensures efficient power delivery from the engine or transmission to the wheels. It facilitates the transfer of torque, generated by the engine, to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and acceleration. A well-maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels, resulting in improved vehicle performance.
2. Balanced Traction:
The rear drive shaft, in conjunction with the rear differential, plays a key role in distributing torque between the rear wheels. This torque distribution ensures balanced traction, especially during acceleration and cornering. Properly functioning rear drive shafts help optimize power distribution, reducing the chances of wheel slippage and providing better grip and stability on various road surfaces.
3. Enhanced Stability:
Stability is a crucial aspect of vehicle dynamics, and rear drive shafts contribute to maintaining stability during various driving conditions. By enabling torque distribution to the rear wheels, the rear drive shaft helps prevent oversteer or understeer tendencies, particularly during cornering. It allows the rear wheels to better grip the road, enhancing the vehicle’s stability and control.
4. Improved Handling:
A properly functioning rear drive shaft contributes to improved handling characteristics of a vehicle. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) configurations, the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels results in a more balanced weight distribution, with a bias towards the rear. This weight distribution enhances the vehicle’s handling by providing better traction and control, especially during cornering maneuvers.
5. Responsiveness:
Properly functioning rear drive shafts contribute to the overall responsiveness of a vehicle. They ensure prompt power delivery and torque transfer, allowing the vehicle to respond quickly to driver inputs. This responsiveness enhances the driving experience, providing a direct and engaging connection between the driver and the road.
6. Off-Road Capability:
For vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, properly functioning rear drive shafts are essential for off-road capability. They enable power distribution to both the front and rear wheels, enhancing traction and control on challenging terrain. By maintaining proper torque transfer, rear drive shafts ensure that the vehicle can navigate rough surfaces, steep inclines, and other off-road obstacles with improved capability and confidence.
7. Drivetrain Efficiency:
Efficient power transmission through properly functioning rear drive shafts contributes to overall drivetrain efficiency. They minimize power losses, mechanical friction, and energy waste, allowing more power to reach the wheels. This not only enhances vehicle performance but also improves fuel efficiency and optimizes the utilization of available power.
In summary, properly functioning rear drive shafts offer several benefits for vehicle dynamics. They ensure efficient power delivery, balanced traction, enhanced stability, improved handling, responsiveness, off-road capability, and drivetrain efficiency. By maintaining and optimizing rear drive shaft performance, manufacturers and drivers can enhance the overall driving experience, vehicle performance, and handling characteristics.


editor by CX 2024-04-02
China wholesaler Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
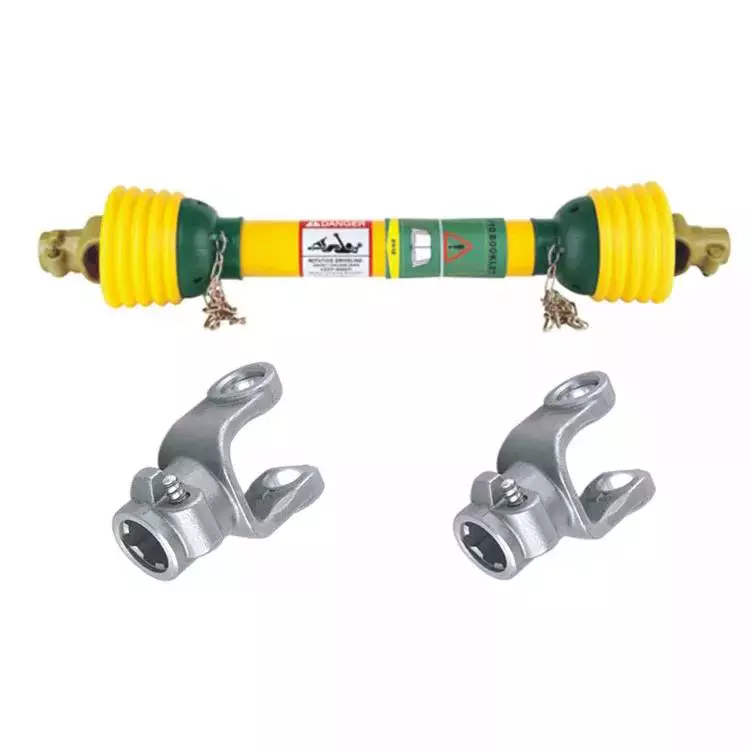

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Efficient Power Transfer While Maintaining Balance?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. At the same time, they must maintain balance to prevent vibrations, reduce stress on drivetrain components, and enhance overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve efficient power transfer while maintaining balance:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully designed and manufactured to achieve balance. Balance refers to the distribution of mass along the length of the drive shaft. Imbalances can lead to vibrations and unwanted forces that affect the smooth operation of the drivetrain. To achieve balance, drive shafts are dynamically balanced during the manufacturing process. This involves adding weights or removing material at specific locations to counteract any uneven distribution of mass. By achieving balance, the drive shaft can rotate smoothly at high speeds, minimizing vibrations and ensuring efficient power transfer.
2. Proper Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are important considerations for maintaining balance. A drive shaft that is too long or too short can result in excessive deflection or bending, leading to vibrations and potential failure. Similarly, an incorrect diameter can affect the stiffness and torsional strength of the drive shaft, resulting in imbalances. Manufacturers carefully calculate the optimal length and diameter of the drive shaft based on the vehicle’s specifications and requirements to ensure proper balance and power transfer.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The selection of high-quality materials is crucial for maintaining balance in rear drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from materials such as steel or aluminum. These materials offer the necessary strength and rigidity while being lightweight. The use of high-quality materials ensures that the drive shaft can withstand the torque and rotational forces without excessive flexing or bending, which can lead to imbalances. Additionally, the materials are chosen for their ability to resist fatigue and vibration, further contributing to balanced operation.
4. Precision Manufacturing:
Rear drive shafts are manufactured with precision to maintain balance. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining, are employed to ensure the drive shaft’s dimensional accuracy and balance. The manufacturing process involves precise machining of the shaft, including the yokes, flanges, and other components, to achieve tight tolerances and minimize any deviations that could affect balance. Strict quality control measures are implemented to verify the balance of each drive shaft before it is installed in a vehicle.
5. Vibration Dampening Techniques:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate vibration dampening techniques to further enhance balance and reduce unwanted vibrations. These techniques may include the use of balancing weights, dampers, or vibration-absorbing materials. Balancing weights can be strategically placed along the drive shaft to counteract any remaining imbalances. Dampers, such as rubber or elastomer components, are employed to absorb and dissipate vibrations, preventing them from propagating throughout the drivetrain. By minimizing vibrations, these techniques help maintain overall balance and contribute to efficient power transfer.
6. Universal Joints or Constant Velocity Joints:
Rear drive shafts incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate changes in angles and maintain balance. These joints allow for angular movement and compensate for variations in the alignment between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. By allowing the drive shaft to flex and articulate, these joints help prevent binding, minimize stress on the drivetrain components, and maintain balance throughout the range of motion.
7. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
Maintaining balance in rear drive shafts requires regular maintenance and inspection. Over time, components may wear or become damaged, leading to imbalances. It is important to periodically inspect the drive shaft for signs of wear, such as worn u-joints or damaged CV joints. Additionally, proper lubrication of the joints and ensuring the drive shaft is properly installed and aligned are essential for maintaining balance. Routine maintenance and inspections help detect and address any issues that could affect the drive shaft’s balance and overall performance.
In summary, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through a combination of balanced design, proper length and diameter, high-quality materials, precision manufacturing, vibration dampening techniques, flexible joints, and regular maintenance. By achieving and maintaining balance, rear drive shafts contribute to smooth operation, minimize vibrations, and enhance the overall performance and longevity of the drivetrain system.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Enhance the Traction and Stability of Off-Road Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enhancing the traction and stability of off-road vehicles. Off-road driving presents unique challenges, such as uneven terrain, steep inclines, loose surfaces, and obstacles, where maintaining traction and stability is vital. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to enhancing the traction and stability of off-road vehicles:
1. Power Distribution:
Rear drive shafts are responsible for transmitting torque from the transfer case or transmission to the rear differential or rear axle in off-road vehicles. This power distribution allows the rear wheels to receive torque and apply it to the ground, enhancing traction. By providing power to the rear wheels, the rear drive shafts ensure that the wheels dig into the terrain, maximizing grip and reducing the chances of wheel spin. This power distribution contributes to maintaining forward momentum and preventing loss of traction in challenging off-road conditions.
2. Rear-Wheel Traction:
Rear drive shafts enable rear-wheel traction, which is crucial for off-road vehicles. When traversing uneven or slippery terrain, the weight of the vehicle shifts to the rear wheels during acceleration. The rear drive shafts deliver torque to the rear wheels, allowing them to maintain traction and effectively propel the vehicle forward. By ensuring rear-wheel traction, the drive shafts help the off-road vehicle overcome obstacles, climb steep inclines, and navigate challenging off-road terrains where maintaining grip is essential.
3. Weight Transfer:
Rear drive shafts contribute to proper weight transfer during off-road driving. As the vehicle encounters obstacles or uneven terrain, weight transfer occurs, with the weight shifting from one wheel to another. The rear drive shafts aid in balancing the weight distribution, preventing excessive weight transfer to a single wheel. This balanced weight transfer improves stability and minimizes the chances of wheel lift or loss of control. It allows the off-road vehicle to maintain stability and traction, enhancing overall safety and performance.
4. Axle Articulation:
Off-road vehicles often require significant axle articulation to maintain contact between the wheels and the ground, especially when navigating rough terrain. Rear drive shafts accommodate the movement and flexing of the suspension system, allowing the rear wheels to articulate independently. This flexibility enables the wheels to maintain contact with the ground, even when encountering large obstacles or uneven surfaces. By adapting to the changing terrain, the rear drive shafts contribute to improved traction and stability, ensuring the off-road vehicle can maintain forward momentum.
5. Torque Control:
Rear drive shafts play a role in torque control, which is essential for maintaining traction and stability off-road. Some off-road vehicles feature differential locks or limited-slip differentials in the rear axle. The rear drive shafts transmit torque to these differentials, allowing for better power distribution between the rear wheels. This torque control helps prevent wheelspin and ensures that power is delivered to the wheels with traction, enhancing overall traction and stability in challenging off-road conditions.
6. Ground Clearance:
Rear drive shafts contribute to improving ground clearance in off-road vehicles. The design and positioning of the drive shafts allow for higher ground clearance compared to vehicles with front-wheel drive configurations. Increased ground clearance reduces the risk of the drive shafts scraping or getting damaged by obstacles, rocks, or uneven surfaces. By providing adequate ground clearance, the rear drive shafts enable the off-road vehicle to navigate rough terrain without hindrance, maintaining traction and stability.
7. Durability and Reliability:
Rear drive shafts in off-road vehicles are designed to withstand the demanding conditions encountered during off-road driving. They are built to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding impacts, vibrations, and extreme articulation. The reliability and strength of the rear drive shafts contribute to maintaining traction and stability by ensuring that the power transmission remains intact, even in challenging off-road situations.
In summary, rear drive shafts enhance the traction and stability of off-road vehicles through power distribution, rear-wheel traction, weight transfer management, axle articulation accommodation, torque control, increased ground clearance, and durability. These factors collectively contribute to maintaining traction, allowing the off-road vehicle to overcome obstacles, navigate challenging terrains, and ensure stability and control in off-road driving conditions.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Impact the Performance and Drivability of Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. As a crucial component of the drivetrain system, the rear drive shaft affects various aspects of a vehicle’s operation, including power delivery, handling, stability, and overall driving experience. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts impact the performance and drivability of vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts play a vital role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, the rear drive shaft transfers this rotational force to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and vehicle movement. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the rear drive shaft directly impact a vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Traction and Stability:
The distribution of power between the rear wheels, controlled by the rear drive shaft and the rear differential, significantly affects a vehicle’s traction and stability. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to each rear wheel based on traction conditions.
Proper power distribution between the rear wheels ensures balanced traction, reducing the likelihood of wheel slippage or loss of control. This enhances the vehicle’s stability, especially during acceleration, cornering, or driving on uneven or slippery surfaces.
3. Handling and Cornering:
Rear drive shafts influence a vehicle’s handling and cornering capabilities. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, the rear drive shaft connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, resulting in a weight distribution biased towards the rear of the vehicle.
This weight distribution, combined with the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels, contributes to better traction and stability during cornering. RWD vehicles typically exhibit a more balanced and predictable handling characteristic, allowing drivers to maintain better control and confidence while navigating turns.
4. Suspension Compatibility:
Rear drive shafts also need to be compatible with a vehicle’s suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move independently, absorbing bumps, road irregularities, and other disturbances for a smoother ride.
The rear drive shaft must accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension without affecting power transmission. It achieves this by incorporating flexible joints or splines that allow the drive shaft to expand or contract in length as the suspension moves. This compatibility ensures that the rear drive shaft does not hinder the suspension’s ability to absorb shocks and maintain tire contact with the road surface.
5. Drivetrain Efficiency:
The efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain system is influenced by the performance of the rear drive shaft. A well-designed and properly maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels and optimizing overall drivetrain efficiency.
Efficient power transmission through the rear drive shaft contributes to improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy waste, and enhanced performance. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and alignment, ensures that the rear drive shaft operates smoothly and maximizes its contribution to drivetrain efficiency.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enabling four-wheel drive capability. The rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
By facilitating power distribution to all four wheels, rear drive shafts enhance the vehicle’s off-road performance, traction, and stability. Four-wheel drive capability allows the vehicle to tackle challenging terrain, slippery conditions, or uneven surfaces with improved control and maneuverability.
In summary, rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. They affect power transmission, traction, stability, handling, suspension compatibility, drivetrain efficiency, and enable four-wheel drive capability. By understanding and optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of rear drive shafts, manufacturers and drivers can enhance a vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and driving experience.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
China wholesaler Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.
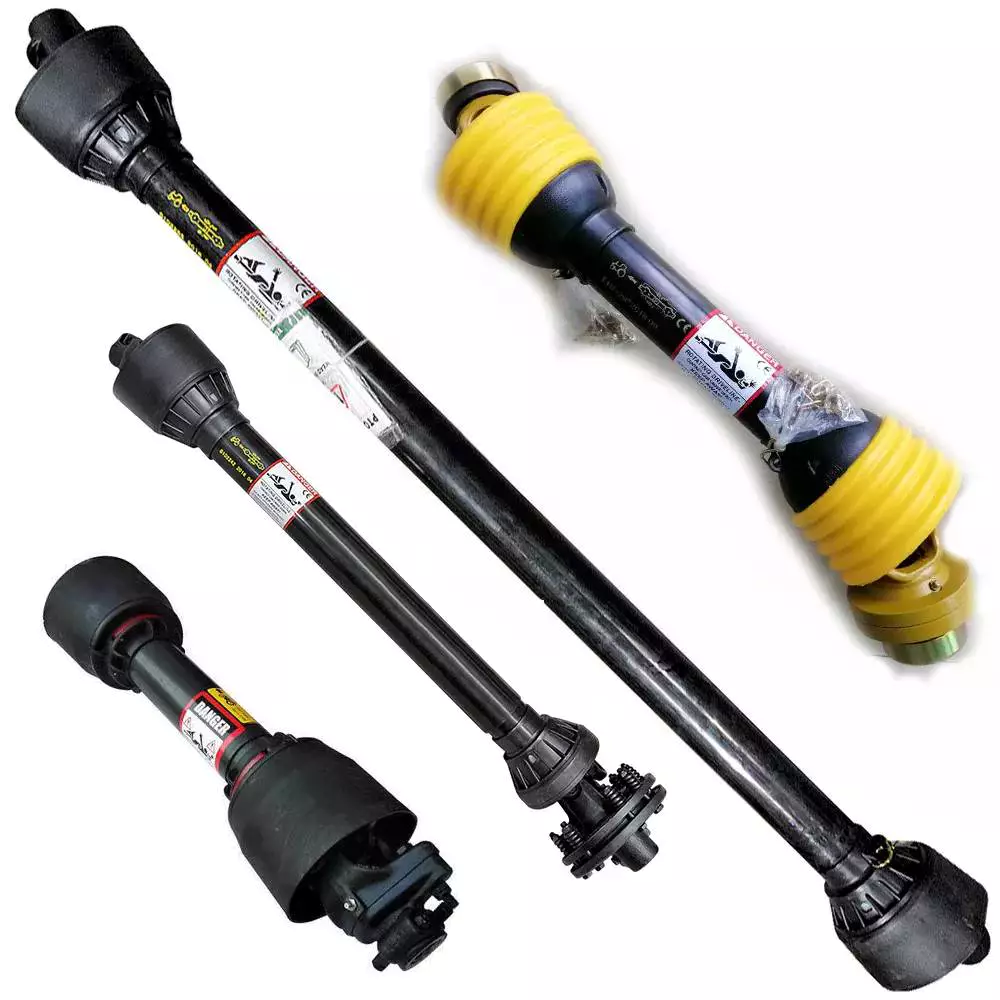

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

Which Types of Vehicles Commonly Use Rear Drive Shafts in Their Drivetrain?
Rear drive shafts are a common feature in several types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) drivetrain configurations. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of vehicles that commonly use rear drive shafts in their drivetrain:
1. Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are most commonly found in RWD vehicles. In RWD configurations, the engine’s power is sent to the rear wheels through the transmission and rear differential. The rear drive shaft connects the output of the transmission or transfer case to the input of the rear differential, allowing power transmission to the rear wheels. This setup is commonly used in sports cars, luxury sedans, pickup trucks, and some SUVs.
2. Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles:
Many 4WD and AWD vehicles also utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles provide power to all four wheels, enhancing traction and off-road capability. In 4WD systems, the rear drive shaft transfers power from the transfer case to the rear differential and front differential, enabling torque distribution to both the front and rear wheels. This setup is commonly found in off-road vehicles, SUVs, trucks, and some performance cars.
3. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. These vehicles often have rear-wheel drive or part-time 4WD systems to handle heavy loads, towing, and demanding work conditions. The rear drive shafts in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to endure higher torque and load capacities, ensuring reliable power transmission to the rear wheels.
4. SUVs and Crossovers:
Many SUVs and crossovers employ rear drive shafts, especially those with RWD or 4WD/AWD configurations. These vehicles often prioritize versatility, off-road capability, and towing capacity. Rear drive shafts enable power transmission to the rear wheels, enhancing traction and stability both on and off the road. SUVs and crossovers with 4WD or AWD systems can distribute torque to all four wheels, improving performance in various weather and terrain conditions.
5. Performance and Sports Cars:
Performance and sports cars frequently utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. RWD configurations are common in these vehicles, as they offer better weight distribution, improved handling, and enhanced control during high-performance driving. Rear drive shafts enable efficient power delivery to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s acceleration, stability, and overall performance.
6. Muscle Cars and Classic Vehicles:
Muscle cars and classic vehicles often feature rear drive shafts due to their traditional RWD setups. These vehicles evoke a nostalgic driving experience and typically prioritize power and rear-wheel traction. Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in transmitting power and torque from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing muscle cars and classic vehicles to deliver the desired performance and driving dynamics.
In summary, rear drive shafts are commonly found in various types of vehicles, including RWD vehicles, 4WD/AWD vehicles, trucks, SUVs, crossovers, performance cars, muscle cars, and classic vehicles. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, ensuring efficient power delivery, traction, and drivetrain performance.


editor by CX 2023-12-15
China Best Sales Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Contribute to the Overall Performance of Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in the overall performance of rear-wheel-drive (RWD) vehicles. They are responsible for transferring torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, which then distributes power to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to the overall performance of RWD vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing for propulsion and forward motion. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission or transfer case to the rear drive shaft. The drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes the power to the rear wheels. The efficiency and effectiveness of this power transmission process directly impact the acceleration, speed, and overall performance of the vehicle.
2. Torque Delivery:
Rear drive shafts ensure efficient torque delivery to the rear wheels, enabling traction and propulsion. By connecting the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, the drive shaft transfers torque generated by the engine to the wheels. The rear wheels receive this torque, allowing them to grip the road surface and propel the vehicle forward. The ability of the rear drive shaft to effectively deliver torque contributes to improved acceleration, responsiveness, and overall performance of RWD vehicles.
3. Weight Distribution:
Rear drive shafts contribute to the proper weight distribution in RWD vehicles. Since the engine is typically positioned at the front of the vehicle, the rear drive shaft helps balance the weight distribution by transferring power to the rear wheels. This balanced weight distribution enhances overall stability, handling, and cornering capabilities. It allows for better control of the vehicle and helps optimize the performance during various driving conditions.
4. Handling and Stability:
Rear drive shafts significantly influence the handling and stability of RWD vehicles. By delivering torque to the rear wheels, the drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s rear-wheel traction. This configuration provides better weight transfer during acceleration, which improves traction and reduces the chances of wheel spin. The rear drive shaft also aids in maintaining stability during cornering by helping to distribute the vehicle’s weight more evenly. RWD vehicles are known for their balanced and predictable handling characteristics, and the rear drive shaft plays a vital role in achieving these attributes.
5. Performance in Various Conditions:
Rear drive shafts impact the performance of RWD vehicles in different driving conditions. In dry or high-grip situations, the rear-wheel traction provided by the drive shaft enables quick acceleration and efficient power delivery. RWD vehicles often exhibit superior handling characteristics in these conditions due to the balanced weight distribution and the rear drive shaft’s ability to transfer torque effectively. However, in low-traction conditions such as rain, snow, or off-road situations, RWD vehicles may require additional driver skill and careful throttle control to maintain traction and stability.
6. Customization and Performance Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can be customized or upgraded to enhance the performance of RWD vehicles. For example, performance-oriented drive shafts made from lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can reduce rotational mass, improving overall vehicle agility and responsiveness. Upgraded drive shafts with strengthened components can handle increased torque and power outputs in high-performance applications. Customization and upgrades to the rear drive shaft allow vehicle owners to tailor the performance characteristics to their specific needs and preferences.
7. Maintenance and Service:
Regular maintenance and service of rear drive shafts are essential for maintaining optimal performance. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and addressing any issues such as worn U-joints or CV joints can prevent driveline vibrations, reduce power losses, and ensure smooth torque transmission. Proper maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the rear drive shaft, allowing it to continue supporting the overall performance of the RWD vehicle.
In summary, rear drive shafts are integral to the overall performance of RWD vehicles. They facilitate power transmission, torque delivery, and weight distribution, contributing to acceleration, traction, handling, and stability. The rear drive shaft’s ability to efficiently transfer torque to the rear wheels is key to the performance characteristics of RWD vehicles. Through customization, upgrades, and regular maintenance, rear drive shafts can be optimized to further enhance the performance of RWD vehicles in various driving conditions and applications.

What Benefits Do Properly Functioning Rear Drive Shafts Offer for Vehicle Dynamics?
A properly functioning rear drive shaft offers several benefits for vehicle dynamics. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power, distributing torque, and maintaining stability, which directly impact the performance and handling characteristics of a vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that properly functioning rear drive shafts offer for vehicle dynamics:
1. Power Delivery:
A properly functioning rear drive shaft ensures efficient power delivery from the engine or transmission to the wheels. It facilitates the transfer of torque, generated by the engine, to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and acceleration. A well-maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels, resulting in improved vehicle performance.
2. Balanced Traction:
The rear drive shaft, in conjunction with the rear differential, plays a key role in distributing torque between the rear wheels. This torque distribution ensures balanced traction, especially during acceleration and cornering. Properly functioning rear drive shafts help optimize power distribution, reducing the chances of wheel slippage and providing better grip and stability on various road surfaces.
3. Enhanced Stability:
Stability is a crucial aspect of vehicle dynamics, and rear drive shafts contribute to maintaining stability during various driving conditions. By enabling torque distribution to the rear wheels, the rear drive shaft helps prevent oversteer or understeer tendencies, particularly during cornering. It allows the rear wheels to better grip the road, enhancing the vehicle’s stability and control.
4. Improved Handling:
A properly functioning rear drive shaft contributes to improved handling characteristics of a vehicle. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) configurations, the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels results in a more balanced weight distribution, with a bias towards the rear. This weight distribution enhances the vehicle’s handling by providing better traction and control, especially during cornering maneuvers.
5. Responsiveness:
Properly functioning rear drive shafts contribute to the overall responsiveness of a vehicle. They ensure prompt power delivery and torque transfer, allowing the vehicle to respond quickly to driver inputs. This responsiveness enhances the driving experience, providing a direct and engaging connection between the driver and the road.
6. Off-Road Capability:
For vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, properly functioning rear drive shafts are essential for off-road capability. They enable power distribution to both the front and rear wheels, enhancing traction and control on challenging terrain. By maintaining proper torque transfer, rear drive shafts ensure that the vehicle can navigate rough surfaces, steep inclines, and other off-road obstacles with improved capability and confidence.
7. Drivetrain Efficiency:
Efficient power transmission through properly functioning rear drive shafts contributes to overall drivetrain efficiency. They minimize power losses, mechanical friction, and energy waste, allowing more power to reach the wheels. This not only enhances vehicle performance but also improves fuel efficiency and optimizes the utilization of available power.
In summary, properly functioning rear drive shafts offer several benefits for vehicle dynamics. They ensure efficient power delivery, balanced traction, enhanced stability, improved handling, responsiveness, off-road capability, and drivetrain efficiency. By maintaining and optimizing rear drive shaft performance, manufacturers and drivers can enhance the overall driving experience, vehicle performance, and handling characteristics.


editor by CX 2023-12-04
China Hot selling Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
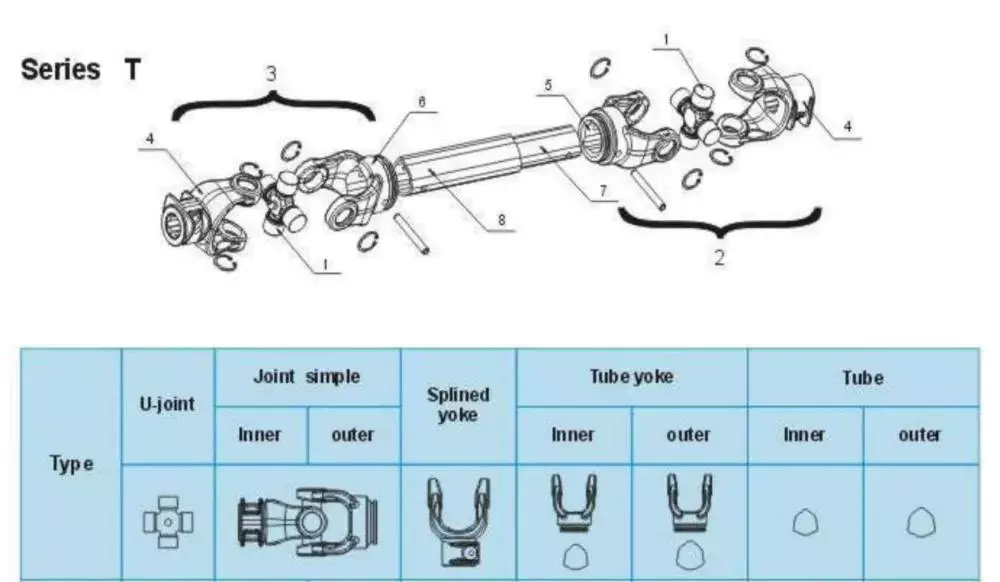
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting the Right Rear Drive Shaft for a Vehicle?
When selecting the right rear drive shaft for a vehicle, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key factors that should be taken into account:
1. Vehicle Specifications:
The specific characteristics of the vehicle play a significant role in determining the appropriate rear drive shaft. Factors such as the vehicle’s weight, horsepower, torque output, wheelbase, suspension design, and intended use (e.g., off-roading, towing, performance driving) need to be considered. These specifications help determine the required torque capacity, length, diameter, and material strength of the drive shaft to handle the vehicle’s demands effectively.
2. Drivetrain Configuration:
The drivetrain configuration of the vehicle influences the selection of the rear drive shaft. Vehicles with rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems have different drivetrain layouts and torque distribution requirements. The drive shaft must be compatible with the vehicle’s drivetrain configuration, including the type of differential, transfer case, and front-wheel drive components, if applicable.
3. Torque and Power Requirements:
The torque and power output of the vehicle’s engine or transmission impact the selection of the rear drive shaft. Higher torque and power levels necessitate a stronger and more robust drive shaft to handle the increased load. It is important to consider the maximum torque and power values of the vehicle and select a drive shaft that can safely and reliably transmit the power without exceeding its rated capacity.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for the rear drive shaft is crucial in ensuring its strength, durability, and weight. Common materials used for drive shafts include steel and aluminum. Steel drive shafts offer high strength and are typically used in heavy-duty applications, while aluminum drive shafts are lighter and can provide weight savings, making them suitable for performance-oriented vehicles. The material selection should also consider factors such as corrosion resistance, cost, and manufacturing feasibility.
5. Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are critical considerations to prevent issues such as vibration, bending, or excessive deflection. The length of the drive shaft depends on the vehicle’s wheelbase and the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. The diameter of the drive shaft is determined by the torque and power requirements, as well as the material properties. Proper sizing ensures the drive shaft can handle the forces and maintain optimal power transmission without compromising safety or performance.
6. Suspension and Drivetrain Movements:
The suspension system and drivetrain movements of the vehicle need to be taken into account when selecting a rear drive shaft. The drive shaft must accommodate the range of motion and articulation of the suspension, as well as the angular movements and changes in alignment between the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. Flexible joints such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are typically used to allow for these movements while maintaining torque transmission.
7. Environmental Factors:
The environmental conditions in which the vehicle will operate should be considered when selecting a rear drive shaft. Factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to moisture, off-road terrain, and corrosive substances can impact the choice of materials, protective coatings, and maintenance requirements of the drive shaft. It is essential to select a drive shaft that can withstand the environmental conditions and maintain its performance and longevity.
8. Manufacturer Quality and Compatibility:
When choosing a rear drive shaft, it is important to consider the reputation and quality of the manufacturer. Selecting a drive shaft from a reputable and experienced manufacturer ensures that the product meets industry standards, undergoes thorough quality control, and is compatible with the vehicle’s specifications and requirements. It is advisable to consult with automotive professionals or refer to manufacturer guidelines to ensure proper selection and compatibility.
In summary, selecting the right rear drive shaft for a vehicle involves considering factors such as vehicle specifications, drivetrain configuration, torque and power requirements, material selection, length and diameter, suspension and drivetrain movements, environmental factors, and manufacturer quality. Taking these factors into account helps ensure that the chosen rear drive shaft is suitable for the vehicle’s needs and provides reliable and efficient power transmission.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

What Is a Rear Drive Shaft and How Does It Contribute to Vehicle Propulsion?
A rear drive shaft is a component of a vehicle’s drivetrain system that connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s propulsion. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a rear drive shaft is and how it contributes to vehicle propulsion:
1. Drivetrain Connection:
The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. It is typically a tubular shaft that rotates at high speeds to transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels.
When the engine generates power, it is transmitted through the transmission or transfer case, which determines the appropriate gear ratio. The rear drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes power to the rear wheels.
2. Torque Transmission:
The primary function of the rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine to the rear wheels. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for propelling the vehicle forward.
As the engine produces torque, it is transferred to the transmission or transfer case. From there, the torque is sent through the rear drive shaft to the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque and sends it to the rear wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle.
3. Power Distribution:
The rear drive shaft plays a critical role in distributing power evenly between the rear wheels. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft ensures that power is distributed to both wheels, enabling balanced propulsion.
By transmitting torque from the engine to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to both rear wheels based on traction conditions. This power distribution ensures that both wheels contribute to vehicle propulsion and provides stability and control during acceleration and cornering.
4. Suspension Movement Compensation:
Another important function of the rear drive shaft is to compensate for the movement of the suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move up and down independently to absorb bumps, uneven road surfaces, and other disturbances.
As the suspension moves, the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential changes. The rear drive shaft accommodates this movement by expanding or contracting its length, allowing the rear wheels to move vertically while maintaining a continuous torque transmission.
5. Drive System Efficiency:
An efficiently operating rear drive shaft contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s drivetrain system. By effectively transmitting torque from the engine to the rear wheels, it minimizes power losses and ensures optimal power delivery.
Efficiency in power transmission reduces energy waste and maximizes the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. A well-maintained rear drive shaft with proper lubrication and alignment helps minimize friction and mechanical losses, maximizing the effectiveness of the drivetrain system.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft is a crucial component for engaging the front wheels for propulsion. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which then distributes power to the front and rear differentials.
By transmitting torque to the transfer case, the rear drive shaft enables four-wheel drive capability, allowing the vehicle to engage all four wheels for enhanced traction and off-road performance.
In summary, a rear drive shaft is a key component in a vehicle’s drivetrain system. It serves as a drivetrain connection, transmits torque from the engine to the rear wheels, distributes power between the rear wheels, compensates for suspension movement, enhances drive system efficiency, and facilitates four-wheel drive capability. By fulfilling these functions, the rear drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s propulsion, stability, and overall performance.


editor by CX 2023-10-27
China Standard Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Efficient Power Transfer While Maintaining Balance?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. At the same time, they must maintain balance to prevent vibrations, reduce stress on drivetrain components, and enhance overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve efficient power transfer while maintaining balance:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully designed and manufactured to achieve balance. Balance refers to the distribution of mass along the length of the drive shaft. Imbalances can lead to vibrations and unwanted forces that affect the smooth operation of the drivetrain. To achieve balance, drive shafts are dynamically balanced during the manufacturing process. This involves adding weights or removing material at specific locations to counteract any uneven distribution of mass. By achieving balance, the drive shaft can rotate smoothly at high speeds, minimizing vibrations and ensuring efficient power transfer.
2. Proper Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are important considerations for maintaining balance. A drive shaft that is too long or too short can result in excessive deflection or bending, leading to vibrations and potential failure. Similarly, an incorrect diameter can affect the stiffness and torsional strength of the drive shaft, resulting in imbalances. Manufacturers carefully calculate the optimal length and diameter of the drive shaft based on the vehicle’s specifications and requirements to ensure proper balance and power transfer.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The selection of high-quality materials is crucial for maintaining balance in rear drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from materials such as steel or aluminum. These materials offer the necessary strength and rigidity while being lightweight. The use of high-quality materials ensures that the drive shaft can withstand the torque and rotational forces without excessive flexing or bending, which can lead to imbalances. Additionally, the materials are chosen for their ability to resist fatigue and vibration, further contributing to balanced operation.
4. Precision Manufacturing:
Rear drive shafts are manufactured with precision to maintain balance. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining, are employed to ensure the drive shaft’s dimensional accuracy and balance. The manufacturing process involves precise machining of the shaft, including the yokes, flanges, and other components, to achieve tight tolerances and minimize any deviations that could affect balance. Strict quality control measures are implemented to verify the balance of each drive shaft before it is installed in a vehicle.
5. Vibration Dampening Techniques:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate vibration dampening techniques to further enhance balance and reduce unwanted vibrations. These techniques may include the use of balancing weights, dampers, or vibration-absorbing materials. Balancing weights can be strategically placed along the drive shaft to counteract any remaining imbalances. Dampers, such as rubber or elastomer components, are employed to absorb and dissipate vibrations, preventing them from propagating throughout the drivetrain. By minimizing vibrations, these techniques help maintain overall balance and contribute to efficient power transfer.
6. Universal Joints or Constant Velocity Joints:
Rear drive shafts incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate changes in angles and maintain balance. These joints allow for angular movement and compensate for variations in the alignment between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. By allowing the drive shaft to flex and articulate, these joints help prevent binding, minimize stress on the drivetrain components, and maintain balance throughout the range of motion.
7. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
Maintaining balance in rear drive shafts requires regular maintenance and inspection. Over time, components may wear or become damaged, leading to imbalances. It is important to periodically inspect the drive shaft for signs of wear, such as worn u-joints or damaged CV joints. Additionally, proper lubrication of the joints and ensuring the drive shaft is properly installed and aligned are essential for maintaining balance. Routine maintenance and inspections help detect and address any issues that could affect the drive shaft’s balance and overall performance.
In summary, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through a combination of balanced design, proper length and diameter, high-quality materials, precision manufacturing, vibration dampening techniques, flexible joints, and regular maintenance. By achieving and maintaining balance, rear drive shafts contribute to smooth operation, minimize vibrations, and enhance the overall performance and longevity of the drivetrain system.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

Which Types of Vehicles Commonly Use Rear Drive Shafts in Their Drivetrain?
Rear drive shafts are a common feature in several types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) drivetrain configurations. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of vehicles that commonly use rear drive shafts in their drivetrain:
1. Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are most commonly found in RWD vehicles. In RWD configurations, the engine’s power is sent to the rear wheels through the transmission and rear differential. The rear drive shaft connects the output of the transmission or transfer case to the input of the rear differential, allowing power transmission to the rear wheels. This setup is commonly used in sports cars, luxury sedans, pickup trucks, and some SUVs.
2. Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles:
Many 4WD and AWD vehicles also utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles provide power to all four wheels, enhancing traction and off-road capability. In 4WD systems, the rear drive shaft transfers power from the transfer case to the rear differential and front differential, enabling torque distribution to both the front and rear wheels. This setup is commonly found in off-road vehicles, SUVs, trucks, and some performance cars.
3. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. These vehicles often have rear-wheel drive or part-time 4WD systems to handle heavy loads, towing, and demanding work conditions. The rear drive shafts in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to endure higher torque and load capacities, ensuring reliable power transmission to the rear wheels.
4. SUVs and Crossovers:
Many SUVs and crossovers employ rear drive shafts, especially those with RWD or 4WD/AWD configurations. These vehicles often prioritize versatility, off-road capability, and towing capacity. Rear drive shafts enable power transmission to the rear wheels, enhancing traction and stability both on and off the road. SUVs and crossovers with 4WD or AWD systems can distribute torque to all four wheels, improving performance in various weather and terrain conditions.
5. Performance and Sports Cars:
Performance and sports cars frequently utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. RWD configurations are common in these vehicles, as they offer better weight distribution, improved handling, and enhanced control during high-performance driving. Rear drive shafts enable efficient power delivery to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s acceleration, stability, and overall performance.
6. Muscle Cars and Classic Vehicles:
Muscle cars and classic vehicles often feature rear drive shafts due to their traditional RWD setups. These vehicles evoke a nostalgic driving experience and typically prioritize power and rear-wheel traction. Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in transmitting power and torque from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing muscle cars and classic vehicles to deliver the desired performance and driving dynamics.
In summary, rear drive shafts are commonly found in various types of vehicles, including RWD vehicles, 4WD/AWD vehicles, trucks, SUVs, crossovers, performance cars, muscle cars, and classic vehicles. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, ensuring efficient power delivery, traction, and drivetrain performance.


editor by CX 2023-09-22