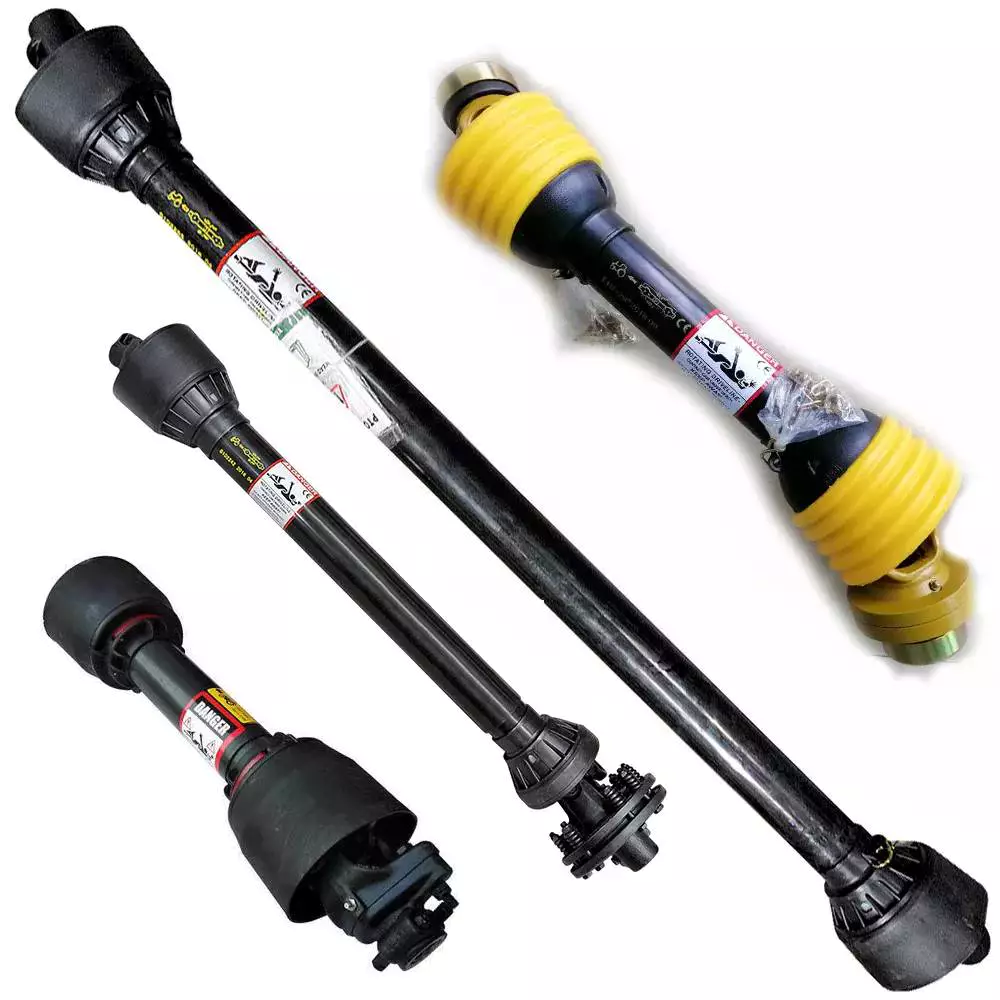
Product Description
PROPELLER SHAFT manufacturer & supplier – CHINAMFG is your best choice
|
Product Name |
Rear Drive Shaft Assembly For CHINAMFG escape |
||
|
Part Number |
936-892, BL8Z4R602A |
||
|
Vehicle Fitment |
For CHINAMFG escape 2-2016 |
||
|
65-9166 |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
65-9112 |
for CHINAMFG F-250 Super Duty |
|
65-2012 |
for CHINAMFG F150 |
65-9667 |
for CHINAMFG F-350 |
|
65-2-2016 |
|||
|
OE NO. |
FITMENT |
OE NO. |
FITMENT |
|
52123110AC |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
5L3Z‐4R602‐W |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
BL8Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
5L34‐4K145‐WD |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
2L8Z4R602BA |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
5L3Z‐4R602‐WB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
3L8Z4R602BA |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
5L3Z‐4R602‐WA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
5L8Z4R602BA |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
6L34‐4K145‐WB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
7L8Z4R602B |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
7L3Z‐4R602‐J |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
DV614K145AC |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
BL3V4602BD |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
5L834K145BA |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
BL3Z4R602H |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
8L8Z4R602C |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
DL3Z4R602B |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
CV6Z4R602B |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
DL3Z4R602Q |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
4641968AE |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
7L3Z4R602K |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
4641968AH |
for CHINAMFG Escape |
5L3Z4R602BB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
26032944 |
for CHINAMFG Expedition |
5L3Z4R602ZA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
2657127 |
for CHINAMFG Expedition |
AL344K145KA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
AL3Z4A376D |
for CHINAMFG Expedition |
AL344K145KB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
F77A4376BB |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
AL3Z4R602KB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
|
XL2Z4A376AA |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
5C3Z4A376G |
for CHINAMFG F250 |
|
ZZR571100 |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
5C3Z4A376EA |
for CHINAMFG F250 |
|
F77A4376BB |
for CHINAMFG EXPLORER |
5C3Z4A376D |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
XL2Z‐4A376‐AA |
for CHINAMFG EXPLORER |
YC3Z4A376EA |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
ZZR0‐25‐100 |
for CHINAMFG EXPLORER |
5C3Z4A376FA |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
7A2Z4R602N |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
F81Z4A376HA |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
7A2Z4R602D |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
F81Z4A376PA |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
7A2Z4R602G |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
5C3Z4A376A |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
7A2Z4R602K |
for CHINAMFG Explorer |
BC3Z4A376A |
for CHINAMFG F-250 |
|
BL3Z4R602D |
for CHINAMFG F150 |
E5TZ4A376C |
for CHINAMFG F-350 |
|
DL3Z4R602E |
for CHINAMFG F150 |
E9TA4376DA |
for CHINAMFG F-350 |
|
DL3Z4R602AL |
for CHINAMFG F150 |
2C3Z4R602FB |
for CHINAMFG F-350 |
|
DL3Z4R602T |
for CHINAMFG F150 |
6F9Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Five |
|
8L3Z4R602B |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
5F9Z4R602AA |
for CHINAMFG Five |
|
8L3Z4R602E |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
6F924R602‐A |
for CHINAMFG Five |
|
8L3Z4R602F |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
5F934K145AE |
for CHINAMFG Five |
|
4L344K145TE |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
6F934K145AC |
for CHINAMFG Five |
|
5L344K145TA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
7E5Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Fusion |
|
5L344K145TC |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
8E5Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Fusion |
|
5L344K145TD |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
AE5Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Fusion |
|
6L344K145HC |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
6R3Z4602B |
for CHINAMFG Mustang |
|
7L344K145TA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
7R3Z4602A |
for CHINAMFG Mustang |
|
8L3Z4R602H |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
8G1Z4R602B |
for CHINAMFG Taurus |
|
52853317AC |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
8G1Z4R602A |
for CHINAMFG Taurus |
|
4L34‐4K145‐RE |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
2657195 |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
4L34‐4K145‐RA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
12479001 |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
8L3Z‐4602‐D |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
5215710AB |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
8L3Z‐4R602‐D |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
5215710AE |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
5L34‐4K145‐RA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
26571466 |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
7L3Z 4R602‐J |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
CN4C154K145AD |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
4L34‐4K145‐WA |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
7C194K357HB |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
4L34‐4K145‐WC |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
7C19‐4K145‐DB |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
5L34‐4K145‐WB |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
CN4C154K357AD |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
5L34‐4K145‐WC |
for CHINAMFG F-150 |
7C19‐4K145‐BB |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
7C19‐4K145‐BB |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
E9TZ4A376B |
for FROD Bronco |
|
E9TZ4A376B |
for FROD Bronco |
F6TZ4A376RA |
for FROD Bronco |
|
F6TZ4A376RA |
for FROD Bronco |
CN4C154K357AD |
for CHINAMFG Transit |
|
DORMAN NO. |
|||
|
938-301 |
936-807 |
936-896 |
946-448 |
|
938-091 |
936-808 |
938-801 |
936-810 |
|
936-846 |
936-973 |
936-805 |
936-809 |
|
936-285 |
938-076 |
936-942 |
936-811 |
|
936-891 |
946-831 |
936-800 |
936-812 |
|
936-892 |
936-801 |
946-830 |
936-288 |
|
976-698 |
938-066 |
936-802 |
938-305 |
|
938-031 |
946-821 |
936-803 |
936-325 |
|
938-082 |
938-802 |
936-806 |
936-327 |
|
936-847 |
938-304 |
938-063 |
936-813 |
|
936‐810 |
938-199 |
|
|
If you need more information about FORD Propeller Shaft, please message or email to us ASAP.
—- OUR ADVANTAGE —-
+700 models for AMERICA & EUROPE marketMOQ: 3PCS / for 1 item, MIN order amount: USD5000
Quality assurance: One Year WarrantyStable delivery time: 45 days
Free Sample DevelopedApply O/A 30-90 days for regular customer
Becides CHINAMFG Propeller Shaft,we have Over 700 items applicable for following vehicles:
—- F A Q —-
Q1: If we don’t find what we need on your website, what should we do?
You can send us the OE number or of the product you need, we will check if we have them.
We also develop new models according to customer’s need;
you can contact us for more detail.
Q2: Can I get a price discount if I order large quantities?Yes, it depends on your purchasing quantity, more quantity more discount.
Q3: What about the delivery time?If we have stock, we can send you the goods within 3 working days,
if we don’t have stock, generally it needs 10 to 40 days.
Q4: What’s our MOQ?Sample order for quality testing 1 piece , normal order 50 pieces for 1 order with mixed models .
Q5: What’s your payment terms and condition ?We can accept T/T , LC, Trade Assurance, Western Union, Paypal, Moneygram ect.
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ford |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Accommodate Variations in Length and Connection Methods?
Rear drive shafts are designed to accommodate variations in length and connection methods to ensure proper fitment and functionality in different vehicle configurations. These variations arise due to differences in vehicle size, drivetrain layout, suspension geometry, and other factors. Rear drive shafts employ several mechanisms and design considerations to adapt to these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods:
1. Telescoping Design:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate a telescoping design that allows for length adjustments. Telescoping drive shafts consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other, enabling changes in length. This design is beneficial when vehicles have adjustable suspension systems or when there is a need to accommodate variations in the distance between the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. By adjusting the telescoping sections, rear drive shafts can be extended or retracted to match the required length, ensuring proper alignment and engagement of the drivetrain components.
2. Slip Yokes:
Slip yokes are commonly used in rear drive shafts to allow for axial movement and compensate for changes in length. A slip yoke is a splined component that connects the drive shaft to the transmission output shaft. It is designed to slide in and out of the drive shaft, allowing for length adjustments. As the suspension moves or the rear axle travels up and down, the slip yoke accommodates the changes in distance between the transmission and the rear axle, maintaining constant engagement and power transfer. Slip yokes are often used in conjunction with telescoping drive shafts to provide a wider range of length adjustability.
3. Universal Joints (U-Joints) and Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Rear drive shafts utilize different types of joints, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate variations in connection methods. U-joints are commonly used in rear drive shafts and allow for angular movement between two shafts. They can handle misalignment and changes in operating angles, making them suitable for applications where the rear axle and transmission output shaft are not perfectly aligned. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in applications that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer, such as in vehicles with independent rear suspension. CV joints accommodate variations in length and allow for a wider range of articulation angles while maintaining a constant velocity of the drive shaft.
4. Flange Connections and Bolt Patterns:
Rear drive shafts feature flange connections at each end to facilitate attachment to the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. The flanges are designed with specific bolt patterns that correspond to the mating surfaces on the transmission and axle. These bolt patterns ensure proper alignment and secure attachment of the drive shaft to the drivetrain components. The bolt patterns may vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer, drivetrain configuration, and specific model. By accommodating different flange connections and bolt patterns, rear drive shafts can be compatible with a wide range of vehicles and drivetrain layouts.
5. Customization and Engineering:
In some cases, rear drive shafts may require customization and engineering to accommodate specific variations in length and connection methods. Vehicle manufacturers, aftermarket suppliers, and drivetrain specialists have the expertise to design and manufacture custom drive shafts to meet unique requirements. This may involve fabricating drive shafts with specific lengths, spline counts, or joint configurations that are not readily available in standard off-the-shelf options. Customization allows for precise adaptation of rear drive shafts to fit vehicles with non-standard drivetrain configurations or to address specific challenges posed by unique suspension setups or vehicle modifications.
In summary, rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods through telescoping designs, slip yokes, universal joints (U-joints), constant velocity (CV) joints, flange connections, bolt patterns, and customization. These features and design considerations ensure proper fitment, alignment, and engagement of the rear drive shaft in different vehicle configurations. By incorporating these mechanisms, rear drive shafts provide the flexibility and adaptability necessary to accommodate variations in length and connection methods, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse drivetrain layouts.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.
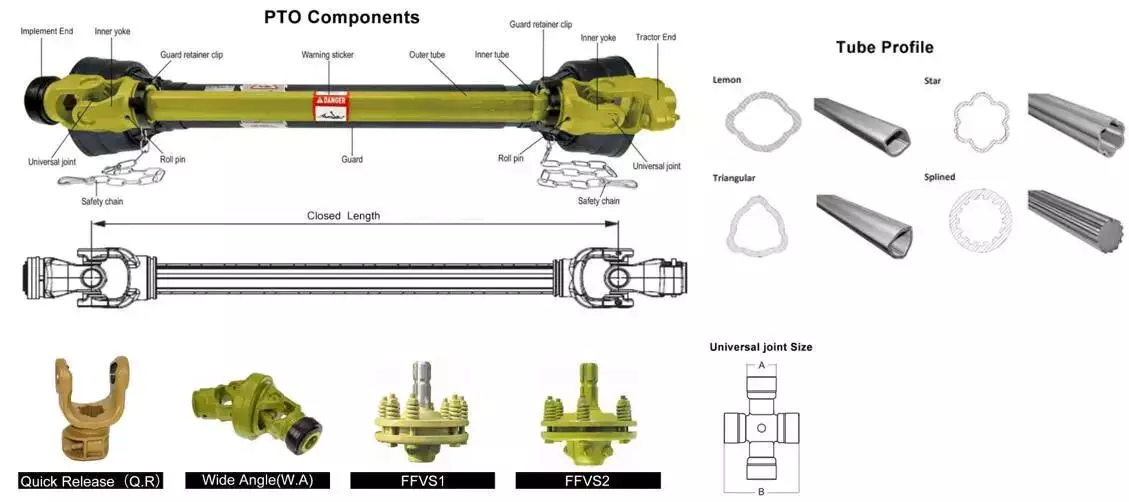
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2023-10-12