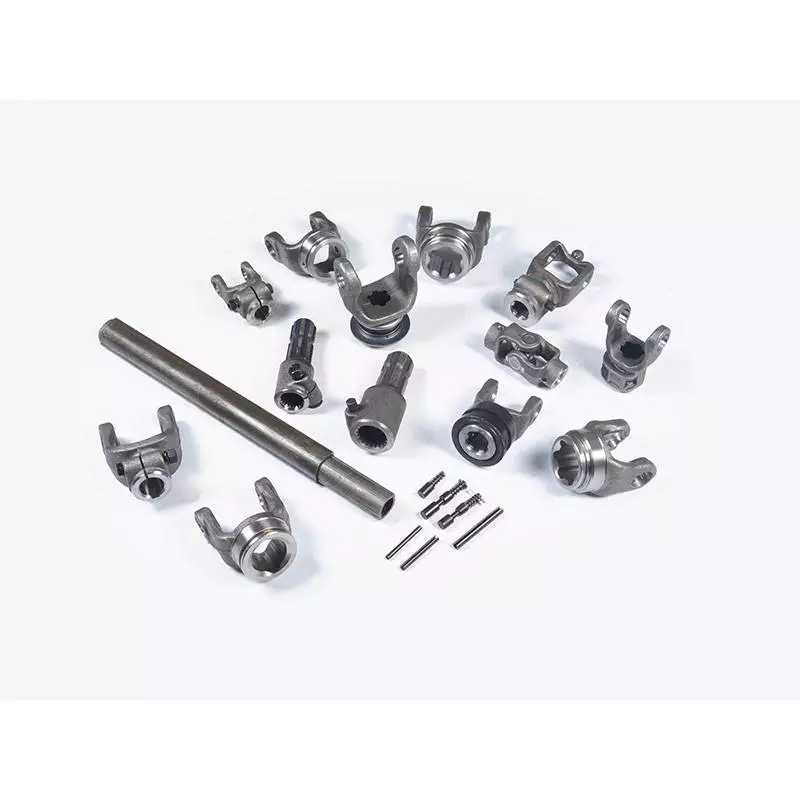
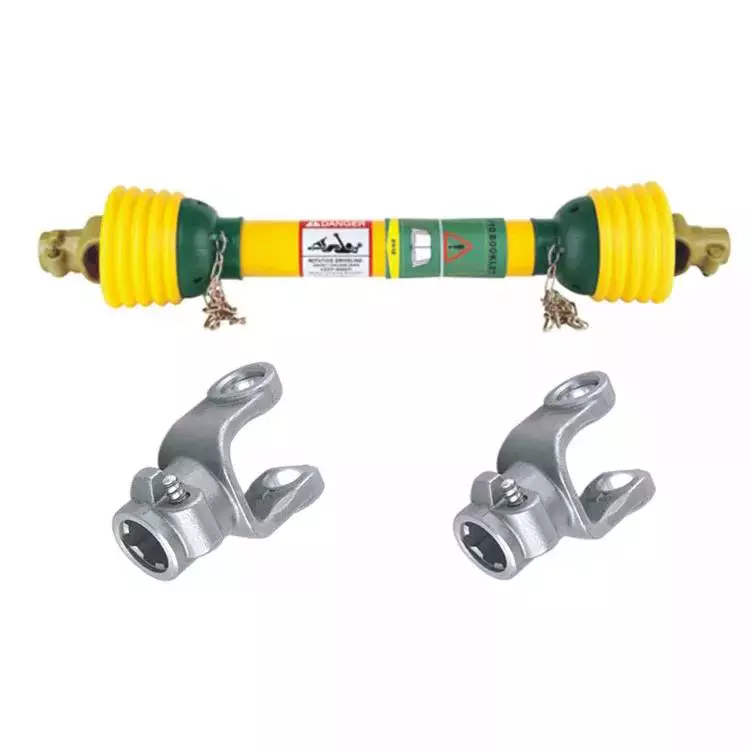
Product Description
PROPELLER SHAFT manufacturer & supplier – CHINAMFG is your best choice
|
Product Name: |
Rear Drive Shaft For BMW E60 525i E61 2 Propshaft Propeller Prop Shafts x1 |
||
|
OE NO.: |
946-994,,, |
||
|
Vehicle Fitment: |
For BMW 525i 2 |
for BMW 318i |
|
|
65-7048 |
for BMW 323ci |
for BMW 318i |
|
|
65-7047 |
for BMW 325i/320i |
for BMW 323I |
|
|
65-7571 |
for BMW 328I |
for BMW 325Ci |
|
|
65-7571 |
for BMW 328i |
for BMW 325e |
|
|
65-7058 |
for BMW 328i |
for BMW 325I |
|
|
65-7061 |
for BMW 3-Series |
26 10 7 551 207 |
for BMW 325I |
|
65-7044 |
for BMW 3-Series |
for BMW 325i |
|
|
65-7019 |
for BMW 745li |
for BMW 325xi |
|
|
65-7018 |
for BMW 760li |
for BMW 328i |
|
|
65-7045 |
for BMW E83 X3 |
for BMW 328i |
|
|
65-7046 |
for BMW E83 X3 |
for BMW 328i |
|
|
65-7 |
for BMW 330Ci |
||
|
65-7 |
for BMW 330Ci |
||
|
65-7016 |
for BMW X5 |
for BMW 5 |
|
|
65-7017 |
for BMW X5 |
for BMW 535i |
|
|
65-7052 |
for BMW X5 |
for BMW 535i |
|
|
65-7054 |
for BMW X5 |
for BMW 745i |
|
|
65-7055 |
for BMW X5 |
261571571 |
for BMW 745i |
|
DORMAN NO. |
FITMENT |
for BMW 745li |
|
|
936-362 |
for BMW 323ci |
for BMW 760Li |
|
|
936-359 |
for BMW 325i/320i |
for BMW E46 |
|
|
936-339 |
for BMW 328i |
for BMW E46 |
|
|
936-587 |
for BMW 328I |
for BMW E60/E61 |
|
|
946-972 |
for BMW 330ci/330i |
261571571 |
for BMW E65 |
|
946-973 |
for BMW 330ci/330i |
for BMW E65 |
|
|
936-340 |
for BMW 3-Series |
for BMW E65 |
|
|
936-310 |
for BMW 3-Series |
for BMW X1 |
|
|
946-994 |
for BMW 525i |
for BMW X3 |
|
|
946-991 |
for BMW 525xi/528xi/530xi |
for BMW X3 |
|
|
936-311 |
for BMW 528i 525i 530i 535i |
for BMW X3 |
|
|
936-398 |
for BMW 535i |
261571 |
for BMW X5 |
|
976-541 |
for BMW 760li |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
936-352 |
for BMW E30 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
936-349 |
for BMW E30 325 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
946-794 |
for BMW E65 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
936-385 |
for BMW E83 X3 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
936-304 |
for BMW X3 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
936-386 |
for BMW X3 |
|
|
|
938-257 |
for BMW X3 |
|
|
|
936-303 |
for BMW X3 E83 |
|
|
|
938-256 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
|
946-982 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
|
967-352 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
|
976-018 |
for BMW X5 |
|
|
|
936-597 |
for BMW X5 E53 |
|
|
If you need more information about BMW Propeller Shaft, please message or email to us ASAP.
—- OUR ADVANTAGE —-
+700 models for AMERICA & EUROPE marketMOQ: 3PCS / for 1 item, MIN order amount: USD5000
Quality assurance: One Year WarrantyStable delivery time: 45 days
Free Sample DevelopedApply O/A 30-90 days for regular customer
Becides BMW Propeller Shaft,we have Over 700 items applicable for following vehicles:
—- F A Q —-
Q1: If we don’t find what we need on your website, what should we do?
You can send us the OE number or of the product you need, we will check if we have them.
We also develop new models according to customer’s need;
you can contact us for more detail.
Q2: Can I get a price discount if I order large quantities?Yes, it depends on your purchasing quantity, more quantity more discount.
Q3: What about the delivery time?If we have stock, we can send you the goods within 3 working days,
if we don’t have stock, generally it needs 10 to 40 days.
Q4: What’s our MOQ?Sample order for quality testing 1 piece , normal order 50 pieces for 1 order with mixed models .
Q5: What’s your payment terms and condition ?We can accept T/T , LC, Trade Assurance, Western Union, Paypal, Moneygram ect.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | BMW |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.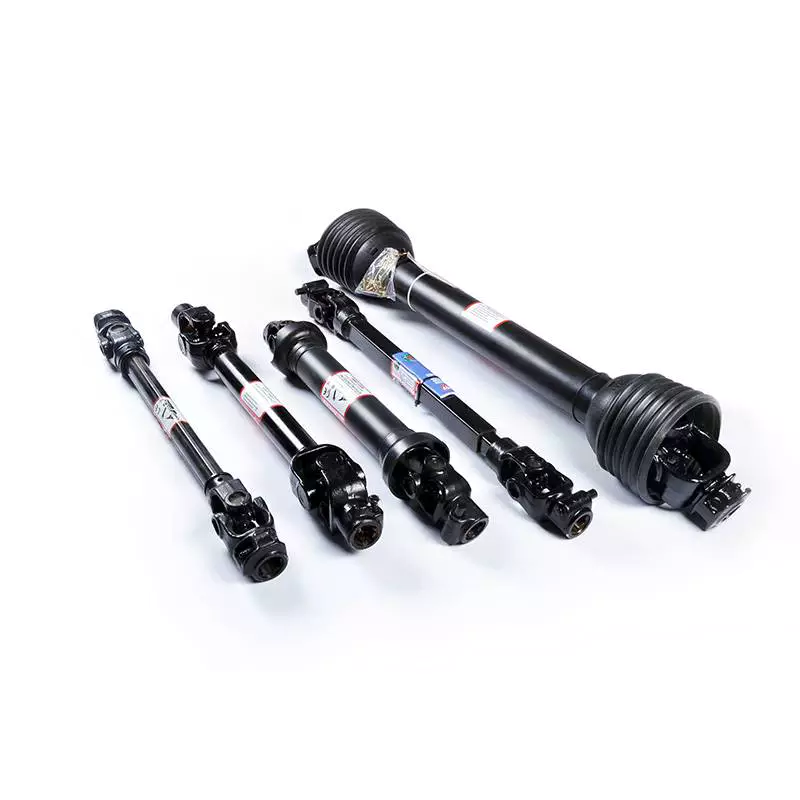
Are There Any Emerging Trends in Rear Drive Shaft Technology, Such as Lightweight Materials?
Rear drive shaft technology has been evolving over the years, and there are indeed emerging trends, including the use of lightweight materials, that are shaping the development of rear drive shafts. These trends aim to improve overall vehicle efficiency, performance, and reliability. Here are some notable emerging trends in rear drive shaft technology:
1. Lightweight Materials:
One significant trend in rear drive shaft technology is the utilization of lightweight materials. Traditional rear drive shafts have been predominantly made of steel due to its strength and durability. However, advancements in materials engineering have introduced lightweight alternatives such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and composite materials. These lightweight materials offer comparable or even superior strength while significantly reducing the weight of the drive shaft. By reducing weight, the overall vehicle weight is decreased, leading to improved fuel efficiency, handling, and performance.
2. Composite Drive Shafts:
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), are gaining popularity in rear drive shaft construction. Composite drive shafts offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent torsional rigidity, and improved damping characteristics compared to traditional steel drive shafts. The use of composites allows for weight reduction while maintaining the necessary structural integrity and performance requirements. Composite drive shafts also exhibit better resistance to corrosion and fatigue, increasing their durability and lifespan.
3. Advanced Manufacturing Techniques:
Advancements in manufacturing techniques have also impacted rear drive shaft technology. Techniques such as automated filament winding and resin transfer molding enable the production of complex shapes and optimized designs for drive shafts. These advanced manufacturing processes allow for precise control over the fiber orientation and resin distribution in composite drive shafts, resulting in enhanced strength, stiffness, and overall performance.
4. Integration of Sensors:
Another emerging trend is the integration of sensors within rear drive shafts. By incorporating sensors, such as strain gauges or torque sensors, into the drive shafts, manufacturers can monitor various parameters, including torque transmission, vibrations, and temperature. This data can be utilized for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimizing vehicle performance. Sensor integration enables early detection of potential issues, improving reliability and reducing the risk of drive shaft failures.
5. Adaptive Drive Shaft Systems:
Some manufacturers are developing adaptive drive shaft systems that can actively adjust torsional stiffness based on driving conditions. These systems utilize technologies like electromagnetic clutches or hydraulic mechanisms to vary the stiffness of the drive shaft. By adapting to different driving situations, such as cornering, acceleration, or off-road conditions, adaptive drive shaft systems can optimize power delivery, improve traction, and enhance vehicle stability.
6. Electric Drive Shafts:
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, electric drive shafts are becoming a notable trend. In these vehicles, electric motors are often integrated into the drivetrain, eliminating the need for a traditional mechanical drive shaft. Instead, electric drive shafts transmit torque from the electric motor to the wheels using electrical power. Electric drive shafts offer efficient power transmission, precise control, and the potential for regenerative braking, contributing to the overall performance and energy efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles.
7. Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Manufacturers are also focusing on reducing noise and vibration levels associated with rear drive shafts. Advanced design techniques, improved material damping properties, and precision manufacturing contribute to minimizing unwanted vibrations and noise transmission to the vehicle’s cabin. By reducing noise and vibration, occupants experience improved comfort and a quieter driving experience.
In summary, emerging trends in rear drive shaft technology include the use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum and composites, advanced manufacturing techniques, sensor integration, adaptive drive shaft systems, electric drive shafts, and efforts to reduce noise and vibrations. These trends aim to enhance vehicle efficiency, performance, durability, and overall driving experience.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Impact the Performance and Drivability of Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. As a crucial component of the drivetrain system, the rear drive shaft affects various aspects of a vehicle’s operation, including power delivery, handling, stability, and overall driving experience. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts impact the performance and drivability of vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts play a vital role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, the rear drive shaft transfers this rotational force to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and vehicle movement. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the rear drive shaft directly impact a vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Traction and Stability:
The distribution of power between the rear wheels, controlled by the rear drive shaft and the rear differential, significantly affects a vehicle’s traction and stability. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to each rear wheel based on traction conditions.
Proper power distribution between the rear wheels ensures balanced traction, reducing the likelihood of wheel slippage or loss of control. This enhances the vehicle’s stability, especially during acceleration, cornering, or driving on uneven or slippery surfaces.
3. Handling and Cornering:
Rear drive shafts influence a vehicle’s handling and cornering capabilities. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, the rear drive shaft connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, resulting in a weight distribution biased towards the rear of the vehicle.
This weight distribution, combined with the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels, contributes to better traction and stability during cornering. RWD vehicles typically exhibit a more balanced and predictable handling characteristic, allowing drivers to maintain better control and confidence while navigating turns.
4. Suspension Compatibility:
Rear drive shafts also need to be compatible with a vehicle’s suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move independently, absorbing bumps, road irregularities, and other disturbances for a smoother ride.
The rear drive shaft must accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension without affecting power transmission. It achieves this by incorporating flexible joints or splines that allow the drive shaft to expand or contract in length as the suspension moves. This compatibility ensures that the rear drive shaft does not hinder the suspension’s ability to absorb shocks and maintain tire contact with the road surface.
5. Drivetrain Efficiency:
The efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain system is influenced by the performance of the rear drive shaft. A well-designed and properly maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels and optimizing overall drivetrain efficiency.
Efficient power transmission through the rear drive shaft contributes to improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy waste, and enhanced performance. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and alignment, ensures that the rear drive shaft operates smoothly and maximizes its contribution to drivetrain efficiency.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enabling four-wheel drive capability. The rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
By facilitating power distribution to all four wheels, rear drive shafts enhance the vehicle’s off-road performance, traction, and stability. Four-wheel drive capability allows the vehicle to tackle challenging terrain, slippery conditions, or uneven surfaces with improved control and maneuverability.
In summary, rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. They affect power transmission, traction, stability, handling, suspension compatibility, drivetrain efficiency, and enable four-wheel drive capability. By understanding and optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of rear drive shafts, manufacturers and drivers can enhance a vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and driving experience.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China Standard CZPT Auto Parts Rear Left Drive Shafts OEM 33213420709 for BMW E83
Product Description
| Description | Frey Auto Parts Rear Left Drive Shafts OEM for BMW E83 |
| OEM Number | OEM |
| Brand | Frey |
| Application | BMW E83 |
| Market Type | Aftermarket |
| Price Term | EXW, FOB HangZhou/HangZhou |
| Payment | T/T, Paypal, West Union, L/C, Cash, etc |
| Quality | Produced according to the OE Parts |
| Certificate | TUV, SGS |
| Packing | Frey Brand, Customer Brand, Neutral Packing |
| Delivery Time | 5-15 days if in stock |
| Export Areas | Sounth America, Europe, Amercia, Asia |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | BMW |

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Efficient Power Transfer While Maintaining Balance?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. At the same time, they must maintain balance to prevent vibrations, reduce stress on drivetrain components, and enhance overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve efficient power transfer while maintaining balance:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully designed and manufactured to achieve balance. Balance refers to the distribution of mass along the length of the drive shaft. Imbalances can lead to vibrations and unwanted forces that affect the smooth operation of the drivetrain. To achieve balance, drive shafts are dynamically balanced during the manufacturing process. This involves adding weights or removing material at specific locations to counteract any uneven distribution of mass. By achieving balance, the drive shaft can rotate smoothly at high speeds, minimizing vibrations and ensuring efficient power transfer.
2. Proper Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are important considerations for maintaining balance. A drive shaft that is too long or too short can result in excessive deflection or bending, leading to vibrations and potential failure. Similarly, an incorrect diameter can affect the stiffness and torsional strength of the drive shaft, resulting in imbalances. Manufacturers carefully calculate the optimal length and diameter of the drive shaft based on the vehicle’s specifications and requirements to ensure proper balance and power transfer.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The selection of high-quality materials is crucial for maintaining balance in rear drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from materials such as steel or aluminum. These materials offer the necessary strength and rigidity while being lightweight. The use of high-quality materials ensures that the drive shaft can withstand the torque and rotational forces without excessive flexing or bending, which can lead to imbalances. Additionally, the materials are chosen for their ability to resist fatigue and vibration, further contributing to balanced operation.
4. Precision Manufacturing:
Rear drive shafts are manufactured with precision to maintain balance. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining, are employed to ensure the drive shaft’s dimensional accuracy and balance. The manufacturing process involves precise machining of the shaft, including the yokes, flanges, and other components, to achieve tight tolerances and minimize any deviations that could affect balance. Strict quality control measures are implemented to verify the balance of each drive shaft before it is installed in a vehicle.
5. Vibration Dampening Techniques:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate vibration dampening techniques to further enhance balance and reduce unwanted vibrations. These techniques may include the use of balancing weights, dampers, or vibration-absorbing materials. Balancing weights can be strategically placed along the drive shaft to counteract any remaining imbalances. Dampers, such as rubber or elastomer components, are employed to absorb and dissipate vibrations, preventing them from propagating throughout the drivetrain. By minimizing vibrations, these techniques help maintain overall balance and contribute to efficient power transfer.
6. Universal Joints or Constant Velocity Joints:
Rear drive shafts incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate changes in angles and maintain balance. These joints allow for angular movement and compensate for variations in the alignment between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. By allowing the drive shaft to flex and articulate, these joints help prevent binding, minimize stress on the drivetrain components, and maintain balance throughout the range of motion.
7. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
Maintaining balance in rear drive shafts requires regular maintenance and inspection. Over time, components may wear or become damaged, leading to imbalances. It is important to periodically inspect the drive shaft for signs of wear, such as worn u-joints or damaged CV joints. Additionally, proper lubrication of the joints and ensuring the drive shaft is properly installed and aligned are essential for maintaining balance. Routine maintenance and inspections help detect and address any issues that could affect the drive shaft’s balance and overall performance.
In summary, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through a combination of balanced design, proper length and diameter, high-quality materials, precision manufacturing, vibration dampening techniques, flexible joints, and regular maintenance. By achieving and maintaining balance, rear drive shafts contribute to smooth operation, minimize vibrations, and enhance the overall performance and longevity of the drivetrain system.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Contribute to the Overall Performance of Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in the overall performance of rear-wheel-drive (RWD) vehicles. They are responsible for transferring torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, which then distributes power to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to the overall performance of RWD vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing for propulsion and forward motion. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission or transfer case to the rear drive shaft. The drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes the power to the rear wheels. The efficiency and effectiveness of this power transmission process directly impact the acceleration, speed, and overall performance of the vehicle.
2. Torque Delivery:
Rear drive shafts ensure efficient torque delivery to the rear wheels, enabling traction and propulsion. By connecting the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, the drive shaft transfers torque generated by the engine to the wheels. The rear wheels receive this torque, allowing them to grip the road surface and propel the vehicle forward. The ability of the rear drive shaft to effectively deliver torque contributes to improved acceleration, responsiveness, and overall performance of RWD vehicles.
3. Weight Distribution:
Rear drive shafts contribute to the proper weight distribution in RWD vehicles. Since the engine is typically positioned at the front of the vehicle, the rear drive shaft helps balance the weight distribution by transferring power to the rear wheels. This balanced weight distribution enhances overall stability, handling, and cornering capabilities. It allows for better control of the vehicle and helps optimize the performance during various driving conditions.
4. Handling and Stability:
Rear drive shafts significantly influence the handling and stability of RWD vehicles. By delivering torque to the rear wheels, the drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s rear-wheel traction. This configuration provides better weight transfer during acceleration, which improves traction and reduces the chances of wheel spin. The rear drive shaft also aids in maintaining stability during cornering by helping to distribute the vehicle’s weight more evenly. RWD vehicles are known for their balanced and predictable handling characteristics, and the rear drive shaft plays a vital role in achieving these attributes.
5. Performance in Various Conditions:
Rear drive shafts impact the performance of RWD vehicles in different driving conditions. In dry or high-grip situations, the rear-wheel traction provided by the drive shaft enables quick acceleration and efficient power delivery. RWD vehicles often exhibit superior handling characteristics in these conditions due to the balanced weight distribution and the rear drive shaft’s ability to transfer torque effectively. However, in low-traction conditions such as rain, snow, or off-road situations, RWD vehicles may require additional driver skill and careful throttle control to maintain traction and stability.
6. Customization and Performance Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can be customized or upgraded to enhance the performance of RWD vehicles. For example, performance-oriented drive shafts made from lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can reduce rotational mass, improving overall vehicle agility and responsiveness. Upgraded drive shafts with strengthened components can handle increased torque and power outputs in high-performance applications. Customization and upgrades to the rear drive shaft allow vehicle owners to tailor the performance characteristics to their specific needs and preferences.
7. Maintenance and Service:
Regular maintenance and service of rear drive shafts are essential for maintaining optimal performance. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and addressing any issues such as worn U-joints or CV joints can prevent driveline vibrations, reduce power losses, and ensure smooth torque transmission. Proper maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the rear drive shaft, allowing it to continue supporting the overall performance of the RWD vehicle.
In summary, rear drive shafts are integral to the overall performance of RWD vehicles. They facilitate power transmission, torque delivery, and weight distribution, contributing to acceleration, traction, handling, and stability. The rear drive shaft’s ability to efficiently transfer torque to the rear wheels is key to the performance characteristics of RWD vehicles. Through customization, upgrades, and regular maintenance, rear drive shafts can be optimized to further enhance the performance of RWD vehicles in various driving conditions and applications.
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China best CZPT Auto Spare Car Parts Factory Wholesale All Front Rear Left Right Drive Shafts for Mercedes Benz Gla Cla S C Class W210 W213 W221 S210 S211 W204 W207 C300
Product Description
Product Description
Complete products, one-stop purchasing, saving your cost and time.
Inventory advantage, stable supply, short delivery time.
High-quality original, made in China, there are more many parts are in stock.
Install and test the products in Chinese market first, to ensure the quality.
Specifications
| Mounting Type | Hydro Bearing |
| Dimension | OEM Standard |
| Material | Steel Elastomer |
| Weight | 2Kg |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
About BBmart Auto Parts
Since establishment in 2005, BBmart Auto Parts has achieved in becoming 1 of the most trust-worthy automobile replacement parts distributors in the industry with Good Credibility, offering our customers a “One stop Shop” experience and constantly ensuring that we place our customers’ needs at the forefront, offering them Good service.We are not only renowned for our professionalism and comprehensive range of replacement products, but also offer our customers a competitive position with our Fair Price. Our manufacturers have passed and acquired various International certifications on safety and quality such as CAPA, Thatcham, E-Mark, SAE, ISO 9000/1, ISO 9002, TS 16949 MQVP and the SABS, thereby assuring Good Quality – Parts you can trust.
Good Credibility
Good Service
Good Quality
Fair Price
These define the way we work and allowed us to be professional to earn and build trust with our customers and suppliers. This trust fortifies our business relationships as partners and has created a CHINAMFG situation for the clients.
Our products have been sold over the world. Our diversified replacement product lines cover the Automotive Lamps, Automotive Body Parts, Suspension Parts, Electric Parts, Engine Parts and Accessories.
BBmart endeavours to understand and precisely respond to our customer’s diverse needs. Our vision is to be “The prime distributor for automotive replacement parts in China.” We are committed to work diligently to deliver best service, high quality and cost-effective products to our customers.
FAQ
Q1.How many years have your company dealt in autoparts?
A: We have been founded for 16 years now.
Q2. What is your company major products?
A: Our main products are Spark Plug, Brake Pad, Oil Fiter. Fuel Filter, Air Fiter, Engine Belt, Shock Absorber, Control Arm, Ball
Joint, Tie Rod End, Stabilizer Link Rod, Wheel Hub Bearing, C.v.joint, Car Light, ect.
Q3. Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are Manufacturing and Trading and Supply Chain company.
Q4. What is the MOQ?
A: Normally we can supply any quantity if we have stock.
Q5. What is the delivery date?
A: It takes 5-7 days if there is stock, but takes about 30 days if there is no stock.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Years Warranty |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Standard CZPT Auto Spare Car Parts Factory Wholesale All Front Rear Left Right Drive Shafts for BMW X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 Z3 Z4 F20 F21 F22 F23 F30 F31 F32 F36 G01 G02
Product Description
Product Description
Complete products, one-stop purchasing, saving your cost and time.
Inventory advantage, stable supply, short delivery time.
High-quality original, made in China, there are more many parts are in stock.
Install and test the products in Chinese market first, to ensure the quality.
Specifications
| Mounting Type | Hydro Bearing |
| Dimension | OEM Standard |
| Material | Steel Elastomer |
| Weight | 2Kg |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
About BBmart Auto Parts
Since establishment in 2005, BBmart Auto Parts has achieved in becoming 1 of the most trust-worthy automobile replacement parts distributors in the industry with Good Credibility, offering our customers a “One stop Shop” experience and constantly ensuring that we place our customers’ needs at the forefront, offering them Good service.We are not only renowned for our professionalism and comprehensive range of replacement products, but also offer our customers a competitive position with our Fair Price. Our manufacturers have passed and acquired various International certifications on safety and quality such as CAPA, Thatcham, E-Mark, SAE, ISO 9000/1, ISO 9002, TS 16949 MQVP and the SABS, thereby assuring Good Quality – Parts you can trust.
Good Credibility
Good Service
Good Quality
Fair Price
These define the way we work and allowed us to be professional to earn and build trust with our customers and suppliers. This trust fortifies our business relationships as partners and has created a CHINAMFG situation for the clients.
Our products have been sold over the world. Our diversified replacement product lines cover the Automotive Lamps, Automotive Body Parts, Suspension Parts, Electric Parts, Engine Parts and Accessories.
BBmart endeavours to understand and precisely respond to our customer’s diverse needs. Our vision is to be “The prime distributor for automotive replacement parts in China.” We are committed to work diligently to deliver best service, high quality and cost-effective products to our customers.
FAQ
Q1.How many years have your company dealt in autoparts?
A: We have been founded for 16 years now.
Q2. What is your company major products?
A: Our main products are Spark Plug, Brake Pad, Oil Fiter. Fuel Filter, Air Fiter, Engine Belt, Shock Absorber, Control Arm, Ball
Joint, Tie Rod End, Stabilizer Link Rod, Wheel Hub Bearing, C.v.joint, Car Light, ect.
Q3. Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are Manufacturing and Trading and Supply Chain company.
Q4. What is the MOQ?
A: Normally we can supply any quantity if we have stock.
Q5. What is the delivery date?
A: It takes 5-7 days if there is stock, but takes about 30 days if there is no stock.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Years Warranty |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Efficient Power Transfer While Maintaining Balance?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. At the same time, they must maintain balance to prevent vibrations, reduce stress on drivetrain components, and enhance overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve efficient power transfer while maintaining balance:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully designed and manufactured to achieve balance. Balance refers to the distribution of mass along the length of the drive shaft. Imbalances can lead to vibrations and unwanted forces that affect the smooth operation of the drivetrain. To achieve balance, drive shafts are dynamically balanced during the manufacturing process. This involves adding weights or removing material at specific locations to counteract any uneven distribution of mass. By achieving balance, the drive shaft can rotate smoothly at high speeds, minimizing vibrations and ensuring efficient power transfer.
2. Proper Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are important considerations for maintaining balance. A drive shaft that is too long or too short can result in excessive deflection or bending, leading to vibrations and potential failure. Similarly, an incorrect diameter can affect the stiffness and torsional strength of the drive shaft, resulting in imbalances. Manufacturers carefully calculate the optimal length and diameter of the drive shaft based on the vehicle’s specifications and requirements to ensure proper balance and power transfer.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The selection of high-quality materials is crucial for maintaining balance in rear drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from materials such as steel or aluminum. These materials offer the necessary strength and rigidity while being lightweight. The use of high-quality materials ensures that the drive shaft can withstand the torque and rotational forces without excessive flexing or bending, which can lead to imbalances. Additionally, the materials are chosen for their ability to resist fatigue and vibration, further contributing to balanced operation.
4. Precision Manufacturing:
Rear drive shafts are manufactured with precision to maintain balance. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining, are employed to ensure the drive shaft’s dimensional accuracy and balance. The manufacturing process involves precise machining of the shaft, including the yokes, flanges, and other components, to achieve tight tolerances and minimize any deviations that could affect balance. Strict quality control measures are implemented to verify the balance of each drive shaft before it is installed in a vehicle.
5. Vibration Dampening Techniques:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate vibration dampening techniques to further enhance balance and reduce unwanted vibrations. These techniques may include the use of balancing weights, dampers, or vibration-absorbing materials. Balancing weights can be strategically placed along the drive shaft to counteract any remaining imbalances. Dampers, such as rubber or elastomer components, are employed to absorb and dissipate vibrations, preventing them from propagating throughout the drivetrain. By minimizing vibrations, these techniques help maintain overall balance and contribute to efficient power transfer.
6. Universal Joints or Constant Velocity Joints:
Rear drive shafts incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate changes in angles and maintain balance. These joints allow for angular movement and compensate for variations in the alignment between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. By allowing the drive shaft to flex and articulate, these joints help prevent binding, minimize stress on the drivetrain components, and maintain balance throughout the range of motion.
7. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
Maintaining balance in rear drive shafts requires regular maintenance and inspection. Over time, components may wear or become damaged, leading to imbalances. It is important to periodically inspect the drive shaft for signs of wear, such as worn u-joints or damaged CV joints. Additionally, proper lubrication of the joints and ensuring the drive shaft is properly installed and aligned are essential for maintaining balance. Routine maintenance and inspections help detect and address any issues that could affect the drive shaft’s balance and overall performance.
In summary, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through a combination of balanced design, proper length and diameter, high-quality materials, precision manufacturing, vibration dampening techniques, flexible joints, and regular maintenance. By achieving and maintaining balance, rear drive shafts contribute to smooth operation, minimize vibrations, and enhance the overall performance and longevity of the drivetrain system.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Contribute to the Overall Performance of Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in the overall performance of rear-wheel-drive (RWD) vehicles. They are responsible for transferring torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, which then distributes power to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to the overall performance of RWD vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing for propulsion and forward motion. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission or transfer case to the rear drive shaft. The drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes the power to the rear wheels. The efficiency and effectiveness of this power transmission process directly impact the acceleration, speed, and overall performance of the vehicle.
2. Torque Delivery:
Rear drive shafts ensure efficient torque delivery to the rear wheels, enabling traction and propulsion. By connecting the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, the drive shaft transfers torque generated by the engine to the wheels. The rear wheels receive this torque, allowing them to grip the road surface and propel the vehicle forward. The ability of the rear drive shaft to effectively deliver torque contributes to improved acceleration, responsiveness, and overall performance of RWD vehicles.
3. Weight Distribution:
Rear drive shafts contribute to the proper weight distribution in RWD vehicles. Since the engine is typically positioned at the front of the vehicle, the rear drive shaft helps balance the weight distribution by transferring power to the rear wheels. This balanced weight distribution enhances overall stability, handling, and cornering capabilities. It allows for better control of the vehicle and helps optimize the performance during various driving conditions.
4. Handling and Stability:
Rear drive shafts significantly influence the handling and stability of RWD vehicles. By delivering torque to the rear wheels, the drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s rear-wheel traction. This configuration provides better weight transfer during acceleration, which improves traction and reduces the chances of wheel spin. The rear drive shaft also aids in maintaining stability during cornering by helping to distribute the vehicle’s weight more evenly. RWD vehicles are known for their balanced and predictable handling characteristics, and the rear drive shaft plays a vital role in achieving these attributes.
5. Performance in Various Conditions:
Rear drive shafts impact the performance of RWD vehicles in different driving conditions. In dry or high-grip situations, the rear-wheel traction provided by the drive shaft enables quick acceleration and efficient power delivery. RWD vehicles often exhibit superior handling characteristics in these conditions due to the balanced weight distribution and the rear drive shaft’s ability to transfer torque effectively. However, in low-traction conditions such as rain, snow, or off-road situations, RWD vehicles may require additional driver skill and careful throttle control to maintain traction and stability.
6. Customization and Performance Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can be customized or upgraded to enhance the performance of RWD vehicles. For example, performance-oriented drive shafts made from lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can reduce rotational mass, improving overall vehicle agility and responsiveness. Upgraded drive shafts with strengthened components can handle increased torque and power outputs in high-performance applications. Customization and upgrades to the rear drive shaft allow vehicle owners to tailor the performance characteristics to their specific needs and preferences.
7. Maintenance and Service:
Regular maintenance and service of rear drive shafts are essential for maintaining optimal performance. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and addressing any issues such as worn U-joints or CV joints can prevent driveline vibrations, reduce power losses, and ensure smooth torque transmission. Proper maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the rear drive shaft, allowing it to continue supporting the overall performance of the RWD vehicle.
In summary, rear drive shafts are integral to the overall performance of RWD vehicles. They facilitate power transmission, torque delivery, and weight distribution, contributing to acceleration, traction, handling, and stability. The rear drive shaft’s ability to efficiently transfer torque to the rear wheels is key to the performance characteristics of RWD vehicles. Through customization, upgrades, and regular maintenance, rear drive shafts can be optimized to further enhance the performance of RWD vehicles in various driving conditions and applications.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Standard Customized Dental Metal Carbon Steel Billiard Pto Propeller Steering Drive Shafts
Product Description
Product Description
Warranty
1 Year
Applicable Industries
Hotels, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms, Restaurant, Home Use, Retail, Food Shop, Printing Shops, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Food & Beverage Shops, Other, Advertising Company
Weight (KG)
1
Showroom Location
Viet Nam
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components
1 Year
Core Components
PLC, Engine, Bearing, Gearbox, Motor, Pressure vessel, Gear, Pump
Material
steel
Place of CZPT
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Structure
Shaft
Coatings
Customized
Torque Capacity
Customized
Model Number
Customized
Brand Name
NON
Description
Shaft
Machining equipment
CNC mill,lathe and grind machine
Material
stainless steel, aluminium, carbon
Surface
Grinding and polishing
Shape
Customized
Sampling time
10days
Production time
20days
Packing
Protective packing
Tolerance
±0.001
OEM
Welcome
Production Process
Company Profile
HangZhou HUANENGDA SPRING CO.,LTD
HangZhou HuaNengDa Spring Co., Ltd. is located in Tong ‘an District, HangZhou City, ZheJiang Province, China. It is a hardware factory specializing in R&D design, manufacture and sales of precision components. The company introduces domestic and foreign advanced equipment and production technology, adopts CNC high-precision computer machine, compression spring machine, CNC five-axis linkage machining center, CNC turning and milling compound, 300 tons of punch and other mechanical equipment,and employs senior engineers with more than 10 years of work experience to debug mechanical equipment and customize production.
With the business philosophy of honesty, pragmatism and excellence, HuaNengDa Spring Company is dedicated to serving customers at home and abroad. We hope that the products of HuaNengDa will help your business to be more brilliant, let us build a bright future in the high-tech era!
The testimony is pragmatic and the attitude of the people. Quality service is the pursuit of the people!
Factory Workshop
Production Procedur
Quality Inspection
Packing And Shipping
Our Service
FAQ
1.Small order quantity is workable
From the initial sample design of the spring to the mass production of the springs, we can quickly reach your manufacturing goals and immediately provide the best products because we have an excellent production management system and expertly trained technical personnel.
2.Committed to high quality production
To keep HuaNengDa Springs at the forefront of the industry, we have implemented a stringent internal quality control system and regularly import the latest manufacturing equipment and instruments. Through our precise manufacturing technology and expert mold making process, we provide our customers with the best products and service.
3.Efficiency in manufacturing
Our company’s machinery and equipment are controlled by CNC computers. In order to respond to international needs and standards, we continuously update and upgrade our equipment every year. Our machines effectively increase production capacity and save on manufacturing costs. The manufacturing department is the most important core of the whole company and by treating it with utmost importance, we reap great benefits in manufacturing efficiency.
4.Excellent customization services
HuaNengDa’s R&D team designs and completes customized products according to the needs of customers. From the selection of materials to the function of the products, we can design and develop products to suite different customers’ requirements. We are constantly involving ourselves in all aspects of the industry because only by having a complete view and analysis of the industry, can there be innovative breakthroughs.
Payment term
*T/T : 30% pre T/T, 70% before delivery.
*Trade Assurance
Service
*Delivery on time.
*Shipped by a convenient and cost-effective way.
*Good after-selling, 24 hours service for you.
Packing
*A: Poly bag, Plstic tray ,small box, carton.
*B: According to customers’ requirements.
Delivery
*Sample: 7-10 days after deposit received.
*Batch goods: 12-15 days after samples approved. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
| Standard: | DIN, ASTM, GOST, GB, JIS, ANSI, BS |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Material: | Steel,Stainless Steel,Iron |
| Application: | Metal Processing Machinery Parts |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-05-13
China Good quality CZPT Auto Spare Car Parts Factory Wholesale All Front Rear Left Right Drive Shafts for VW Polo Golf Touareg Passat Lavida Bora Jetta Caddy Beetle Hot Selling
Product Description
Product Description
Complete products, one-stop purchasing, saving your cost and time.
Inventory advantage, stable supply, short delivery time.
High-quality original, made in China, there are more many parts are in stock.
Install and test the products in Chinese market first, to ensure the quality.
Specifications
| Mounting Type | Hydro Bearing |
| Dimension | OEM Standard |
| Material | Steel Elastomer |
| Weight | 2Kg |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
About BBmart Auto Parts
Since establishment in 2005, BBmart Auto Parts has achieved in becoming 1 of the most trust-worthy automobile replacement parts distributors in the industry with Good Credibility, offering our customers a “One stop Shop” experience and constantly ensuring that we place our customers’ needs at the forefront, offering them Good service.We are not only renowned for our professionalism and comprehensive range of replacement products, but also offer our customers a competitive position with our Fair Price. Our manufacturers have passed and acquired various International certifications on safety and quality such as CAPA, Thatcham, E-Mark, SAE, ISO 9000/1, ISO 9002, TS 16949 MQVP and the SABS, thereby assuring Good Quality – Parts you can trust.
Good Credibility
Good Service
Good Quality
Fair Price
These define the way we work and allowed us to be professional to earn and build trust with our customers and suppliers. This trust fortifies our business relationships as partners and has created a CHINAMFG situation for the clients.
Our products have been sold over the world. Our diversified replacement product lines cover the Automotive Lamps, Automotive Body Parts, Suspension Parts, Electric Parts, Engine Parts and Accessories.
BBmart endeavours to understand and precisely respond to our customer’s diverse needs. Our vision is to be “The prime distributor for automotive replacement parts in China.” We are committed to work diligently to deliver best service, high quality and cost-effective products to our customers.
FAQ
Q1.How many years have your company dealt in autoparts?
A: We have been founded for 16 years now.
Q2. What is your company major products?
A: Our main products are Spark Plug, Brake Pad, Oil Fiter. Fuel Filter, Air Fiter, Engine Belt, Shock Absorber, Control Arm, Ball
Joint, Tie Rod End, Stabilizer Link Rod, Wheel Hub Bearing, C.v.joint, Car Light, ect.
Q3. Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are Manufacturing and Trading and Supply Chain company.
Q4. What is the MOQ?
A: Normally we can supply any quantity if we have stock.
Q5. What is the delivery date?
A: It takes 5-7 days if there is stock, but takes about 30 days if there is no stock.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Years Warranty |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
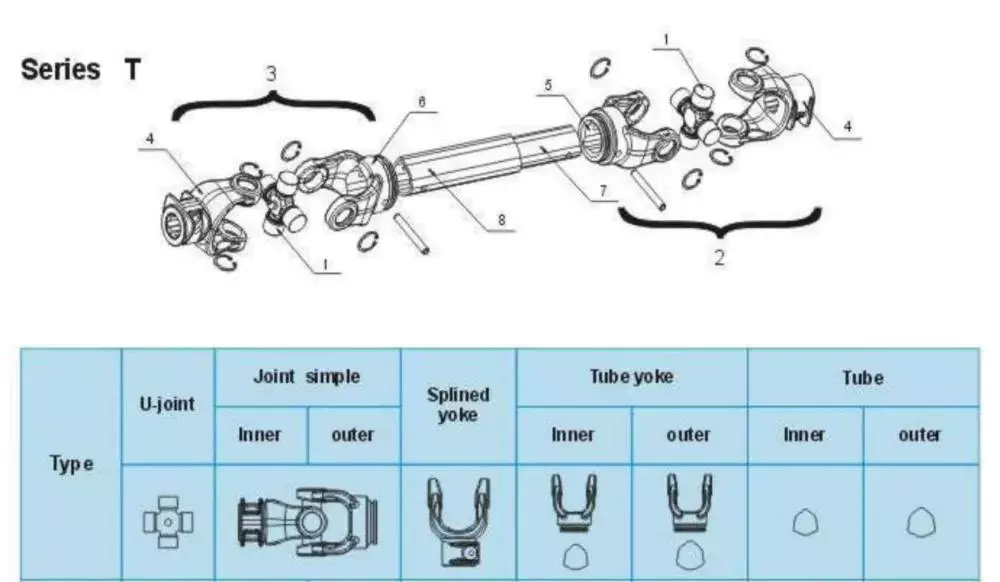
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting the Right Rear Drive Shaft for a Vehicle?
When selecting the right rear drive shaft for a vehicle, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key factors that should be taken into account:
1. Vehicle Specifications:
The specific characteristics of the vehicle play a significant role in determining the appropriate rear drive shaft. Factors such as the vehicle’s weight, horsepower, torque output, wheelbase, suspension design, and intended use (e.g., off-roading, towing, performance driving) need to be considered. These specifications help determine the required torque capacity, length, diameter, and material strength of the drive shaft to handle the vehicle’s demands effectively.
2. Drivetrain Configuration:
The drivetrain configuration of the vehicle influences the selection of the rear drive shaft. Vehicles with rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems have different drivetrain layouts and torque distribution requirements. The drive shaft must be compatible with the vehicle’s drivetrain configuration, including the type of differential, transfer case, and front-wheel drive components, if applicable.
3. Torque and Power Requirements:
The torque and power output of the vehicle’s engine or transmission impact the selection of the rear drive shaft. Higher torque and power levels necessitate a stronger and more robust drive shaft to handle the increased load. It is important to consider the maximum torque and power values of the vehicle and select a drive shaft that can safely and reliably transmit the power without exceeding its rated capacity.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for the rear drive shaft is crucial in ensuring its strength, durability, and weight. Common materials used for drive shafts include steel and aluminum. Steel drive shafts offer high strength and are typically used in heavy-duty applications, while aluminum drive shafts are lighter and can provide weight savings, making them suitable for performance-oriented vehicles. The material selection should also consider factors such as corrosion resistance, cost, and manufacturing feasibility.
5. Length and Diameter:
The length and diameter of the rear drive shaft are critical considerations to prevent issues such as vibration, bending, or excessive deflection. The length of the drive shaft depends on the vehicle’s wheelbase and the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. The diameter of the drive shaft is determined by the torque and power requirements, as well as the material properties. Proper sizing ensures the drive shaft can handle the forces and maintain optimal power transmission without compromising safety or performance.
6. Suspension and Drivetrain Movements:
The suspension system and drivetrain movements of the vehicle need to be taken into account when selecting a rear drive shaft. The drive shaft must accommodate the range of motion and articulation of the suspension, as well as the angular movements and changes in alignment between the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. Flexible joints such as universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are typically used to allow for these movements while maintaining torque transmission.
7. Environmental Factors:
The environmental conditions in which the vehicle will operate should be considered when selecting a rear drive shaft. Factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to moisture, off-road terrain, and corrosive substances can impact the choice of materials, protective coatings, and maintenance requirements of the drive shaft. It is essential to select a drive shaft that can withstand the environmental conditions and maintain its performance and longevity.
8. Manufacturer Quality and Compatibility:
When choosing a rear drive shaft, it is important to consider the reputation and quality of the manufacturer. Selecting a drive shaft from a reputable and experienced manufacturer ensures that the product meets industry standards, undergoes thorough quality control, and is compatible with the vehicle’s specifications and requirements. It is advisable to consult with automotive professionals or refer to manufacturer guidelines to ensure proper selection and compatibility.
In summary, selecting the right rear drive shaft for a vehicle involves considering factors such as vehicle specifications, drivetrain configuration, torque and power requirements, material selection, length and diameter, suspension and drivetrain movements, environmental factors, and manufacturer quality. Taking these factors into account helps ensure that the chosen rear drive shaft is suitable for the vehicle’s needs and provides reliable and efficient power transmission.
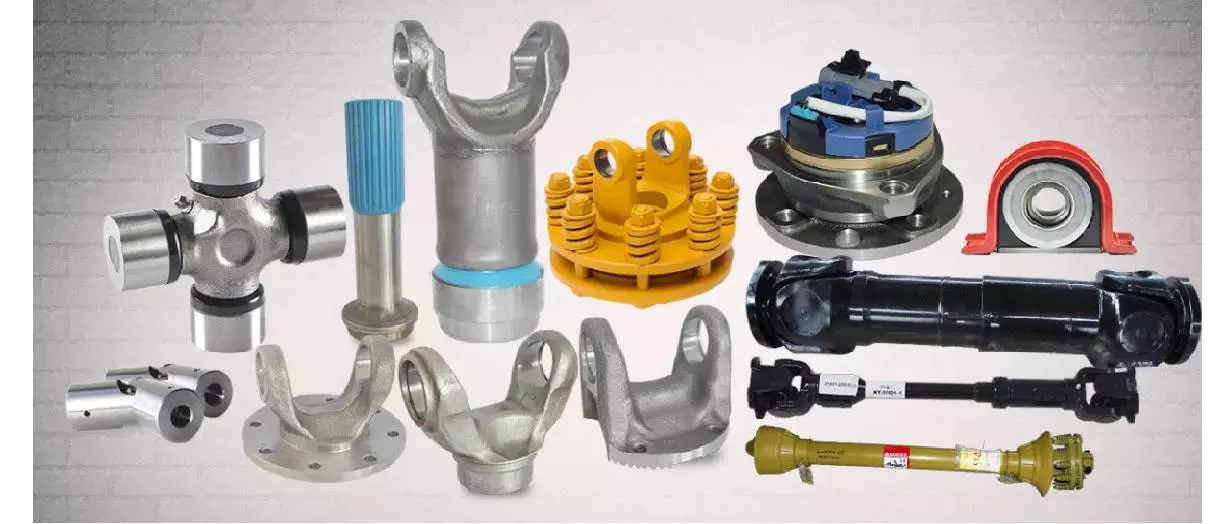

What Safety Precautions Should Be Followed When Working with Rear Drive Shafts?
Working with rear drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage to the vehicle or surrounding components. Here are detailed safety precautions that should be followed when working with rear drive shafts:
1. Wear Protective Gear:
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with rear drive shafts. This includes safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from debris, gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges or moving parts, and sturdy footwear to provide foot protection in case of accidents or dropped tools.
2. Ensure Vehicle Stability:
Prioritize vehicle stability when working with rear drive shafts. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. If necessary, use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling. Additionally, if you are raising the vehicle using a jack or lift, ensure that it is securely supported with jack stands or appropriate lift points to prevent accidental movement or collapse.
3. Disconnect the Battery:
Before beginning any work on the rear drive shaft, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This precaution helps prevent accidental engagement of the starter motor or other electrical components, reducing the risk of injury or damage during the maintenance or replacement process.
4. Release Tension on the Drivetrain:
Release tension on the drivetrain components before removing the rear drive shaft. If applicable, release tension on the parking brake, shift the transmission into neutral, and engage the wheel chocks. This step helps prevent unexpected movement of the vehicle or drivetrain components while working on the drive shaft.
5. Secure the Drive Shaft:
Prior to removing the rear drive shaft, ensure it is securely supported and immobilized. Use a drive shaft support fixture or a transmission jack to hold the drive shaft in place. This prevents the drive shaft from falling or causing injury when it is disconnected from the transmission or differential.
6. Mark Alignment Points:
Before disconnecting the rear drive shaft, mark alignment points on the drive shaft and the surrounding components. This will help ensure proper reinstallation and alignment during assembly. Marking the orientation of the drive shaft also aids in identifying any imbalance or misalignment issues that may arise during reinstallation.
7. Use Proper Tools and Techniques:
Always use the appropriate tools and techniques when working with rear drive shafts. Use socket wrenches, torque wrenches, and other specialized tools designed for drive shaft removal and installation. Avoid using improper tools or excessive force, as this can lead to damage or personal injury. Follow manufacturer guidelines and service manuals for specific procedures and torque specifications.
8. Handle with Care:
Handle the rear drive shaft with care to avoid unnecessary damage or injury. Avoid dropping or striking the drive shaft against hard surfaces, as this can cause dents, bends, or other structural damage. Additionally, be cautious of sharp edges or splines on the drive shaft that can cause cuts or abrasions. Always handle the drive shaft by gripping secure areas and wearing appropriate gloves for added protection.
9. Inspect for Damage and Wear:
Before reinstalling or replacing the rear drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, dents, corrosion, or loose components. Also, inspect the U-joints or CV joints for excessive play, rust, or damaged seals. If any issues are detected, it is advisable to replace the damaged parts or the entire drive shaft to ensure safe and reliable operation.
10. Follow Proper Reinstallation Procedures:
When reinstalling the rear drive shaft, follow proper procedures to ensure correct alignment and engagement with the transmission output shaft and differential input flange. Use the alignment marks made during disassembly as a guide. Tighten all fasteners to the recommended torque specifications, and ensure that all retaining clips or bolts are properly secured.
11. Test for Proper Functioning:
After completing the rear drive shaft work, conduct a thorough test to ensure proper functioning. Check for any abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks during vehicle operation. If any issues are observed, reinspect the drive shaft installation and address the problem promptly.
12. Consult Professional Assistance if Needed:
If you are uncertain about any aspect of working with rear drive shafts or encounter difficulties during the process, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician or automotive service center. Theycan provide the necessary expertise and ensure the work is carried out safely and correctly.
By following these safety precautions when working with rear drive shafts, you can help protect yourself, prevent damage to the vehicle, and maintain a safe working environment. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution throughout the entire process.

What Is a Rear Drive Shaft and How Does It Contribute to Vehicle Propulsion?
A rear drive shaft is a component of a vehicle’s drivetrain system that connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s propulsion. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a rear drive shaft is and how it contributes to vehicle propulsion:
1. Drivetrain Connection:
The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. It is typically a tubular shaft that rotates at high speeds to transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels.
When the engine generates power, it is transmitted through the transmission or transfer case, which determines the appropriate gear ratio. The rear drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes power to the rear wheels.
2. Torque Transmission:
The primary function of the rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine to the rear wheels. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for propelling the vehicle forward.
As the engine produces torque, it is transferred to the transmission or transfer case. From there, the torque is sent through the rear drive shaft to the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque and sends it to the rear wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle.
3. Power Distribution:
The rear drive shaft plays a critical role in distributing power evenly between the rear wheels. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft ensures that power is distributed to both wheels, enabling balanced propulsion.
By transmitting torque from the engine to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to both rear wheels based on traction conditions. This power distribution ensures that both wheels contribute to vehicle propulsion and provides stability and control during acceleration and cornering.
4. Suspension Movement Compensation:
Another important function of the rear drive shaft is to compensate for the movement of the suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move up and down independently to absorb bumps, uneven road surfaces, and other disturbances.
As the suspension moves, the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential changes. The rear drive shaft accommodates this movement by expanding or contracting its length, allowing the rear wheels to move vertically while maintaining a continuous torque transmission.
5. Drive System Efficiency:
An efficiently operating rear drive shaft contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s drivetrain system. By effectively transmitting torque from the engine to the rear wheels, it minimizes power losses and ensures optimal power delivery.
Efficiency in power transmission reduces energy waste and maximizes the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. A well-maintained rear drive shaft with proper lubrication and alignment helps minimize friction and mechanical losses, maximizing the effectiveness of the drivetrain system.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft is a crucial component for engaging the front wheels for propulsion. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which then distributes power to the front and rear differentials.
By transmitting torque to the transfer case, the rear drive shaft enables four-wheel drive capability, allowing the vehicle to engage all four wheels for enhanced traction and off-road performance.
In summary, a rear drive shaft is a key component in a vehicle’s drivetrain system. It serves as a drivetrain connection, transmits torque from the engine to the rear wheels, distributes power between the rear wheels, compensates for suspension movement, enhances drive system efficiency, and facilitates four-wheel drive capability. By fulfilling these functions, the rear drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s propulsion, stability, and overall performance.


editor by CX 2024-05-10
China high quality OEM 33207582141 Rear Drive Shafts for BMW F15 F16 E71 CZPT Auto Car Parts
Product Description
| Description | OEM Rear Drive Shafts for BMW F15 F16 E71 CHINAMFG Auto Car Parts |
| OEM Number | OEM |
| Brand | Frey |
| Application | BMW F15 F16 E71 |
| Market Type | Aftermarket |
| Price Term | EXW, FOB HangZhou/HangZhou |
| Payment | T/T, Paypal, West Union, L/C, Cash, etc |
| Quality | Produced according to the OE Parts |
| Certificate | TUV, SGS |
| Packing | Frey Brand, Customer Brand, Neutral Packing |
| Delivery Time | 5-15 days if in stock |
| Export Areas | Sounth America, Europe, Amercia, Asia |
Frey, since 2004, is a Supply Chain Management Co, Ltd.For automotive after-market integrating R8D, operation, sales,service,import and export trade of automo-bile parts. Our core products focus on serving the CHINAMFG brand such as Mer-cedes Benz and BMW And we are a brand supplier with the most complete SkU in automotive aftermar-ket in China.ln China, CHINAMFG has morethan 150 agency outlets, and the sales of prod-ucts have covered more than 110 countries and regions around theworld, basicallyrealizing the sales network all over the world.As a wel-known global auto partsbrand,Frey has a global supply intelligence distribution centers in HangZhoucover-ing a total area of 15000 square meters. in the digital modern industrial system, through the introduction of perfect ware-housing and logistics system and SAPintelligent management system, CHINAMFG prod-ucts are more rigorous and meticulous in the production and operation.warehousingmanagement,accurate distribution and other series of operation processes.
In the past 17 years, CHINAMFG Brand has always adhered to independent researchand development,with technologyas the driving force and products as the core.Soevery year, more than 800 new products are introduced, with atotal of more than15000 products. The products produced by CHINAMFG Brand have successfully passed the SO 9001quality management systemcertification by TUV South Germany group.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Contribute to the Overall Performance of Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in the overall performance of rear-wheel-drive (RWD) vehicles. They are responsible for transferring torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, which then distributes power to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to the overall performance of RWD vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing for propulsion and forward motion. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission or transfer case to the rear drive shaft. The drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes the power to the rear wheels. The efficiency and effectiveness of this power transmission process directly impact the acceleration, speed, and overall performance of the vehicle.
2. Torque Delivery:
Rear drive shafts ensure efficient torque delivery to the rear wheels, enabling traction and propulsion. By connecting the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, the drive shaft transfers torque generated by the engine to the wheels. The rear wheels receive this torque, allowing them to grip the road surface and propel the vehicle forward. The ability of the rear drive shaft to effectively deliver torque contributes to improved acceleration, responsiveness, and overall performance of RWD vehicles.
3. Weight Distribution:
Rear drive shafts contribute to the proper weight distribution in RWD vehicles. Since the engine is typically positioned at the front of the vehicle, the rear drive shaft helps balance the weight distribution by transferring power to the rear wheels. This balanced weight distribution enhances overall stability, handling, and cornering capabilities. It allows for better control of the vehicle and helps optimize the performance during various driving conditions.
4. Handling and Stability:
Rear drive shafts significantly influence the handling and stability of RWD vehicles. By delivering torque to the rear wheels, the drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s rear-wheel traction. This configuration provides better weight transfer during acceleration, which improves traction and reduces the chances of wheel spin. The rear drive shaft also aids in maintaining stability during cornering by helping to distribute the vehicle’s weight more evenly. RWD vehicles are known for their balanced and predictable handling characteristics, and the rear drive shaft plays a vital role in achieving these attributes.
5. Performance in Various Conditions:
Rear drive shafts impact the performance of RWD vehicles in different driving conditions. In dry or high-grip situations, the rear-wheel traction provided by the drive shaft enables quick acceleration and efficient power delivery. RWD vehicles often exhibit superior handling characteristics in these conditions due to the balanced weight distribution and the rear drive shaft’s ability to transfer torque effectively. However, in low-traction conditions such as rain, snow, or off-road situations, RWD vehicles may require additional driver skill and careful throttle control to maintain traction and stability.
6. Customization and Performance Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can be customized or upgraded to enhance the performance of RWD vehicles. For example, performance-oriented drive shafts made from lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can reduce rotational mass, improving overall vehicle agility and responsiveness. Upgraded drive shafts with strengthened components can handle increased torque and power outputs in high-performance applications. Customization and upgrades to the rear drive shaft allow vehicle owners to tailor the performance characteristics to their specific needs and preferences.
7. Maintenance and Service:
Regular maintenance and service of rear drive shafts are essential for maintaining optimal performance. Periodic inspections, lubrication, and addressing any issues such as worn U-joints or CV joints can prevent driveline vibrations, reduce power losses, and ensure smooth torque transmission. Proper maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the rear drive shaft, allowing it to continue supporting the overall performance of the RWD vehicle.
In summary, rear drive shafts are integral to the overall performance of RWD vehicles. They facilitate power transmission, torque delivery, and weight distribution, contributing to acceleration, traction, handling, and stability. The rear drive shaft’s ability to efficiently transfer torque to the rear wheels is key to the performance characteristics of RWD vehicles. Through customization, upgrades, and regular maintenance, rear drive shafts can be optimized to further enhance the performance of RWD vehicles in various driving conditions and applications.
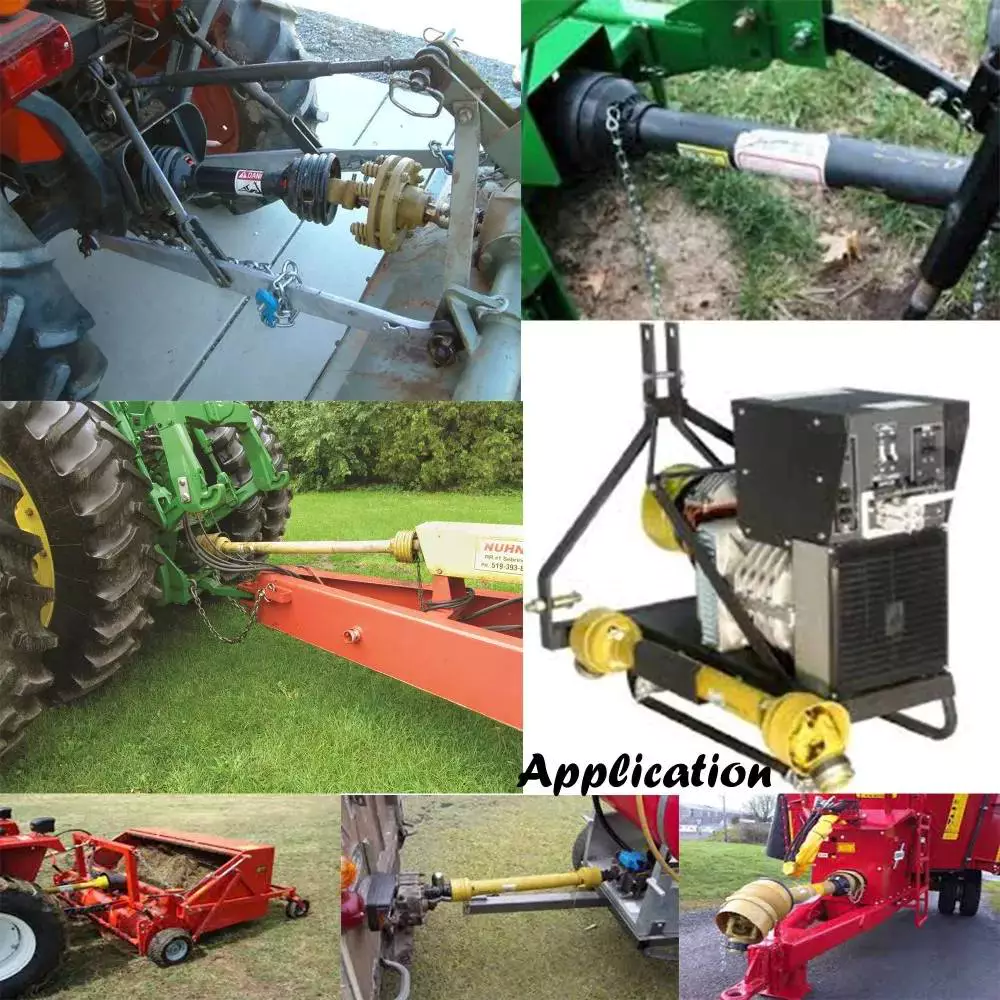

Can You Explain the Role of a Rear Drive Shaft in Power Distribution to the Wheels?
A rear drive shaft plays a crucial role in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It is responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and controlling the distribution of power. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a rear drive shaft in power distribution to the wheels:
1. Torque Transmission:
One of the primary functions of a rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for powering the wheels and enabling vehicle movement.
As the engine or transmission produces torque, it is transferred through the drivetrain system, which includes the rear drive shaft. The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link, transmitting the torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential.
2. Rear Differential:
The rear differential is a component that sits between the rear drive shaft and the rear wheels. Its primary function is to distribute torque received from the rear drive shaft to the individual rear wheels.
When torque is transmitted through the rear drive shaft, it reaches the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque into two outputs, one for each rear wheel. This distribution of torque allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, ensuring smooth and controlled vehicle maneuverability.
3. Power Distribution:
A rear drive shaft plays a critical role in power distribution between the rear wheels. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, it enables the differential to distribute power to each wheel based on traction conditions and driving demands.
When a vehicle is in motion, the rear wheels may encounter different road conditions or have varying levels of traction. The rear differential, controlled by the rear drive shaft, ensures that power is distributed to the wheels with better traction, enhancing overall vehicle stability and control.
4. Drive System Configuration:
The presence of a rear drive shaft is often associated with specific drive system configurations in vehicles. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles typically employ a rear drive shaft to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels.
In RWD vehicles, the rear drive shaft is an integral part of the drivetrain system. It allows the engine’s power to be directed to the rear wheels, providing the necessary propulsion for the vehicle to move forward or backward.
5. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, the rear drive shaft also plays a role in power distribution to all four wheels. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
The transfer case receives torque from the rear drive shaft and splits it between the front and rear axles, allowing power to be distributed to all four wheels. This enables enhanced traction, off-road capability, and improved vehicle performance in various driving conditions.
In summary, the rear drive shaft is a critical component in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It transmits torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential, which distributes power to the rear wheels. The rear drive shaft enables power distribution between the wheels, ensures stability and control, and is integral to specific drive system configurations, such as rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. Its role is essential in enabling vehicle propulsion and optimizing power distribution for various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-09
China supplier Auto Part Axle Shaft Rear Front CV Axle Shaft Drive Shafts for Jeep CZPT Dodge Chevrolet American Car
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | ||
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | ||
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | ||
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ameican Car |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
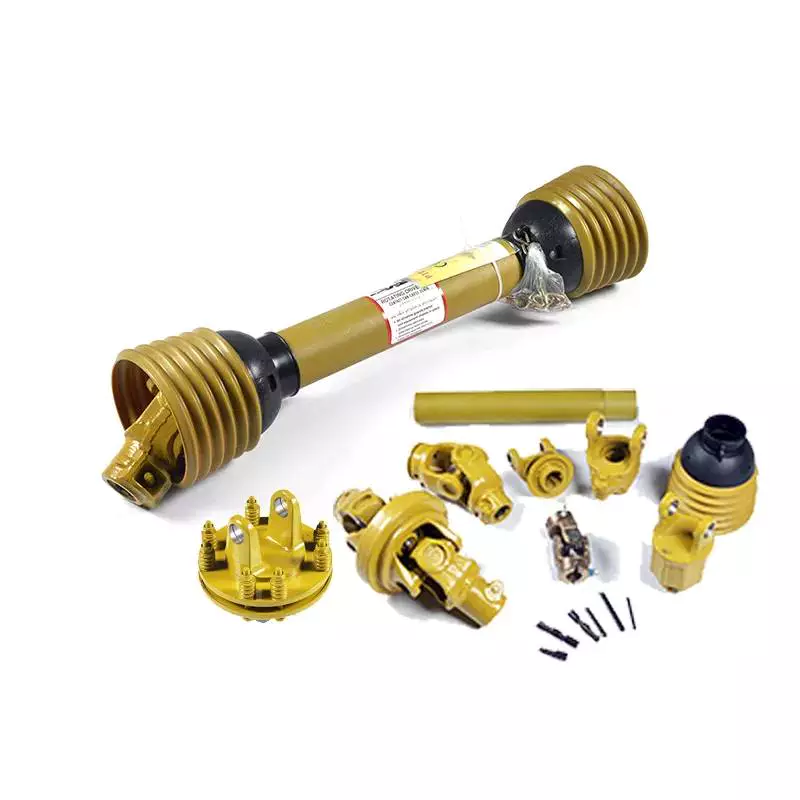

What Maintenance Practices Are Essential for Prolonging the Lifespan of Rear Drive Shafts?
Maintaining rear drive shafts is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. By following proper maintenance practices, you can prolong the lifespan of rear drive shafts and prevent premature failures. Here are the key maintenance practices that are essential for maximizing the lifespan of rear drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is crucial for identifying any early signs of wear, damage, or misalignment in the rear drive shaft. Inspect the drive shaft for any visible cracks, dents, or corrosion. Pay attention to the condition of the universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, as they are prone to wear. Look for excessive play or looseness in the joints, and check for leaks or torn boots that could allow dirt and moisture to enter. Regular inspections help catch potential issues before they escalate and cause significant damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of the drive shaft’s u-joints or CV joints is critical for reducing friction, preventing wear, and maintaining smooth operation. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the recommended lubricant and interval for greasing the joints. Use high-quality lubricants that are compatible with the specific joint type and follow the correct greasing procedure. Insufficient lubrication can lead to accelerated wear and premature failure of the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the joints’ condition during the greasing process to ensure they are adequately lubricated and in good working order.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Keep the rear drive shaft properly balanced and aligned to prevent vibrations and excessive stress on the drivetrain components. If you notice vibrations, especially at higher speeds, have the drive shaft’s balance checked by a professional. Imbalances can occur due to the accumulation of dirt or debris, damaged balancing weights, or wear on the drive shaft. Similarly, if you experience driveline vibrations or notice uneven tire wear, it may indicate misalignment. Have the drive shaft alignment checked and adjusted as necessary. Proper balancing and alignment contribute to a smoother and more reliable operation, minimizing wear on the drive shaft.
4. Protection from Moisture and Contaminants:
Rear drive shafts are susceptible to moisture, dirt, and other contaminants that can lead to corrosion, accelerated wear, and joint failure. Avoid driving through deep water or muddy conditions that can submerge or coat the drive shaft with corrosive substances. If the drive shaft becomes wet or dirty, clean it promptly using a gentle stream of water and mild soap, and ensure it is thoroughly dried. Applying a protective coating or lubricant to exposed surfaces can help prevent corrosion. Additionally, inspect and replace damaged or torn joint boots to prevent dirt and moisture from entering and causing damage.
5. Proper Torque and Fastener Inspection:
Ensure that all fasteners, such as bolts and nuts, are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to vibrations, misalignment, and damage to the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the fasteners for any signs of loosening or damage and tighten them as necessary. During maintenance or repairs that involve removing the drive shaft, ensure that the fasteners are properly reinstalled and torqued to the recommended specifications. Following the correct torque values and fastener inspection practices helps maintain the integrity and safety of the rear drive shaft.
6. Professional Maintenance and Repairs:
While some maintenance tasks can be performed by vehicle owners, certain maintenance and repair procedures are best left to professionals with specialized knowledge and equipment. If you encounter significant issues, such as severe wear, damaged joints, or suspected balance or alignment problems, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or drivetrain specialist. They can conduct thorough inspections, provide accurate diagnoses, and perform the necessary repairs or replacements to ensure the rear drive shaft’s longevity and proper functioning.
7. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to your vehicle’s rear drive shaft. Manufacturers provide valuable information regarding maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, inspection procedures, and other important considerations. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that you follow the best practices and requirements specified for your particular drive shaft model, contributing to its prolonged lifespan.
In summary, regular inspection, proper lubrication, balancing and alignment, protection from moisture and contaminants, proper torque and fastener inspection, professional maintenance and repairs when necessary, and following manufacturer guidelines are essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of rear drive shafts. By implementing these practices, you can enhance the reliability, durability, and performanceof the rear drive shaft, ultimately extending its lifespan and reducing the risk of unexpected failures or costly repairs.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-07
China Hot selling Quality Shaft Selection: Drive, Gear, Cardan, Transmission, Rotor, Propeller, Motor, Spline, Axle, Steel, Flexible, and Pto Shafts Available
Product Description
Quality Shaft Selection: Drive, Gear, Cardan, Transmission, Rotor, Propeller, Motor, Spline, Axle, Steel, Flexible, and PTO Shafts Available
| Materials | Carbon steel: 10#, 18#, 1018, 22#, 1571, 40Cr, 45#, 1045, 50#, 55#, 60#, 65Mn, 70#, 72B, 80#, 82B Alloy Structure Steel: B7, 20CrMo, 42Crmo, SCM415, SCM440, 4140 High-carbon chromium bearing steel: GCr15, 52100, SUJ2 Free-cutting steel: 12L14, 12L15 Stainless steel: 1Cr13, 2Cr13, 3Cr13, 4Cr13, 1Cr17, SUS410, SUS420, SUS430, SUS416, SUS440C, 17-4, 17-4PH, 130M, 200, 201, 202, 205, 303, 303Cu, 304, 316, 316L Aluminum grade: 6061, 6063 Brass: Hpb58-2.5 (C38000), Hpb59-1 (C37710), Hpb61-1 (C37100), Hpb62-0.8 (C35000), Hpb63-0.1 (C34900), Hpb63-3 (C34500), H60, H62, H63, H65 |
| Diameter | Ø0.3-Ø25 |
| Diameter tolerance | 0.002mm |
| Roundness | 0.0005mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.05 |
| Straightness | 0.005mm |
| Hardness: | HRC/HV |
| Length | 2mm-1000mm |
| Heat treatment | 1. Oil Quenching 2. High frequency quenching 3. Carburization 4. Vacuum Heat treatment 5. Mesh belt CZPT heat treatment |
| Surface treatment | 1. Plating nickel 2. Plating zinc 3. Plating passivation 4. Plating phosphating 5. Black coating 6. Anodized treatment |
| Package | Plastic bags inside and standard cartons outside. Shipment by pallets or according to customer’s packing specifications. |
| Warranty Policy | We confirm our qualities satisfy to 99.9%, and have 6-month quality warranty |
| After Sales Service | We will follow up the requst strictly for customers and will help customers solve problems after sale. |
Swiss High-Precision CNC Machining Process
Other Category From Cold Forging Process
Company Profile
HangZhou CZPT is an integrated manufacturing and trading enterprise with over 30 years of experience. We specialize in providing customized solutions for non-standard fasteners, CNC machined parts, stamping parts, and other metal products. With a sprawling facility covering an area of 5,500 square meters, we have 3 workshops including cold heading, stamping, and cnc machining.
At Hanyee Metal, we take pride in our commitment to delivering high-quality products and tailor-made solutions to meet our customers’ specific needs. Our team of skilled professionals ensures precision and CZPT in every aspect of the manufacturing process. Whether it’s fasteners for unique applications, intricately machined parts, or precision-stamped components, we have the capabilities to exceed your expectations.
Hanyee’s products exporting to more than 30 countries, especially in North American and European markets. Being the supplier for famous brands like : ITW, Ruen, Infenion, WMG,Fnox, ects. many years.
inspection
Exhibiting
Customer reception
Packaging and transportation
Customer feedback
FAQ
Q: Please send your price list for our reference.
A: We do not have standard price list because we produce according to customer design.
We can provide the quotation for your inquiries in a shortest possible time.
Q:Please quote the price for me
A: Our standard response time is 2 working hours, once you confirm the demand and drawing we shall provide the quote within 12 working hours.
Q:Can I get some sample?
A: Sure. We believe sample order is a good way to start our cooperation.
If it is a standard product, it would be for free but freight on your account.
If customized, we shall prepare the sample after receipt of development cost.
Q: Have FASTENERS 100% assembled well in stock?
A: Some of standard size is in stock. Most is OEM item out of stock.
Q: Could I use my own LOGO or design on goods?
A: Yes, Customized logo and design on mass production are available.
Q: What is the delivery time?
A: Our lead time for samples is 1 week; 15-30 days for mass production. It is usually according to the quantity and items.
Q:What payment do you accept?
A: We accept T/T, West Union,L/C,Trade Assurance in Alibaba.
Q: Can I trust you?
A: Absolutely! We are “Made In China” & “Alibaba” verified supplier.
Q: May I visit your factory?
A: You are welcome to visit us anytime. We can also pick you up from nearest airport and Train station.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Transmission Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Flexible Shaft |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT01-IT5 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Stepped Shaft |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
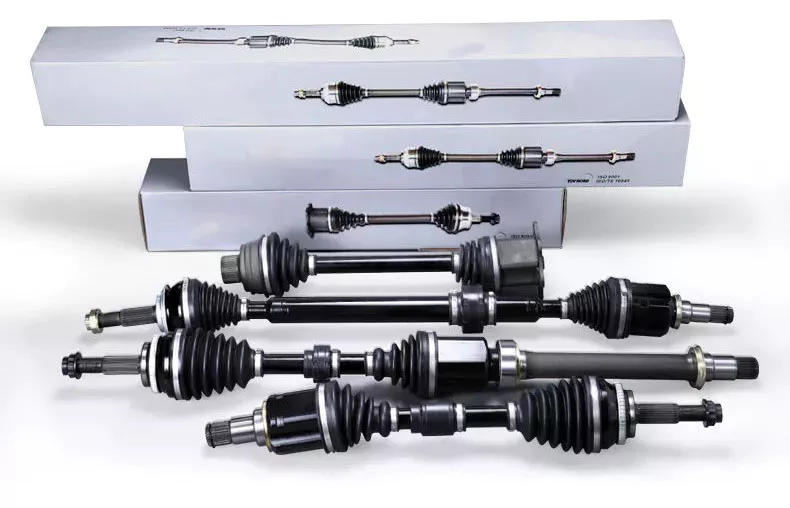

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-06
China Standard CZPT Auto Spare Car Parts Factory Wholesale All Front Rear Left Right Drive Shafts for Audi A1 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q5 Q7 Q8 Tt R8 S RS C6 C7 B3 B4 RS2
Product Description
Product Description
Complete products, one-stop purchasing, saving your cost and time.
Inventory advantage, stable supply, short delivery time.
High-quality original, made in China, there are more many parts are in stock.
Install and test the products in Chinese market first, to ensure the quality.
Specifications
| Mounting Type | Hydro Bearing |
| Dimension | OEM Standard |
| Material | Steel Elastomer |
| Weight | 2Kg |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
About BBmart Auto Parts
Since establishment in 2005, BBmart Auto Parts has achieved in becoming 1 of the most trust-worthy automobile replacement parts distributors in the industry with Good Credibility, offering our customers a “One stop Shop” experience and constantly ensuring that we place our customers’ needs at the forefront, offering them Good service.We are not only renowned for our professionalism and comprehensive range of replacement products, but also offer our customers a competitive position with our Fair Price. Our manufacturers have passed and acquired various International certifications on safety and quality such as CAPA, Thatcham, E-Mark, SAE, ISO 9000/1, ISO 9002, TS 16949 MQVP and the SABS, thereby assuring Good Quality – Parts you can trust.
Good Credibility
Good Service
Good Quality
Fair Price
These define the way we work and allowed us to be professional to earn and build trust with our customers and suppliers. This trust fortifies our business relationships as partners and has created a CHINAMFG situation for the clients.
Our products have been sold over the world. Our diversified replacement product lines cover the Automotive Lamps, Automotive Body Parts, Suspension Parts, Electric Parts, Engine Parts and Accessories.
BBmart endeavours to understand and precisely respond to our customer’s diverse needs. Our vision is to be “The prime distributor for automotive replacement parts in China.” We are committed to work diligently to deliver best service, high quality and cost-effective products to our customers.
FAQ
Q1.How many years have your company dealt in autoparts?
A: We have been founded for 16 years now.
Q2. What is your company major products?
A: Our main products are Spark Plug, Brake Pad, Oil Fiter. Fuel Filter, Air Fiter, Engine Belt, Shock Absorber, Control Arm, Ball
Joint, Tie Rod End, Stabilizer Link Rod, Wheel Hub Bearing, C.v.joint, Car Light, ect.
Q3. Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are Manufacturing and Trading and Supply Chain company.
Q4. What is the MOQ?
A: Normally we can supply any quantity if we have stock.
Q5. What is the delivery date?
A: It takes 5-7 days if there is stock, but takes about 30 days if there is no stock.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Years Warranty |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Accommodate Variations in Length and Connection Methods?
Rear drive shafts are designed to accommodate variations in length and connection methods to ensure proper fitment and functionality in different vehicle configurations. These variations arise due to differences in vehicle size, drivetrain layout, suspension geometry, and other factors. Rear drive shafts employ several mechanisms and design considerations to adapt to these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods:
1. Telescoping Design:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate a telescoping design that allows for length adjustments. Telescoping drive shafts consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other, enabling changes in length. This design is beneficial when vehicles have adjustable suspension systems or when there is a need to accommodate variations in the distance between the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. By adjusting the telescoping sections, rear drive shafts can be extended or retracted to match the required length, ensuring proper alignment and engagement of the drivetrain components.
2. Slip Yokes:
Slip yokes are commonly used in rear drive shafts to allow for axial movement and compensate for changes in length. A slip yoke is a splined component that connects the drive shaft to the transmission output shaft. It is designed to slide in and out of the drive shaft, allowing for length adjustments. As the suspension moves or the rear axle travels up and down, the slip yoke accommodates the changes in distance between the transmission and the rear axle, maintaining constant engagement and power transfer. Slip yokes are often used in conjunction with telescoping drive shafts to provide a wider range of length adjustability.
3. Universal Joints (U-Joints) and Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Rear drive shafts utilize different types of joints, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate variations in connection methods. U-joints are commonly used in rear drive shafts and allow for angular movement between two shafts. They can handle misalignment and changes in operating angles, making them suitable for applications where the rear axle and transmission output shaft are not perfectly aligned. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in applications that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer, such as in vehicles with independent rear suspension. CV joints accommodate variations in length and allow for a wider range of articulation angles while maintaining a constant velocity of the drive shaft.
4. Flange Connections and Bolt Patterns:
Rear drive shafts feature flange connections at each end to facilitate attachment to the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. The flanges are designed with specific bolt patterns that correspond to the mating surfaces on the transmission and axle. These bolt patterns ensure proper alignment and secure attachment of the drive shaft to the drivetrain components. The bolt patterns may vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer, drivetrain configuration, and specific model. By accommodating different flange connections and bolt patterns, rear drive shafts can be compatible with a wide range of vehicles and drivetrain layouts.
5. Customization and Engineering:
In some cases, rear drive shafts may require customization and engineering to accommodate specific variations in length and connection methods. Vehicle manufacturers, aftermarket suppliers, and drivetrain specialists have the expertise to design and manufacture custom drive shafts to meet unique requirements. This may involve fabricating drive shafts with specific lengths, spline counts, or joint configurations that are not readily available in standard off-the-shelf options. Customization allows for precise adaptation of rear drive shafts to fit vehicles with non-standard drivetrain configurations or to address specific challenges posed by unique suspension setups or vehicle modifications.
In summary, rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods through telescoping designs, slip yokes, universal joints (U-joints), constant velocity (CV) joints, flange connections, bolt patterns, and customization. These features and design considerations ensure proper fitment, alignment, and engagement of the rear drive shaft in different vehicle configurations. By incorporating these mechanisms, rear drive shafts provide the flexibility and adaptability necessary to accommodate variations in length and connection methods, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse drivetrain layouts.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Enhance the Traction and Stability of Off-Road Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enhancing the traction and stability of off-road vehicles. Off-road driving presents unique challenges, such as uneven terrain, steep inclines, loose surfaces, and obstacles, where maintaining traction and stability is vital. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts contribute to enhancing the traction and stability of off-road vehicles:
1. Power Distribution:
Rear drive shafts are responsible for transmitting torque from the transfer case or transmission to the rear differential or rear axle in off-road vehicles. This power distribution allows the rear wheels to receive torque and apply it to the ground, enhancing traction. By providing power to the rear wheels, the rear drive shafts ensure that the wheels dig into the terrain, maximizing grip and reducing the chances of wheel spin. This power distribution contributes to maintaining forward momentum and preventing loss of traction in challenging off-road conditions.
2. Rear-Wheel Traction:
Rear drive shafts enable rear-wheel traction, which is crucial for off-road vehicles. When traversing uneven or slippery terrain, the weight of the vehicle shifts to the rear wheels during acceleration. The rear drive shafts deliver torque to the rear wheels, allowing them to maintain traction and effectively propel the vehicle forward. By ensuring rear-wheel traction, the drive shafts help the off-road vehicle overcome obstacles, climb steep inclines, and navigate challenging off-road terrains where maintaining grip is essential.
3. Weight Transfer:
Rear drive shafts contribute to proper weight transfer during off-road driving. As the vehicle encounters obstacles or uneven terrain, weight transfer occurs, with the weight shifting from one wheel to another. The rear drive shafts aid in balancing the weight distribution, preventing excessive weight transfer to a single wheel. This balanced weight transfer improves stability and minimizes the chances of wheel lift or loss of control. It allows the off-road vehicle to maintain stability and traction, enhancing overall safety and performance.
4. Axle Articulation:
Off-road vehicles often require significant axle articulation to maintain contact between the wheels and the ground, especially when navigating rough terrain. Rear drive shafts accommodate the movement and flexing of the suspension system, allowing the rear wheels to articulate independently. This flexibility enables the wheels to maintain contact with the ground, even when encountering large obstacles or uneven surfaces. By adapting to the changing terrain, the rear drive shafts contribute to improved traction and stability, ensuring the off-road vehicle can maintain forward momentum.
5. Torque Control:
Rear drive shafts play a role in torque control, which is essential for maintaining traction and stability off-road. Some off-road vehicles feature differential locks or limited-slip differentials in the rear axle. The rear drive shafts transmit torque to these differentials, allowing for better power distribution between the rear wheels. This torque control helps prevent wheelspin and ensures that power is delivered to the wheels with traction, enhancing overall traction and stability in challenging off-road conditions.
6. Ground Clearance:
Rear drive shafts contribute to improving ground clearance in off-road vehicles. The design and positioning of the drive shafts allow for higher ground clearance compared to vehicles with front-wheel drive configurations. Increased ground clearance reduces the risk of the drive shafts scraping or getting damaged by obstacles, rocks, or uneven surfaces. By providing adequate ground clearance, the rear drive shafts enable the off-road vehicle to navigate rough terrain without hindrance, maintaining traction and stability.
7. Durability and Reliability:
Rear drive shafts in off-road vehicles are designed to withstand the demanding conditions encountered during off-road driving. They are built to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding impacts, vibrations, and extreme articulation. The reliability and strength of the rear drive shafts contribute to maintaining traction and stability by ensuring that the power transmission remains intact, even in challenging off-road situations.
In summary, rear drive shafts enhance the traction and stability of off-road vehicles through power distribution, rear-wheel traction, weight transfer management, axle articulation accommodation, torque control, increased ground clearance, and durability. These factors collectively contribute to maintaining traction, allowing the off-road vehicle to overcome obstacles, navigate challenging terrains, and ensure stability and control in off-road driving conditions.

Can You Explain the Role of a Rear Drive Shaft in Power Distribution to the Wheels?
A rear drive shaft plays a crucial role in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It is responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and controlling the distribution of power. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a rear drive shaft in power distribution to the wheels:
1. Torque Transmission:
One of the primary functions of a rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for powering the wheels and enabling vehicle movement.
As the engine or transmission produces torque, it is transferred through the drivetrain system, which includes the rear drive shaft. The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link, transmitting the torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential.
2. Rear Differential:
The rear differential is a component that sits between the rear drive shaft and the rear wheels. Its primary function is to distribute torque received from the rear drive shaft to the individual rear wheels.
When torque is transmitted through the rear drive shaft, it reaches the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque into two outputs, one for each rear wheel. This distribution of torque allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, ensuring smooth and controlled vehicle maneuverability.
3. Power Distribution:
A rear drive shaft plays a critical role in power distribution between the rear wheels. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, it enables the differential to distribute power to each wheel based on traction conditions and driving demands.
When a vehicle is in motion, the rear wheels may encounter different road conditions or have varying levels of traction. The rear differential, controlled by the rear drive shaft, ensures that power is distributed to the wheels with better traction, enhancing overall vehicle stability and control.
4. Drive System Configuration:
The presence of a rear drive shaft is often associated with specific drive system configurations in vehicles. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles typically employ a rear drive shaft to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels.
In RWD vehicles, the rear drive shaft is an integral part of the drivetrain system. It allows the engine’s power to be directed to the rear wheels, providing the necessary propulsion for the vehicle to move forward or backward.
5. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, the rear drive shaft also plays a role in power distribution to all four wheels. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
The transfer case receives torque from the rear drive shaft and splits it between the front and rear axles, allowing power to be distributed to all four wheels. This enables enhanced traction, off-road capability, and improved vehicle performance in various driving conditions.
In summary, the rear drive shaft is a critical component in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It transmits torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential, which distributes power to the rear wheels. The rear drive shaft enables power distribution between the wheels, ensures stability and control, and is integral to specific drive system configurations, such as rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. Its role is essential in enabling vehicle propulsion and optimizing power distribution for various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-05-02