Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
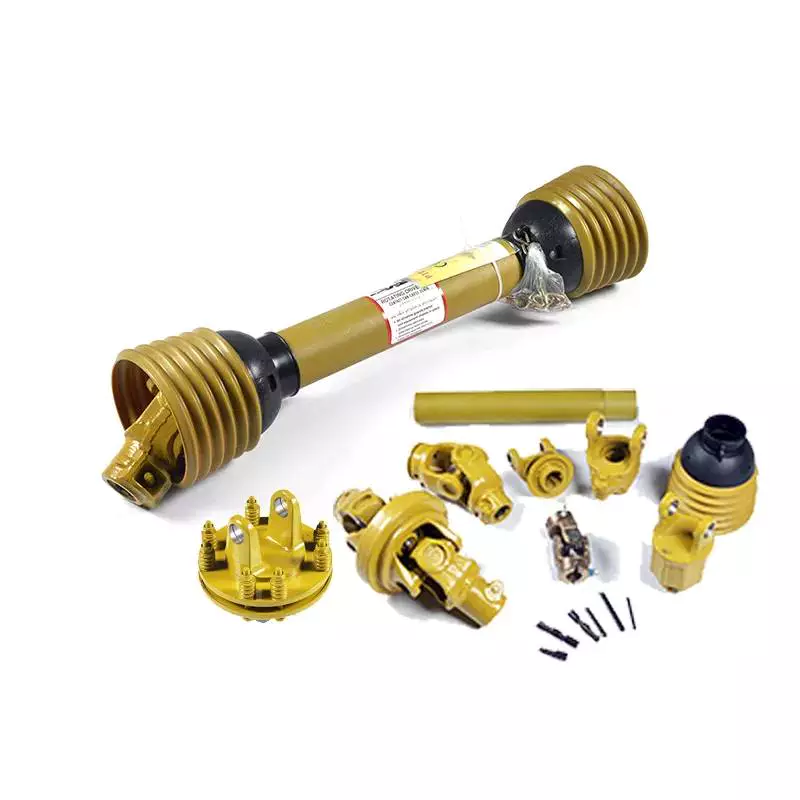
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
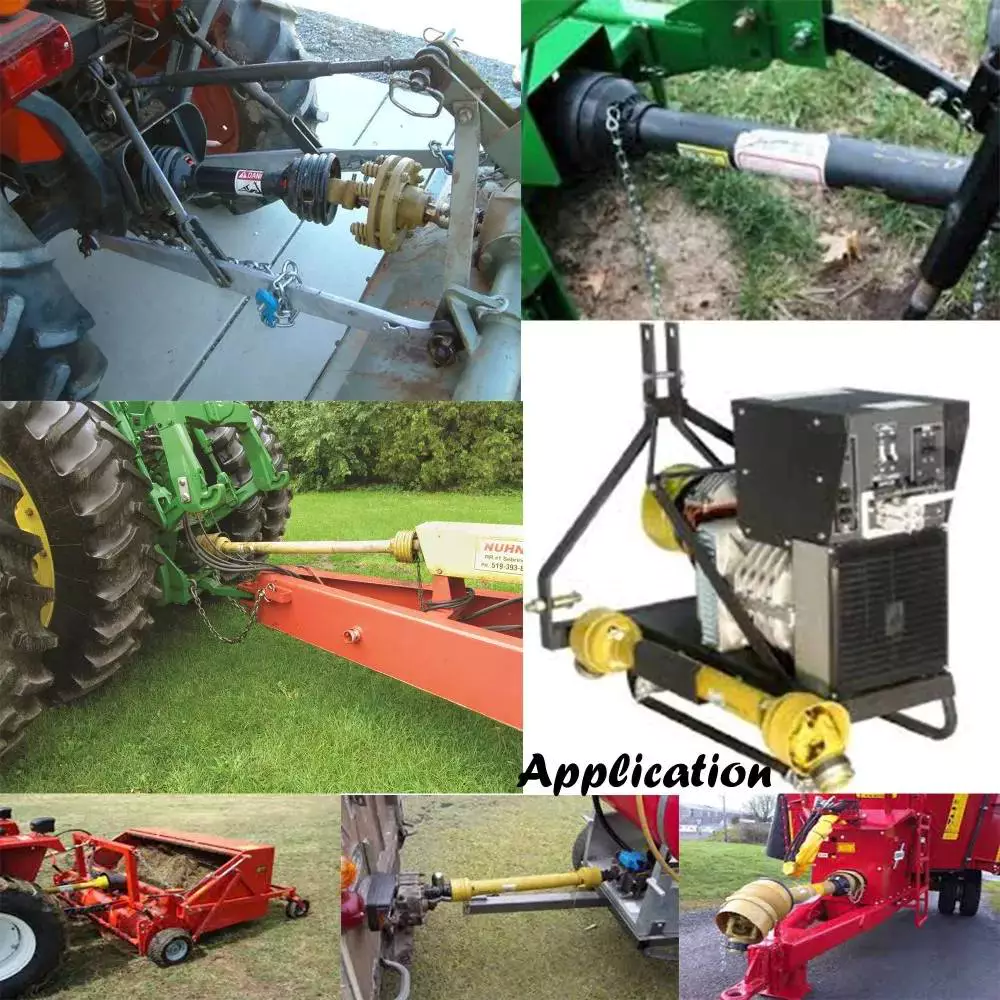
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.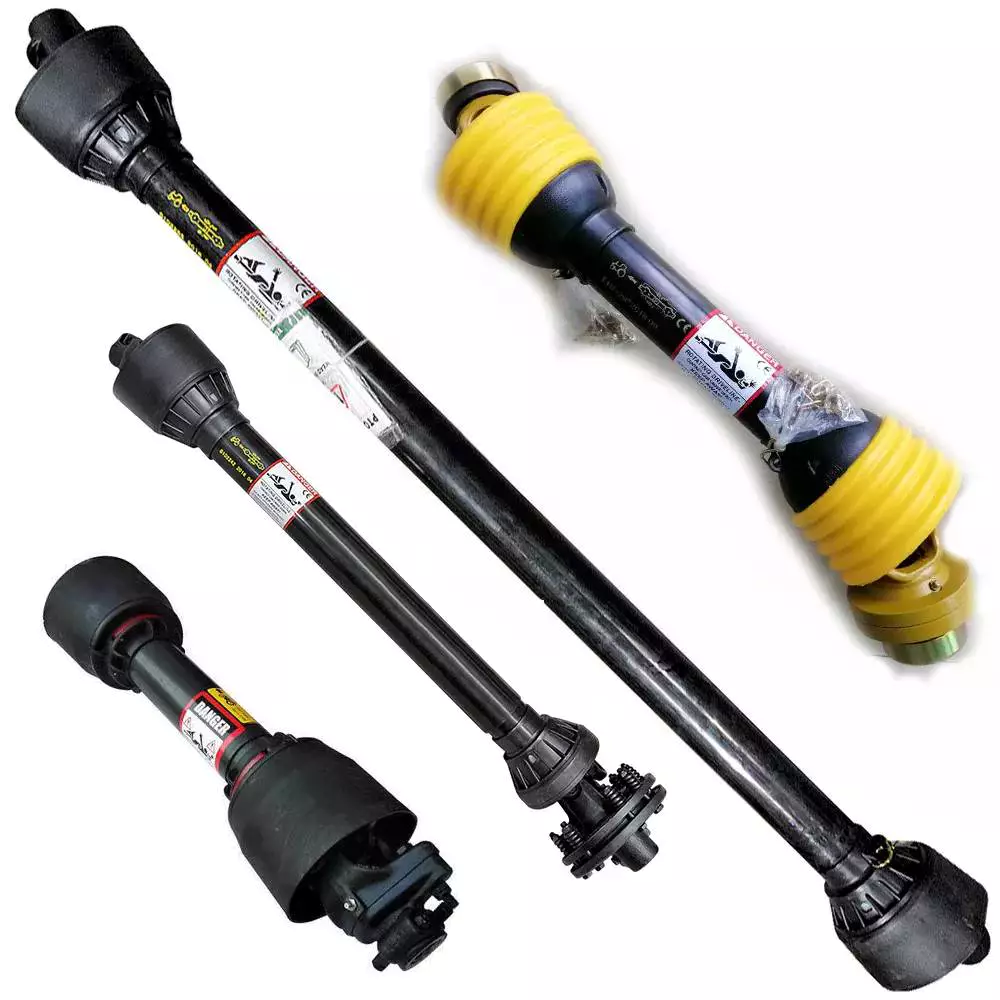
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

Can You Explain the Role of a Rear Drive Shaft in Power Distribution to the Wheels?
A rear drive shaft plays a crucial role in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It is responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and controlling the distribution of power. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a rear drive shaft in power distribution to the wheels:
1. Torque Transmission:
One of the primary functions of a rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for powering the wheels and enabling vehicle movement.
As the engine or transmission produces torque, it is transferred through the drivetrain system, which includes the rear drive shaft. The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link, transmitting the torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential.
2. Rear Differential:
The rear differential is a component that sits between the rear drive shaft and the rear wheels. Its primary function is to distribute torque received from the rear drive shaft to the individual rear wheels.
When torque is transmitted through the rear drive shaft, it reaches the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque into two outputs, one for each rear wheel. This distribution of torque allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, ensuring smooth and controlled vehicle maneuverability.
3. Power Distribution:
A rear drive shaft plays a critical role in power distribution between the rear wheels. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, it enables the differential to distribute power to each wheel based on traction conditions and driving demands.
When a vehicle is in motion, the rear wheels may encounter different road conditions or have varying levels of traction. The rear differential, controlled by the rear drive shaft, ensures that power is distributed to the wheels with better traction, enhancing overall vehicle stability and control.
4. Drive System Configuration:
The presence of a rear drive shaft is often associated with specific drive system configurations in vehicles. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles typically employ a rear drive shaft to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels.
In RWD vehicles, the rear drive shaft is an integral part of the drivetrain system. It allows the engine’s power to be directed to the rear wheels, providing the necessary propulsion for the vehicle to move forward or backward.
5. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, the rear drive shaft also plays a role in power distribution to all four wheels. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
The transfer case receives torque from the rear drive shaft and splits it between the front and rear axles, allowing power to be distributed to all four wheels. This enables enhanced traction, off-road capability, and improved vehicle performance in various driving conditions.
In summary, the rear drive shaft is a critical component in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It transmits torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential, which distributes power to the rear wheels. The rear drive shaft enables power distribution between the wheels, ensures stability and control, and is integral to specific drive system configurations, such as rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. Its role is essential in enabling vehicle propulsion and optimizing power distribution for various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-04-26
China supplier Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Tractor Pto Driveshaft Driveline Factory Hollow Spline Cardan Adapter Universal Joint Yoke Flexible Front Prop Rear CV Axle Propeller Automobile Drive Shaft
Product Description
Agricultural truck universal joint steering
PTO Shaft
| Function of PTO Shaft | Drive Shaft Parts & Power Transmission |
| Usage of PTO Shaft | Kinds of Tractors & Farm Implements |
| Yoke Types for PTO Shaft | Double push pin, Bolt pins, Split pins, Pushpin, Quick release, Ball attachment, Collar….. |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| PTO Shaft Plastic Cover | YW; BW; YS; BS; Etc |
| Colors of PTO Shaft | Green; Orange; Yellow; Black Ect. |
| PTO Shaft Series | T1-T10; L1-L6;S6-S10;10HP-150HP with SA,RA,SB,SFF,WA,CV Etc |
| Tube Types for PTO Shaft | Lemon, Triangular, Star, Square, Hexangular, Spline, Special Ect |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Types for PTO Shaft | 1 1/8″ Z6;1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8″ Z21 ;1 3/4″ Z20; 1 3/4″ Z6; 8-38*32*6 8-42*36*7; 8-48*42*8; |
We also sell accessories for the pto shaft, including :
Yoke: CV socket yoke, CV weld yoke, flange yoke, end yoke, weld yoke, slip yoke
CV center housing, tube, spline, CV socket flange, u-joint, dust cap
Light vehicle drive line
Our products can be used for transmission shafts of the following brands
Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Isu zu, Suzuki, Dafa, Honda, Hyundai, Mazda, Fiat, Re nault, Kia, Dacia, Ford. Dodge, Land Rover, Peu geot, Volkswagen Audi, BMW Benz Volvo, Russian models
Gear shaft
Company Profile
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 38/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can drive shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there may be some differences in design and specifications based on the specific application requirements, the fundamental principles and functions of drive shafts remain applicable in both contexts. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts serve the primary purpose of transmitting rotational power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components, which can be wheels, machinery, or other mechanical systems. This fundamental function applies to both automotive and industrial settings. Whether it’s delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle or transferring torque to industrial machinery, the basic principle of power transmission remains the same for drive shafts in both contexts.
2. Design Considerations:
While there may be variations in design based on specific applications, the core design considerations for drive shafts are similar in both automotive and industrial settings. Factors such as torque requirements, operating speeds, length, and material selection are taken into account in both cases. Automotive drive shafts are typically designed to accommodate the dynamic nature of vehicle operation, including variations in speed, angles, and suspension movement. Industrial drive shafts, on the other hand, may be designed for specific machinery and equipment, taking into consideration factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and alignment requirements. However, the underlying principles of ensuring proper dimensions, strength, and balance are essential in both automotive and industrial drive shaft designs.
3. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is influenced by the specific requirements of the application, whether in automotive or industrial settings. In automotive applications, drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. In industrial settings, drive shafts may be made from a broader range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, or even specialized alloys, depending on factors such as load capacity, corrosion resistance, or temperature tolerance. The material selection is tailored to meet the specific needs of the application while ensuring efficient power transfer and durability.
4. Joint Configurations:
Both automotive and industrial drive shafts may incorporate various joint configurations to accommodate the specific requirements of the application. Universal joints (U-joints) are commonly used in both contexts to allow for angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the drive shaft and driven components. Constant velocity (CV) joints are also utilized, particularly in automotive drive shafts, to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and accommodate varying operating angles. These joint configurations are adapted and optimized based on the specific needs of automotive or industrial applications.
5. Maintenance and Service:
While maintenance practices may vary between automotive and industrial settings, the importance of regular inspection, lubrication, and balancing remains crucial in both cases. Both automotive and industrial drive shafts benefit from periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues, and prolong the lifespan of the drive shafts. Lubrication of joints, inspection for wear or damage, and balancing procedures are common maintenance tasks for drive shafts in both automotive and industrial applications.
6. Customization and Adaptation:
Drive shafts can be customized and adapted to meet the specific requirements of various automotive and industrial applications. Manufacturers often offer drive shafts with different lengths, diameters, and joint configurations to accommodate a wide range of vehicles or machinery. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of drive shafts to suit the specific torque, speed, and dimensional requirements of different applications, whether in automotive or industrial settings.
In summary, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the specific requirements of each application. While there may be variations in design, materials, joint configurations, and maintenance practices, the fundamental principles of power transmission, design considerations, and customization options remain applicable in both contexts. Drive shafts play a crucial role in both automotive and industrial applications, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in a wide range of mechanical systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2024-04-22
China supplier Machinery Parts Rotor Gear Shaft Customized Machining Knurling High Precision with Factory Price for Auto Drive Factory Price
Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ12(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.008mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.4 |
| Straightness | 0.01mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 32mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-04-19
China supplier Drive Shaft Rear Axle Right for BMW 33211226860 Bm-8-909A 205004 300693 23564
Product Description
| Type: Rear Axle |
| Length: 578mm |
| ABS Ring Teeth: 48 |
| Sealing Ring Diameter: 63.6mm |
| Connector Diameter at the Wheel Side: 94mm |
| Joint Diameter on the Transmission Side: 100mm |
| External Engagement Gear Side: 27mm |
Drawing of Driving Shaft
OEM Number
|
BMW : 33211225942 BMW : 33211225943 BMW : 33211226860 BMW : 33211226901 |
Reference Number
|
655-1096
T68300A BW3073 205004 300693 121463 221463 BM105ALR VKJC1148 23564
|
Car Applicaition
BMW 3 (E30) 320 i
BMW 3 (E30) 320 is
BMW 3 (E30) 324 d
BMW 3 (E30) 324 td
BMW 3 (E30) 325 i
BMW 3 (E30) 325 i X
BMW 3 (E30) M3 2.3
BMW 3 Convertible (E30) 320 i
BMW 3 Convertible (E30) 320 i
BMW 3 Convertible (E30) 325 i
BMW 3 Convertible (E30) M3 2.3
Company Profile
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co. Ltd is a professional manufacturer of auto bearings for more than 20 years. We provide a one-stop service for our customers. Our main products include wheel bearings & hub assembly, belt tensioners, clutch release bearings, and other parts.
Relying on the professional and rich manufacturing experience and many substantial factories which stable cooperated for many years, Mighty suppliers customers high-quality products at very competitive prices.
Customer satisfaction is our First Priority, We adhere to the concept of ” Quality First, Customer First”. We will continue to provide high-quality products and the best services to our customers and build up CHINAMFG long-time friendship partners.
Our Advantage
More than 20 years of manufacturing and exporting experience
OEM manufacturing available
Full range, large stock
Quickly feedback
One year warranty
One-stop service
On-time delivery
Packing & Shipping
FAQ
1. What‘s the minimum order quantity?
We don’t have the minimum order quantity. We can also provide free samples, but you need to pay the freight.
2. Do you provide ODM&OEM order service?
Yes, we provide ODM&OEM services to customers around the world, and we can customize different brands and different sizes of packaging boxes according to customers’ requirements.
3. After-sales service and warranty time
We guarantee that our products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship within 12 months from the date of delivery. The warranty is void due to improper use, incorrect installation, and physical damage.
4. How to place an order?
Send us an email of the models, brand, quantity, consignee information, model of transportation, and payment
Confirm payment and arrange the production.
5. What are your packing conditions?
We use standardized export packaging and environmental protection packaging materials. If you have a legally registered patent, we will package the goods in your brand box after receiving your authorization
6. What are your payment terms?
T/T is 30% of the payment in advance and 70% balance before delivery. Before you pay the balance, we will show you photos or videos of the products and packaging.
7. How long is your delivery time?
The delivery time of the sample order is 3-5 days, and that of a batch order is 5-45 days. The exact delivery time depends on the item and the quantity you ordered.
8. Do you test all products before delivery?
Yes, according to ISO standards, we have professional Q/C personnel, precision testing instruments, and an internal inspection system. We control the quality of every process from material receiving to packaging to ensure that you receive high-quality products
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | One Year |
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Natural Color |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Structure: | Single |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What Maintenance Practices Are Essential for Prolonging the Lifespan of Rear Drive Shafts?
Maintaining rear drive shafts is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. By following proper maintenance practices, you can prolong the lifespan of rear drive shafts and prevent premature failures. Here are the key maintenance practices that are essential for maximizing the lifespan of rear drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is crucial for identifying any early signs of wear, damage, or misalignment in the rear drive shaft. Inspect the drive shaft for any visible cracks, dents, or corrosion. Pay attention to the condition of the universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, as they are prone to wear. Look for excessive play or looseness in the joints, and check for leaks or torn boots that could allow dirt and moisture to enter. Regular inspections help catch potential issues before they escalate and cause significant damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of the drive shaft’s u-joints or CV joints is critical for reducing friction, preventing wear, and maintaining smooth operation. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the recommended lubricant and interval for greasing the joints. Use high-quality lubricants that are compatible with the specific joint type and follow the correct greasing procedure. Insufficient lubrication can lead to accelerated wear and premature failure of the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the joints’ condition during the greasing process to ensure they are adequately lubricated and in good working order.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Keep the rear drive shaft properly balanced and aligned to prevent vibrations and excessive stress on the drivetrain components. If you notice vibrations, especially at higher speeds, have the drive shaft’s balance checked by a professional. Imbalances can occur due to the accumulation of dirt or debris, damaged balancing weights, or wear on the drive shaft. Similarly, if you experience driveline vibrations or notice uneven tire wear, it may indicate misalignment. Have the drive shaft alignment checked and adjusted as necessary. Proper balancing and alignment contribute to a smoother and more reliable operation, minimizing wear on the drive shaft.
4. Protection from Moisture and Contaminants:
Rear drive shafts are susceptible to moisture, dirt, and other contaminants that can lead to corrosion, accelerated wear, and joint failure. Avoid driving through deep water or muddy conditions that can submerge or coat the drive shaft with corrosive substances. If the drive shaft becomes wet or dirty, clean it promptly using a gentle stream of water and mild soap, and ensure it is thoroughly dried. Applying a protective coating or lubricant to exposed surfaces can help prevent corrosion. Additionally, inspect and replace damaged or torn joint boots to prevent dirt and moisture from entering and causing damage.
5. Proper Torque and Fastener Inspection:
Ensure that all fasteners, such as bolts and nuts, are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to vibrations, misalignment, and damage to the drive shaft. Regularly inspect the fasteners for any signs of loosening or damage and tighten them as necessary. During maintenance or repairs that involve removing the drive shaft, ensure that the fasteners are properly reinstalled and torqued to the recommended specifications. Following the correct torque values and fastener inspection practices helps maintain the integrity and safety of the rear drive shaft.
6. Professional Maintenance and Repairs:
While some maintenance tasks can be performed by vehicle owners, certain maintenance and repair procedures are best left to professionals with specialized knowledge and equipment. If you encounter significant issues, such as severe wear, damaged joints, or suspected balance or alignment problems, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or drivetrain specialist. They can conduct thorough inspections, provide accurate diagnoses, and perform the necessary repairs or replacements to ensure the rear drive shaft’s longevity and proper functioning.
7. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to your vehicle’s rear drive shaft. Manufacturers provide valuable information regarding maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, inspection procedures, and other important considerations. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that you follow the best practices and requirements specified for your particular drive shaft model, contributing to its prolonged lifespan.
In summary, regular inspection, proper lubrication, balancing and alignment, protection from moisture and contaminants, proper torque and fastener inspection, professional maintenance and repairs when necessary, and following manufacturer guidelines are essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of rear drive shafts. By implementing these practices, you can enhance the reliability, durability, and performanceof the rear drive shaft, ultimately extending its lifespan and reducing the risk of unexpected failures or costly repairs.

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Ensure Smooth Power Delivery and Minimize Vibration in Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration in vehicles. They are designed to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or axle, allowing the wheels to propel the vehicle forward. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration:
1. Balanced Design:
Rear drive shafts are carefully engineered to achieve a balanced design. This involves taking into consideration factors such as length, diameter, material properties, and weight distribution. By achieving balance, the drive shaft minimizes the occurrence of vibrations that can result from uneven weight distribution or misalignment. Balanced drive shafts reduce the chances of vibration-induced discomfort, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
The manufacturing process of rear drive shafts involves precision techniques to ensure the highest level of accuracy and quality. Computer numerical control (CNC) machining and advanced welding methods are employed to create drive shafts with precise dimensions and alignment. This precision manufacturing helps to reduce any imperfections or inconsistencies that could contribute to vibration. By producing drive shafts with tight tolerances, manufacturers strive to achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration.
3. High-Quality Materials:
The choice of materials for rear drive shafts greatly influences their ability to ensure smooth power delivery and minimize vibration. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. These materials are selected for their strength, durability, and vibration-damping properties. High-quality materials with excellent torsional rigidity and appropriate damping characteristics help absorb and dissipate vibrations, resulting in smoother power delivery and a reduction in unwanted vibrations.
4. Dampening Techniques:
Vibration dampening techniques are employed in rear drive shafts to further minimize vibrations. These techniques include the use of rubber or polyurethane bushings and isolators at the connection points between the drive shaft and other components, such as the transmission, transfer case, and differential. These bushings act as vibration absorbers, reducing the transfer of vibrations from the drive shaft to the rest of the vehicle’s drivetrain. By effectively isolating vibrations, rear drive shafts contribute to a smoother power delivery and a more comfortable driving experience.
5. Drive Shaft Angles:
The angles at which the rear drive shaft operates can impact power delivery and vibration. Rear drive shafts are designed with proper operating angles to minimize vibration. These angles, known as the driveshaft angles or u-joint angles, are carefully calculated to ensure optimal alignment and reduce vibration-causing forces. Improperly aligned drive shaft angles can result in driveline vibrations, so proper alignment is crucial for smooth power delivery and minimal vibration.
6. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, rear drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing. Dynamic balancing involves spinning the drive shaft and adding small counterweights to eliminate any imbalances. This process ensures that the drive shaft is evenly weighted and free from vibration-causing irregularities. Dynamic balancing helps achieve smooth power delivery and minimizes vibration by eliminating the effects of imbalance that can arise from manufacturing tolerances or material variations.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance and inspection of rear drive shafts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and minimize vibration. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of universal joints and ensuring the integrity of the drive shaft’s components are also important maintenance tasks. By keeping rear drive shafts in good condition, potential sources of vibration can be identified and addressed promptly, contributing to smooth power delivery and minimizing vibration.
In summary, rear drive shafts achieve smooth power delivery and minimize vibration through balanced design, precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, dampening techniques, proper drive shaft angles, dynamic balancing, and regular maintenance. These measures collectively contribute to a comfortable and efficient driving experience while reducing the risk of drivetrain-related vibration and potential damage to the vehicle.

Which Types of Vehicles Commonly Use Rear Drive Shafts in Their Drivetrain?
Rear drive shafts are a common feature in several types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) drivetrain configurations. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of vehicles that commonly use rear drive shafts in their drivetrain:
1. Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are most commonly found in RWD vehicles. In RWD configurations, the engine’s power is sent to the rear wheels through the transmission and rear differential. The rear drive shaft connects the output of the transmission or transfer case to the input of the rear differential, allowing power transmission to the rear wheels. This setup is commonly used in sports cars, luxury sedans, pickup trucks, and some SUVs.
2. Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles:
Many 4WD and AWD vehicles also utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles provide power to all four wheels, enhancing traction and off-road capability. In 4WD systems, the rear drive shaft transfers power from the transfer case to the rear differential and front differential, enabling torque distribution to both the front and rear wheels. This setup is commonly found in off-road vehicles, SUVs, trucks, and some performance cars.
3. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Rear drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. These vehicles often have rear-wheel drive or part-time 4WD systems to handle heavy loads, towing, and demanding work conditions. The rear drive shafts in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to endure higher torque and load capacities, ensuring reliable power transmission to the rear wheels.
4. SUVs and Crossovers:
Many SUVs and crossovers employ rear drive shafts, especially those with RWD or 4WD/AWD configurations. These vehicles often prioritize versatility, off-road capability, and towing capacity. Rear drive shafts enable power transmission to the rear wheels, enhancing traction and stability both on and off the road. SUVs and crossovers with 4WD or AWD systems can distribute torque to all four wheels, improving performance in various weather and terrain conditions.
5. Performance and Sports Cars:
Performance and sports cars frequently utilize rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. RWD configurations are common in these vehicles, as they offer better weight distribution, improved handling, and enhanced control during high-performance driving. Rear drive shafts enable efficient power delivery to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s acceleration, stability, and overall performance.
6. Muscle Cars and Classic Vehicles:
Muscle cars and classic vehicles often feature rear drive shafts due to their traditional RWD setups. These vehicles evoke a nostalgic driving experience and typically prioritize power and rear-wheel traction. Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in transmitting power and torque from the engine to the rear wheels, allowing muscle cars and classic vehicles to deliver the desired performance and driving dynamics.
In summary, rear drive shafts are commonly found in various types of vehicles, including RWD vehicles, 4WD/AWD vehicles, trucks, SUVs, crossovers, performance cars, muscle cars, and classic vehicles. These vehicles rely on rear drive shafts to transmit power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, ensuring efficient power delivery, traction, and drivetrain performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-19
China Professional China Supplier ISO Standard Stainless Steel Rear Axle Shaft
Product Description
Q: How can I get samples?
A: Free samples and freight collect, except for special circumstances.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity for the items in the order?
A: 2000pcs for each part except for sample.
Q: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a manufacturer, specialized in manufacturing and exporting of qualified precision micro shafts.
Q: What are your usual terms of payment?
A: We generally ask for payment by T/T in advance and L/C at sight.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.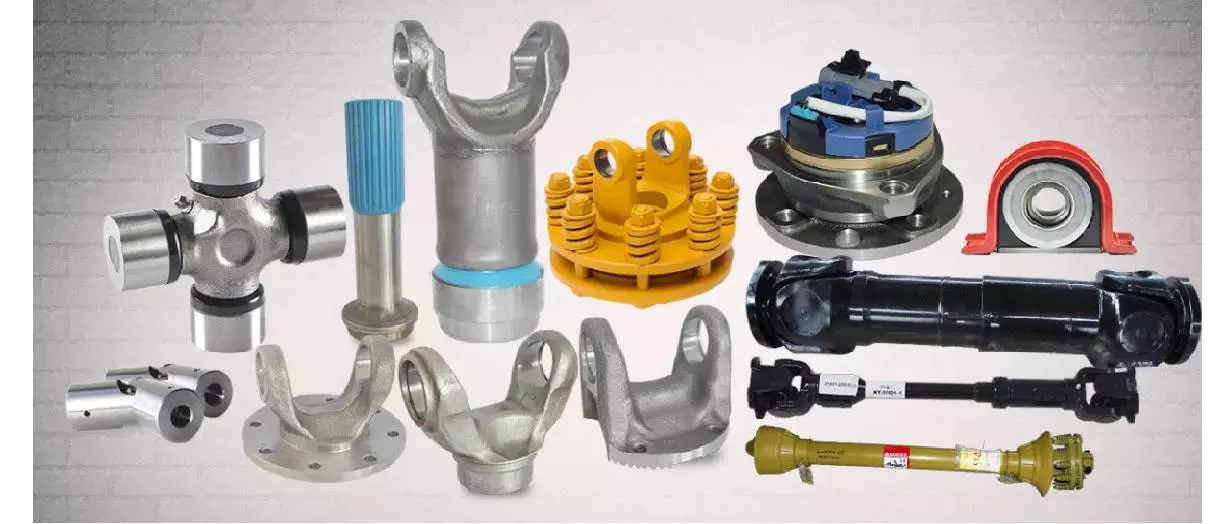
What Safety Precautions Should Be Followed When Working with Rear Drive Shafts?
Working with rear drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage to the vehicle or surrounding components. Here are detailed safety precautions that should be followed when working with rear drive shafts:
1. Wear Protective Gear:
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with rear drive shafts. This includes safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from debris, gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges or moving parts, and sturdy footwear to provide foot protection in case of accidents or dropped tools.
2. Ensure Vehicle Stability:
Prioritize vehicle stability when working with rear drive shafts. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. If necessary, use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling. Additionally, if you are raising the vehicle using a jack or lift, ensure that it is securely supported with jack stands or appropriate lift points to prevent accidental movement or collapse.
3. Disconnect the Battery:
Before beginning any work on the rear drive shaft, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This precaution helps prevent accidental engagement of the starter motor or other electrical components, reducing the risk of injury or damage during the maintenance or replacement process.
4. Release Tension on the Drivetrain:
Release tension on the drivetrain components before removing the rear drive shaft. If applicable, release tension on the parking brake, shift the transmission into neutral, and engage the wheel chocks. This step helps prevent unexpected movement of the vehicle or drivetrain components while working on the drive shaft.
5. Secure the Drive Shaft:
Prior to removing the rear drive shaft, ensure it is securely supported and immobilized. Use a drive shaft support fixture or a transmission jack to hold the drive shaft in place. This prevents the drive shaft from falling or causing injury when it is disconnected from the transmission or differential.
6. Mark Alignment Points:
Before disconnecting the rear drive shaft, mark alignment points on the drive shaft and the surrounding components. This will help ensure proper reinstallation and alignment during assembly. Marking the orientation of the drive shaft also aids in identifying any imbalance or misalignment issues that may arise during reinstallation.
7. Use Proper Tools and Techniques:
Always use the appropriate tools and techniques when working with rear drive shafts. Use socket wrenches, torque wrenches, and other specialized tools designed for drive shaft removal and installation. Avoid using improper tools or excessive force, as this can lead to damage or personal injury. Follow manufacturer guidelines and service manuals for specific procedures and torque specifications.
8. Handle with Care:
Handle the rear drive shaft with care to avoid unnecessary damage or injury. Avoid dropping or striking the drive shaft against hard surfaces, as this can cause dents, bends, or other structural damage. Additionally, be cautious of sharp edges or splines on the drive shaft that can cause cuts or abrasions. Always handle the drive shaft by gripping secure areas and wearing appropriate gloves for added protection.
9. Inspect for Damage and Wear:
Before reinstalling or replacing the rear drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, dents, corrosion, or loose components. Also, inspect the U-joints or CV joints for excessive play, rust, or damaged seals. If any issues are detected, it is advisable to replace the damaged parts or the entire drive shaft to ensure safe and reliable operation.
10. Follow Proper Reinstallation Procedures:
When reinstalling the rear drive shaft, follow proper procedures to ensure correct alignment and engagement with the transmission output shaft and differential input flange. Use the alignment marks made during disassembly as a guide. Tighten all fasteners to the recommended torque specifications, and ensure that all retaining clips or bolts are properly secured.
11. Test for Proper Functioning:
After completing the rear drive shaft work, conduct a thorough test to ensure proper functioning. Check for any abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks during vehicle operation. If any issues are observed, reinspect the drive shaft installation and address the problem promptly.
12. Consult Professional Assistance if Needed:
If you are uncertain about any aspect of working with rear drive shafts or encounter difficulties during the process, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician or automotive service center. Theycan provide the necessary expertise and ensure the work is carried out safely and correctly.
By following these safety precautions when working with rear drive shafts, you can help protect yourself, prevent damage to the vehicle, and maintain a safe working environment. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution throughout the entire process.

Can You Explain the Role of a Rear Drive Shaft in Power Distribution to the Wheels?
A rear drive shaft plays a crucial role in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It is responsible for transmitting torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and controlling the distribution of power. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of a rear drive shaft in power distribution to the wheels:
1. Torque Transmission:
One of the primary functions of a rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for powering the wheels and enabling vehicle movement.
As the engine or transmission produces torque, it is transferred through the drivetrain system, which includes the rear drive shaft. The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link, transmitting the torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential.
2. Rear Differential:
The rear differential is a component that sits between the rear drive shaft and the rear wheels. Its primary function is to distribute torque received from the rear drive shaft to the individual rear wheels.
When torque is transmitted through the rear drive shaft, it reaches the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque into two outputs, one for each rear wheel. This distribution of torque allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, ensuring smooth and controlled vehicle maneuverability.
3. Power Distribution:
A rear drive shaft plays a critical role in power distribution between the rear wheels. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, it enables the differential to distribute power to each wheel based on traction conditions and driving demands.
When a vehicle is in motion, the rear wheels may encounter different road conditions or have varying levels of traction. The rear differential, controlled by the rear drive shaft, ensures that power is distributed to the wheels with better traction, enhancing overall vehicle stability and control.
4. Drive System Configuration:
The presence of a rear drive shaft is often associated with specific drive system configurations in vehicles. Rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles typically employ a rear drive shaft to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels.
In RWD vehicles, the rear drive shaft is an integral part of the drivetrain system. It allows the engine’s power to be directed to the rear wheels, providing the necessary propulsion for the vehicle to move forward or backward.
5. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, the rear drive shaft also plays a role in power distribution to all four wheels. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
The transfer case receives torque from the rear drive shaft and splits it between the front and rear axles, allowing power to be distributed to all four wheels. This enables enhanced traction, off-road capability, and improved vehicle performance in various driving conditions.
In summary, the rear drive shaft is a critical component in power distribution to the wheels of a vehicle. It transmits torque from the engine or transmission to the rear differential, which distributes power to the rear wheels. The rear drive shaft enables power distribution between the wheels, ensures stability and control, and is integral to specific drive system configurations, such as rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. Its role is essential in enabling vehicle propulsion and optimizing power distribution for various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-04-17
China supplier 65-9453 Rear Drive Shaft Propeller Driveshaft Prop Shaft Fit 1997-1998 CZPT F-150 F150 4WD M. T
Product Description
PROPELLER SHAFT manufacturer & supplier – CHINAMFG is your best choice
|
Product Name |
65-9453 New Propeller Prop Drive Shaft Rear for CHINAMFG F150 |
|
Part Number |
65-9453 |
|
Vehicle Fitment |
For CHINAMFG F150 1997-1998 |
|
Length |
49.65″ |
|
MOQ |
1pc if we have them in stock or 15pcs |
|
Delivery time |
1-7 days for stock items, 25 days for production items |
|
Note |
Have stock in China and US! |
For FORD Propeller Shaft, we have over 1-2016
65-9166
for CHINAMFG F-150
65-9112
for CHINAMFG F-250 Super Duty
65-2012
for CHINAMFG F150
65-9667
for CHINAMFG F-350
65-2-2016
OE NO.
FITMENT
OE NO.
FITMENT
52123110AC
for CHINAMFG Escape
5L3Z‐4R602‐W
for CHINAMFG F-150
BL8Z4R602A
for CHINAMFG Escape
5L34‐4K145‐WD
for CHINAMFG F-150
2L8Z4R602BA
for CHINAMFG Escape
5L3Z‐4R602‐WB
for CHINAMFG F-150
3L8Z4R602BA
for CHINAMFG Escape
5L3Z‐4R602‐WA
for CHINAMFG F-150
5L8Z4R602BA
for CHINAMFG Escape
6L34‐4K145‐WB
for CHINAMFG F-150
7L8Z4R602B
for CHINAMFG Escape
7L3Z‐4R602‐J
for CHINAMFG F-150
DV614K145AC
for CHINAMFG Escape
BL3V4602BD
for CHINAMFG F-150
5L834K145BA
for CHINAMFG Escape
BL3Z4R602H
for CHINAMFG F-150
8L8Z4R602C
for CHINAMFG Escape
DL3Z4R602B
for CHINAMFG F-150
CV6Z4R602B
for CHINAMFG Escape
DL3Z4R602Q
for CHINAMFG F-150
4641968AE
for CHINAMFG Escape
7L3Z4R602K
for CHINAMFG F-150
4641968AH
for CHINAMFG Escape
5L3Z4R602BB
for CHINAMFG F-150
26032944
for CHINAMFG Expedition
5L3Z4R602ZA
for CHINAMFG F-150
2657127
for CHINAMFG Expedition
AL344K145KA
for CHINAMFG F-150
AL3Z4A376D
for CHINAMFG Expedition
AL344K145KB
for CHINAMFG F-150
F77A4376BB
for CHINAMFG Explorer
AL3Z4R602KB
for CHINAMFG F-150
XL2Z4A376AA
for CHINAMFG Explorer
5C3Z4A376G
for CHINAMFG F250
ZZR5711AC
for CHINAMFG F-150
8G1Z4R602A
for CHINAMFG Taurus
4L34‐4K145‐RE
for CHINAMFG F-150
2657195
for CHINAMFG Transit
4L34‐4K145‐RA
for CHINAMFG F-150
12479AB
for CHINAMFG Transit
8L3Z‐4R602‐D
for CHINAMFG F-150
5215710AE
for CHINAMFG Transit
5L34‐4K145‐RA
for CHINAMFG F-150
26571466
for CHINAMFG Transit
7L3Z 4R602‐J
for CHINAMFG F-150
CN4C154K145AD
for CHINAMFG Transit
4L34‐4K145‐WA
for CHINAMFG F-150
7C194K357HB
for CHINAMFG Transit
4L34‐4K145‐WC
for CHINAMFG F-150
7C19‐4K145‐DB
for CHINAMFG Transit
5L34‐4K145‐WB
for CHINAMFG F-150
CN4C154K357AD
for CHINAMFG Transit
5L34‐4K145‐WC
for CHINAMFG F-150
7C19‐4K145‐BB
for CHINAMFG Transit
7C19‐4K145‐BB
for CHINAMFG Transit
E9TZ4A376B
for FROD CHINAMFG
E9TZ4A376B
for FROD CHINAMFG
F6TZ4A376RA
for FROD CHINAMFG
F6TZ4A376RA
for FROD CHINAMFG
CN4C154K357AD
for CHINAMFG Transit
DORMAN NO.
938-301
936-807
936-896
946-448
938-091
936-808
938-801
936-810
936-846
936-973
936-805
936-809
936-285
938-076
936-942
936-811
936-891
946-831
936-800
936-812
936-892
936-801
946-830
936-288
976-698
938-066
936-802
938-305
938-031
946-821
936-803
936-325
938-082
938-802
936-806
936-327
936-847
938-304
938-063
936-813
936‐810
938-199
If you need more information about FORD Propeller Shaft, please message or email to us ASAP.
—- OUR ADVANTAGE —-
+700 models for AMERICA & EUROPE marketMOQ: 3PCS / for 1 item, MIN order amount: USD5000
Quality assurance: One Year WarrantyStable delivery time: 45 days
Free Sample DevelopedApply O/A 30-90 days for regular customer
Becides CHINAMFG Propeller Shaft,we have Over 700 items applicable for following vehicles:
—- F A Q —-
Q1: If we don’t find what we need on your website, what should we do?
You can send us the OE number or of the product you need, we will check if we have them.
We also develop new models according to customer’s need;
you can contact us for more detail.
Q2: Can I get a price discount if I order large quantities?Yes, it depends on your purchasing quantity, more quantity more discount.
Q3: What about the delivery time?If we have stock, we can send you the goods within 3 working days,
if we don’t have stock, generally it needs 10 to 40 days.
Q4: What’s our MOQ?Sample order for quality testing 1 piece , normal order 50 pieces for 1 order with mixed models .
Q5: What’s your payment terms and condition ?We can accept T/T , LC, Trade Assurance, Western Union, Paypal, Moneygram ect.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ford |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Accommodate Variations in Length and Connection Methods?
Rear drive shafts are designed to accommodate variations in length and connection methods to ensure proper fitment and functionality in different vehicle configurations. These variations arise due to differences in vehicle size, drivetrain layout, suspension geometry, and other factors. Rear drive shafts employ several mechanisms and design considerations to adapt to these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods:
1. Telescoping Design:
Rear drive shafts often incorporate a telescoping design that allows for length adjustments. Telescoping drive shafts consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other, enabling changes in length. This design is beneficial when vehicles have adjustable suspension systems or when there is a need to accommodate variations in the distance between the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. By adjusting the telescoping sections, rear drive shafts can be extended or retracted to match the required length, ensuring proper alignment and engagement of the drivetrain components.
2. Slip Yokes:
Slip yokes are commonly used in rear drive shafts to allow for axial movement and compensate for changes in length. A slip yoke is a splined component that connects the drive shaft to the transmission output shaft. It is designed to slide in and out of the drive shaft, allowing for length adjustments. As the suspension moves or the rear axle travels up and down, the slip yoke accommodates the changes in distance between the transmission and the rear axle, maintaining constant engagement and power transfer. Slip yokes are often used in conjunction with telescoping drive shafts to provide a wider range of length adjustability.
3. Universal Joints (U-Joints) and Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Rear drive shafts utilize different types of joints, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate variations in connection methods. U-joints are commonly used in rear drive shafts and allow for angular movement between two shafts. They can handle misalignment and changes in operating angles, making them suitable for applications where the rear axle and transmission output shaft are not perfectly aligned. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in applications that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer, such as in vehicles with independent rear suspension. CV joints accommodate variations in length and allow for a wider range of articulation angles while maintaining a constant velocity of the drive shaft.
4. Flange Connections and Bolt Patterns:
Rear drive shafts feature flange connections at each end to facilitate attachment to the transmission output shaft and the rear axle. The flanges are designed with specific bolt patterns that correspond to the mating surfaces on the transmission and axle. These bolt patterns ensure proper alignment and secure attachment of the drive shaft to the drivetrain components. The bolt patterns may vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer, drivetrain configuration, and specific model. By accommodating different flange connections and bolt patterns, rear drive shafts can be compatible with a wide range of vehicles and drivetrain layouts.
5. Customization and Engineering:
In some cases, rear drive shafts may require customization and engineering to accommodate specific variations in length and connection methods. Vehicle manufacturers, aftermarket suppliers, and drivetrain specialists have the expertise to design and manufacture custom drive shafts to meet unique requirements. This may involve fabricating drive shafts with specific lengths, spline counts, or joint configurations that are not readily available in standard off-the-shelf options. Customization allows for precise adaptation of rear drive shafts to fit vehicles with non-standard drivetrain configurations or to address specific challenges posed by unique suspension setups or vehicle modifications.
In summary, rear drive shafts accommodate variations in length and connection methods through telescoping designs, slip yokes, universal joints (U-joints), constant velocity (CV) joints, flange connections, bolt patterns, and customization. These features and design considerations ensure proper fitment, alignment, and engagement of the rear drive shaft in different vehicle configurations. By incorporating these mechanisms, rear drive shafts provide the flexibility and adaptability necessary to accommodate variations in length and connection methods, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse drivetrain layouts.

Can You Provide Real-World Examples of Vehicles Where Rear Drive Shafts Are Crucial?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in various types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) systems. Here are real-world examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial:
1. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Many sports cars and high-performance vehicles rely on rear-wheel drive configurations for their dynamic handling and performance characteristics. Rear drive shafts are crucial components in these vehicles as they transfer power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient acceleration and delivering torque for precise handling. Examples of sports cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Corvette, Porsche 911, Ford Mustang, and BMW M3.
2. Pickup Trucks and SUVs:
Pickup trucks and SUVs often employ rear-wheel drive or 4WD systems for their towing and off-road capabilities. Rear drive shafts are essential in these vehicles as they transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power distribution to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved traction and towing capacity. Examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial in the pickup truck and SUV segment include the Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado, Toyota Tacoma, and Jeep Wrangler.
3. Commercial Vehicles and Vans:
Many commercial vehicles and vans utilize rear-wheel drive for their cargo-carrying capacity and towing capabilities. Rear drive shafts are critical in these vehicles as they transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient propulsion and load-carrying capabilities. Examples of commercial vehicles and vans where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter, Ford Transit, Chevrolet Express, and Ram ProMaster.
4. Muscle Cars and Classic Cars:
Muscle cars and classic cars often feature rear-wheel drive configurations, and rear drive shafts are essential components in these vehicles. They transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels, providing the iconic rear-wheel drive performance and driving experience typically associated with these vehicles. Examples of muscle cars and classic cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Camaro, Ford Mustang, Dodge Challenger, and Chevrolet Chevelle.
5. Off-Road and 4×4 Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles and 4×4 vehicles rely on rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles often have a transfer case that distributes power to both the front and rear axles. Rear drive shafts play a critical role in transmitting torque from the transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power delivery to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved off-road traction and maneuverability. Examples of off-road and 4×4 vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Jeep Wrangler, Land Rover Defender, Toyota Land Cruiser, and Ford Bronco.
6. Luxury and Executive Vehicles:
Many luxury and executive vehicles feature rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive configurations, where rear drive shafts are essential components. Rear drive shafts transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or rear axle, providing power distribution to the rear wheels. These vehicles prioritize comfort, performance, and refined driving experiences. Examples of luxury and executive vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz S-Class, BMW 7 Series, Audi A8, and Lexus LS.
In summary, rear drive shafts are crucial in a wide range of vehicles, including sports cars, pickup trucks, SUVs, commercial vehicles, muscle cars, off-road vehicles, and luxury vehicles. They play a vital role in power transmission, torque delivery, and overall performance, enabling efficient acceleration, traction, and handling. Rear drive shafts are integral components in these vehicles, contributing to their specific characteristics and capabilities.
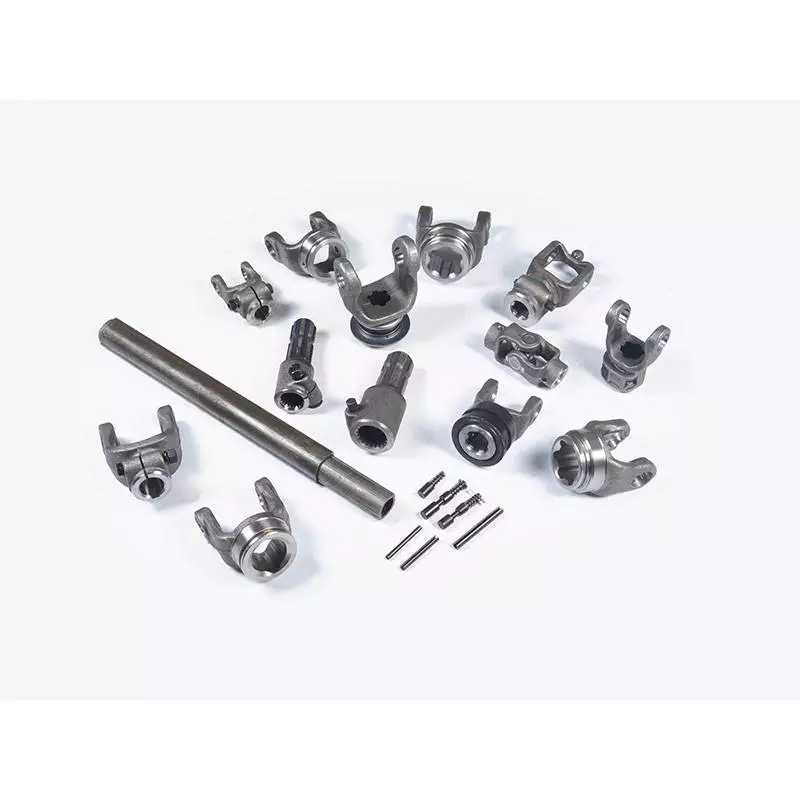

How Do Rear Drive Shafts Impact the Performance and Drivability of Vehicles?
Rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. As a crucial component of the drivetrain system, the rear drive shaft affects various aspects of a vehicle’s operation, including power delivery, handling, stability, and overall driving experience. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts impact the performance and drivability of vehicles:
1. Power Transmission:
Rear drive shafts play a vital role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, the rear drive shaft transfers this rotational force to the rear wheels, enabling propulsion and vehicle movement. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the rear drive shaft directly impact a vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and overall performance.
2. Traction and Stability:
The distribution of power between the rear wheels, controlled by the rear drive shaft and the rear differential, significantly affects a vehicle’s traction and stability. By transmitting torque to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to each rear wheel based on traction conditions.
Proper power distribution between the rear wheels ensures balanced traction, reducing the likelihood of wheel slippage or loss of control. This enhances the vehicle’s stability, especially during acceleration, cornering, or driving on uneven or slippery surfaces.
3. Handling and Cornering:
Rear drive shafts influence a vehicle’s handling and cornering capabilities. In rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, the rear drive shaft connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, resulting in a weight distribution biased towards the rear of the vehicle.
This weight distribution, combined with the rear drive shaft’s torque transmission to the rear wheels, contributes to better traction and stability during cornering. RWD vehicles typically exhibit a more balanced and predictable handling characteristic, allowing drivers to maintain better control and confidence while navigating turns.
4. Suspension Compatibility:
Rear drive shafts also need to be compatible with a vehicle’s suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move independently, absorbing bumps, road irregularities, and other disturbances for a smoother ride.
The rear drive shaft must accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension without affecting power transmission. It achieves this by incorporating flexible joints or splines that allow the drive shaft to expand or contract in length as the suspension moves. This compatibility ensures that the rear drive shaft does not hinder the suspension’s ability to absorb shocks and maintain tire contact with the road surface.
5. Drivetrain Efficiency:
The efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain system is influenced by the performance of the rear drive shaft. A well-designed and properly maintained rear drive shaft minimizes power losses and mechanical friction, allowing more power to reach the wheels and optimizing overall drivetrain efficiency.
Efficient power transmission through the rear drive shaft contributes to improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy waste, and enhanced performance. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and alignment, ensures that the rear drive shaft operates smoothly and maximizes its contribution to drivetrain efficiency.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, rear drive shafts play a crucial role in enabling four-wheel drive capability. The rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which distributes power to both the front and rear differentials.
By facilitating power distribution to all four wheels, rear drive shafts enhance the vehicle’s off-road performance, traction, and stability. Four-wheel drive capability allows the vehicle to tackle challenging terrain, slippery conditions, or uneven surfaces with improved control and maneuverability.
In summary, rear drive shafts have a significant impact on the performance and drivability of vehicles. They affect power transmission, traction, stability, handling, suspension compatibility, drivetrain efficiency, and enable four-wheel drive capability. By understanding and optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of rear drive shafts, manufacturers and drivers can enhance a vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and driving experience.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China supplier Agriculture Machine Accessory Drive Axle Transmission Shaft Power Drive Pto Shaft
Product Description
GOOD QUALITY AGRICULTURE MACHINE ACCESSORY PROPRLLER SHAFT TRACTOR PARTS TRANSMISSION SHAFT DRIVE AXLE POWER DRIVE SHAFT PTO SHAFT
Product Description
Our rotary PTO SHAFT is a powerful assistant in agricultural production, known for its high efficiency and durability. environment for CZPT cultivation.
Product Features:
High strength materials: The PTO SHAFT is made of high-strength materials, which have excellent durability and fatigue resistance and can be used for a long time.
Efficient farming: PTO SHAFT Labor-saving and easy to operate: using a rotary tiller for land plowing is easy and labor-saving, easy to operate, and suitable for various terrains.
Easy maintenance: The PTO SHAFT has a simple structure, low maintenance cost, and long service life.
Strong adaptability: Suitable for various types of soil, whether in paddy fields, dry fields, or mountainous areas, it can demonstrate excellent performance.
Usage :
Choose the appropriate model of PTO SHAFT according to the land conditions.
Install the PTO SHAFT on agricultural machinery.
Start agricultural machinery and start plowing the land.
Precautions :
Please read the product manual carefully before use.
Please use this product under safe conditions.
This product is only used for agricultural tillage and cannot be used for other purposes.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
GOOD QUALITY AGRICULTURE MACHINE ACCESSORY PROPRLLER SHAFT TRACTOR PARTS TRANSMISSION SHAFT DRIVE AXLE POWER DRIVE SHAFT PTO SHAFT
Packaging & Shipping
Our Advantages
1. High quality steel raw materials, suitable hardness, not easy to break or deform.
2. Automatic temperature control system used on both heating treatment and tempering, to guaratee the products heated evenly, the outside and interior have uniform structure, so as to get longer work life.
3.Precise and high strength moulds get precise shaping during thermo-forming.
4. Special gas used in tempering, to make up the chemical elements which lost during heating treatment, to double the work life than normal technology, proprietary heat treatment technology designed and developed by JIELIKE.
5. The whole product body and shape has been adjusted precisely by mechanics to pass the balance test both in static and moving states.
6. Products use electrostatic painting or brand water-based paint, environment-protective, to get excellent surface and long time rust-protective. And drying process is added for liquid painting to improve the quality of the paint adhesion to blade surface.
7. Automatic shot peening surface treatment, excellent appearance.
8. Provide OEM & ODM Service.
9. Provide customized products.
After Sales Service
We provide comprehensive after-sales service, including product consultation, user guidance, repair and maintenance, etc. If you encounter any problems during use, please feel free to contact us at any time.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Tillage |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
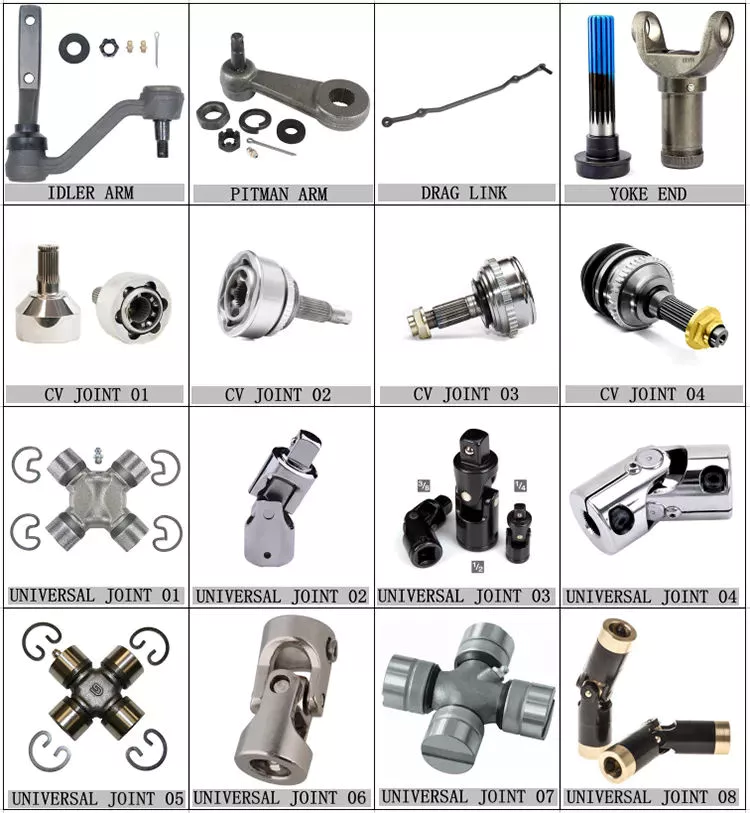

How do drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in speed and torque during operation by employing specific mechanisms and configurations. These mechanisms allow the drive shafts to accommodate the changing demands of power transmission while maintaining smooth and efficient operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque:
1. Flexible Couplings:
Drive shafts often incorporate flexible couplings, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to handle variations in speed and torque. These couplings provide flexibility and allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned. U-joints consist of two yokes connected by a cross-shaped bearing, allowing for angular movement between the drive shaft sections. This flexibility accommodates variations in speed and torque and compensates for misalignment. CV joints, which are commonly used in automotive drive shafts, maintain a constant velocity of rotation while accommodating changing operating angles. These flexible couplings enable smooth power transmission and reduce vibrations and wear caused by speed and torque variations.
2. Slip Joints:
In some drive shaft designs, slip joints are incorporated to handle variations in length and accommodate changes in distance between the driving and driven components. A slip joint consists of an inner and outer tubular section with splines or a telescoping mechanism. As the drive shaft experiences changes in length due to suspension movement or other factors, the slip joint allows the shaft to extend or compress without affecting the power transmission. By allowing axial movement, slip joints help prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft during variations in speed and torque, ensuring smooth operation.
3. Balancing:
Drive shafts undergo balancing procedures to optimize their performance and minimize vibrations caused by speed and torque variations. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, which not only affect the comfort of vehicle occupants but also increase wear and tear on the shaft and its associated components. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the drive shaft to achieve even weight distribution, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance. Dynamic balancing, which typically involves adding or removing small weights, ensures that the drive shaft operates smoothly even under varying speeds and torque loads.
4. Material Selection and Design:
The selection of materials and the design of drive shafts play a crucial role in handling variations in speed and torque. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their ability to withstand the forces and stresses associated with varying operating conditions. The diameter and wall thickness of the drive shaft are also carefully determined to ensure sufficient strength and stiffness. Additionally, the design incorporates considerations for factors such as critical speed, torsional rigidity, and resonance avoidance, which help maintain stability and performance during speed and torque variations.
5. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for drive shafts to handle variations in speed and torque. Lubricating the joints, such as U-joints or CV joints, reduces friction and heat generated during operation, ensuring smooth movement and minimizing wear. Adequate lubrication also helps prevent the binding of components, allowing the drive shaft to accommodate speed and torque variations more effectively. Regular lubrication maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the drive shaft.
6. System Monitoring:
Monitoring the performance of the drive shaft system is important to identify any issues related to variations in speed and torque. Unusual vibrations, noises, or changes in power transmission can indicate potential problems with the drive shaft. Regular inspections and maintenance checks allow for the early detection and resolution of issues, helping to prevent further damage and ensure the drive shaft continues to handle speed and torque variations effectively.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation through the use of flexible couplings, slip joints, balancing procedures, appropriate material selection and design, lubrication, and system monitoring. These mechanisms and practices allow the drive shaft to accommodate misalignment, changes in length, and variations in power demands, ensuring efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reduced wear and tear in various applications.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-04-11
China Professional Auto Parts Supplier CV Joint Axle Rear Front Drive Shaft 3815-A308 for CZPT Japanese Car Parts
Product Description
Products Description
CV Axle Driveshaft ,Half-Shaft Assembl
CV Axles are engineered to provide OE fit, form, and function – premium materials, coupled with precise machining and balancing, ensure smooth, vibration free performance in all driving conditions.
Since boot failure is the main cause of CV axle failure, our axles use only premium grade neoprene boots that ensure robust abrasion and extreme temperature resistance, preserving boot integrity.
Assembled with a specially formulated, high-temperature Moly grease that resists friction and wear, contributing to a lifetime of smooth, dependable performance.
All axles are thoroughly inspected for quality and workmanship, and because we believe in the exceptional quality of our components, every axle comes with warranty.
Solve problem:
- Half shaft oil leakage
- The car has an abnormal sound
- Body shake
Features:
- Genuine OEM – Complete axle, specifically designed.
- Perfect Fit – Factory axle with heavy duty outboard and inboard CV joints.
- Superior Quality – Precision ground components with high-strength shaft.
- Heavy Duty – Neoprene boots ensure excellent CHINAMFG resistance which eliminates cracking, a leading cause of boot failure, packed with heavy duty grease.
- Built to Last – High-temperature, high capacity bearings.
- Boot clamps are pneumatically crimped creating a perfect seal between the boot and housing
- High quality grease withstands high-temperature and high-torque demands which extends joint life
- High-tech grinding machines maintain the original design of the outer housing, race and cage to guarantee reliable performance.
Package
Company Profile
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Years |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | CE, DIN, ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Iveco, Toyota, Ford |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
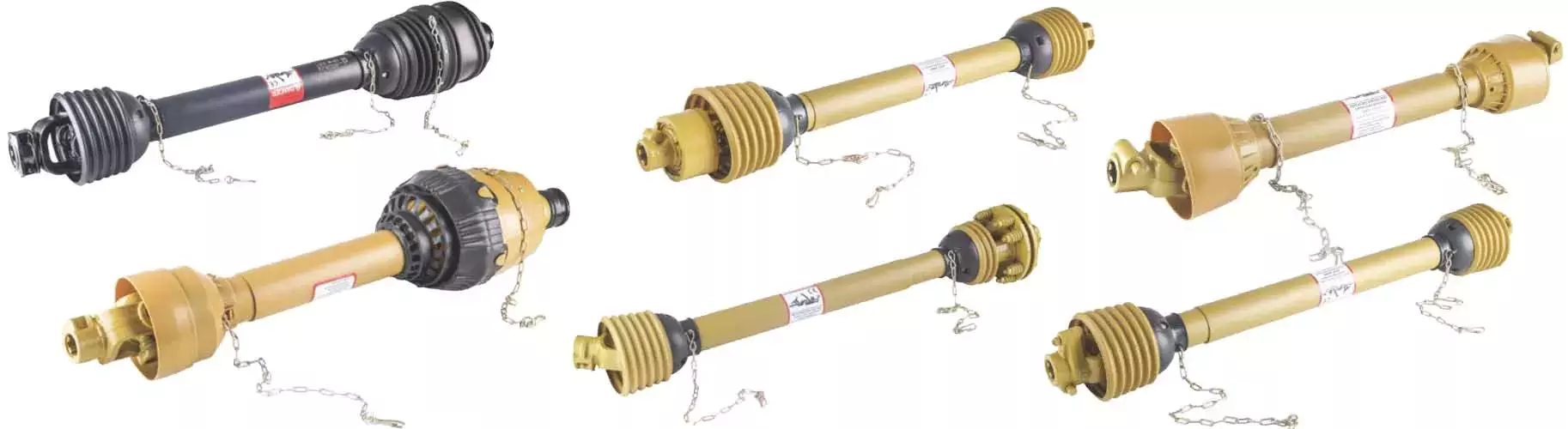

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Adapted for Use in Various Automotive and Industrial Settings?
Rear drive shafts are versatile components that can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings. While their primary function is to transfer power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels of a vehicle, their design and characteristics allow for customization and integration into different applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in different settings:
1. Automotive Applications:
Rear drive shafts are commonly used in a wide range of automotive applications, including passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and commercial vehicles. They are designed to accommodate different drivetrain configurations, such as rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD), and all-wheel drive (AWD). Rear drive shafts can be adapted to specific vehicle models by considering factors such as length, diameter, material selection, and joint type (u-joints or CV joints). Additionally, rear drive shafts can be modified for high-performance vehicles or off-road applications, where they may require enhanced strength, improved balance, or increased articulation capability.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Aside from automotive applications, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various industrial machinery. These applications often involve the transfer of power from the engine or motor to driven components, such as pumps, generators, compressors, or industrial equipment. Rear drive shafts used in industrial settings may have different design considerations compared to automotive applications. They may need to withstand higher torque loads, operate under harsh environmental conditions, or have specific dimensional requirements to fit within the machinery’s space constraints. Customization of rear drive shafts allows for seamless integration into diverse industrial applications.
3. Agricultural Equipment:
Rear drive shafts find utility in agricultural equipment as well. Tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery often require the transfer of power to various implements, such as plows, seeders, or harvesters. Rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in these applications by considering the specific power requirements, torque limitations, and environmental conditions encountered in agricultural settings. They may need to be designed for durability, resistance to debris and moisture, and ease of maintenance. Agricultural rear drive shafts can vary in size, configuration, and material depending on the specific machinery and its intended use.
4. Construction and Off-Road Equipment:
In construction and off-road equipment, rear drive shafts are utilized to transfer power to drivetrain components, such as axles or wheels. These applications often involve challenging operating conditions, including uneven terrain, heavy loads, and extreme temperatures. Rear drive shafts adapted for construction and off-road equipment may require additional reinforcement, specialized joints, or protective coatings to withstand the demanding environments. They may also feature enhanced articulation capability to accommodate the suspension movements and maintain power transfer during off-road or rough terrain operation.
5. Specialized Vehicles and Custom Applications:
Rear drive shafts can be customized and adapted for specialized vehicles and unique applications. Examples include racing cars, military vehicles, armored vehicles, and custom-built off-road vehicles. These applications often demand specific performance characteristics, such as lightweight materials for improved acceleration, high-strength alloys for durability, or advanced joint designs for enhanced articulation. Rear drive shafts can be engineered to meet the unique requirements of these specialized vehicles and custom applications, ensuring efficient power transfer while withstanding the challenges posed by their intended use.
6. Retrofitting and Upgrades:
Rear drive shafts can also be adapted through retrofitting or upgrades to improve the performance or functionality of existing vehicles or machinery. Upgrading to stronger materials, replacing worn-out joints, or modifying the drive shaft’s length or diameter can enhance power transfer efficiency, reduce vibration, or accommodate changes in the vehicle’s configuration. Retrofitting rear drive shafts allows for customization and optimization without the need for complete system redesign, making it a cost-effective way to adapt existing equipment to new requirements or to address specific performance issues.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be adapted for use in various automotive and industrial settings by considering factors such as drivetrain configuration, power requirements, environmental conditions, and specific application needs. Whether it’s for automotive, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, construction and off-road vehicles, specialized vehicles, or retrofitting purposes, rear drive shafts offer versatility and customization options to ensure efficient power transfer and reliable operation in diverse settings.

Can Rear Drive Shafts Be Customized for Specific Vehicle Configurations or Upgrades?
Rear drive shafts can indeed be customized to accommodate specific vehicle configurations or upgrades. Customization allows for optimal fitment, performance, and compatibility with modified drivetrain systems or unique vehicle configurations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts can be customized for specific vehicle configurations or upgrades:
1. Length and Diameter:
Custom rear drive shafts can be manufactured with specific lengths and diameters to suit different vehicle configurations. When modifying a vehicle’s drivetrain, such as installing a lift kit, altering suspension components, or changing the transmission or differential, the drive shaft’s length and diameter may need to be adjusted accordingly. Modifying these dimensions ensures proper alignment and engagement with the transmission output shaft and differential input flange, allowing for smooth and efficient power transfer.
2. Material Selection:
Custom rear drive shafts can be crafted from different materials depending on the specific vehicle requirements or upgrades. While steel is commonly used for its strength and durability, alternative materials like aluminum or carbon fiber can be chosen to reduce weight and improve overall vehicle performance. The choice of material will depend on factors such as the vehicle’s weight, power output, intended use, and budget considerations.
3. U-Joints and CV Joints:
U-joints and CV joints are critical components of rear drive shafts, allowing for flex and rotational movement while transmitting torque. When customizing a rear drive shaft, the type and size of U-joints or CV joints can be selected based on the specific vehicle configuration or upgrade. Heavy-duty or high-performance U-joints or CV joints may be chosen to handle increased power, torque, or off-road demands. Upgraded joints can provide improved strength, reliability, and articulation angles, ensuring optimal performance in modified drivetrain setups.
4. Balancing and Harmonics:
Custom rear drive shafts can be carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and harmonics. Balancing is crucial to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive wear on drivetrain components. When modifying or upgrading the vehicle’s drivetrain, changes in weight distribution, rotational speeds, or component stiffness can affect the dynamic balance of the drive shaft. Custom balancing techniques, such as precision weights or dynamic balancing machines, can be employed to achieve optimal balance and reduce vibrations, ensuring a comfortable and reliable driving experience.
5. Performance Enhancements:
Custom rear drive shafts can be tailored to enhance performance in specific vehicle configurations or upgrades. For example, in high-performance applications or off-road vehicles, reinforced drive shafts with thicker walls or additional gussets can be fabricated to handle increased power and torque loads. Upgraded materials, such as heat-treated alloys, can be utilized to improve strength and durability. By customizing the rear drive shaft, vehicle owners can ensure that the drivetrain system can effectively handle the demands of their specific applications.
6. Compatibility with Differential Ratios:
When changing the differential gear ratios in a vehicle, the rear drive shaft’s rotational speed and torque requirements may be affected. Custom rear drive shafts can be designed to accommodate these changes in gear ratios, ensuring proper torque transmission and maintaining compatibility between the transmission, transfer case (if applicable), and the differential. This customization helps maintain optimal drivetrain performance and prevents potential driveline vibrations or failures that may arise from mismatched gear ratios.
7. Professional Consultation and Expertise:
Customizing rear drive shafts for specific vehicle configurations or upgrades often requires professional consultation and expertise. Working with experienced drivetrain specialists, automotive engineers, or aftermarket manufacturers can help ensure that the customization aligns with the vehicle’s requirements and performance goals. These experts can provide valuable insights and recommendations, taking into account factors such as vehicle weight, powertrain modifications, intended use, and budget constraints.
In summary, rear drive shafts can be customized to suit specific vehicle configurations or upgrades. Customization options include adjusting the length and diameter, selecting appropriate materials, choosing the right type and size of U-joints or CV joints, balancing the drive shaft, incorporating performance enhancements, ensuring compatibility with differential ratios, and seeking professional consultation and expertise. By customizing rear drive shafts, vehicle owners can optimize drivetrain performance, ensure compatibility with modified configurations, and meet the unique demands of their specific applications or upgrades.

What Is a Rear Drive Shaft and How Does It Contribute to Vehicle Propulsion?
A rear drive shaft is a component of a vehicle’s drivetrain system that connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. It plays a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine to the rear wheels, contributing to the vehicle’s propulsion. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a rear drive shaft is and how it contributes to vehicle propulsion:
1. Drivetrain Connection:
The rear drive shaft serves as a mechanical link between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential. It is typically a tubular shaft that rotates at high speeds to transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels.
When the engine generates power, it is transmitted through the transmission or transfer case, which determines the appropriate gear ratio. The rear drive shaft then transmits this torque to the rear differential, which further distributes power to the rear wheels.
2. Torque Transmission:
The primary function of the rear drive shaft is to transmit torque from the engine to the rear wheels. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, and it is essential for propelling the vehicle forward.
As the engine produces torque, it is transferred to the transmission or transfer case. From there, the torque is sent through the rear drive shaft to the rear differential. The rear differential then splits the torque and sends it to the rear wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle.
3. Power Distribution:
The rear drive shaft plays a critical role in distributing power evenly between the rear wheels. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft ensures that power is distributed to both wheels, enabling balanced propulsion.
By transmitting torque from the engine to the rear differential, the rear drive shaft allows the differential to distribute power to both rear wheels based on traction conditions. This power distribution ensures that both wheels contribute to vehicle propulsion and provides stability and control during acceleration and cornering.
4. Suspension Movement Compensation:
Another important function of the rear drive shaft is to compensate for the movement of the suspension system. The suspension system allows the wheels to move up and down independently to absorb bumps, uneven road surfaces, and other disturbances.
As the suspension moves, the distance between the transmission or transfer case and the rear differential changes. The rear drive shaft accommodates this movement by expanding or contracting its length, allowing the rear wheels to move vertically while maintaining a continuous torque transmission.
5. Drive System Efficiency:
An efficiently operating rear drive shaft contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s drivetrain system. By effectively transmitting torque from the engine to the rear wheels, it minimizes power losses and ensures optimal power delivery.
Efficiency in power transmission reduces energy waste and maximizes the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. A well-maintained rear drive shaft with proper lubrication and alignment helps minimize friction and mechanical losses, maximizing the effectiveness of the drivetrain system.
6. Four-Wheel Drive Capability:
In vehicles equipped with four-wheel drive systems, the rear drive shaft is a crucial component for engaging the front wheels for propulsion. In these systems, the rear drive shaft transfers torque to the transfer case, which then distributes power to the front and rear differentials.
By transmitting torque to the transfer case, the rear drive shaft enables four-wheel drive capability, allowing the vehicle to engage all four wheels for enhanced traction and off-road performance.
In summary, a rear drive shaft is a key component in a vehicle’s drivetrain system. It serves as a drivetrain connection, transmits torque from the engine to the rear wheels, distributes power between the rear wheels, compensates for suspension movement, enhances drive system efficiency, and facilitates four-wheel drive capability. By fulfilling these functions, the rear drive shaft contributes to the vehicle’s propulsion, stability, and overall performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China best China Supplier Non-Standard Custom Made Rear Axle Shaft
Product Description
Q: How can I get samples?
A: Free samples and freight collect, except for special circumstances.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity for the items in the order?
A: 2000pcs for each part except for sample.
Q: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a manufacturer, specialized in manufacturing and exporting of qualified precision micro shafts.
Q: What are your usual terms of payment?
A: We generally ask for payment by T/T in advance and L/C at sight.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are There Any Signs of Wear or Damage That Indicate a Need for Rear Drive Shaft Replacement?
Over time, rear drive shafts can experience wear and damage due to various factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Recognizing the signs of wear or damage is crucial as it helps determine whether a rear drive shaft replacement is necessary. Here are some detailed explanations of the signs that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement:
1. Vibrations and Shaking:
If you notice excessive vibrations or shaking coming from underneath the vehicle, it can be a sign of an unbalanced or worn-out rear drive shaft. Imbalances can occur due to damaged or worn-out universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints. As the drive shaft rotates, these imbalances can cause vibrations to transfer to the vehicle’s body, resulting in noticeable shaking or tremors. If the vibrations persist even after balancing the tires and inspecting other drivetrain components, it may indicate that the rear drive shaft needs replacement.
2. Clunking or Knocking Noises:
Unusual clunking or knocking noises while accelerating, decelerating, or shifting gears could be indicative of a damaged or worn-out rear drive shaft. These noises may suggest issues with the U-joints, CV joints, or slip yoke. Worn-out U-joints can cause a clunking sound when there is excessive play or movement in the joint. Similarly, worn-out CV joints or slip yokes can generate knocking noises as they fail to maintain proper engagement and alignment. If you hear persistent clunking or knocking noises, it is advisable to have the rear drive shaft inspected and replaced if necessary.
3. Excessive Vibration During Acceleration:
If you experience strong vibrations specifically during acceleration, it could indicate an issue with the rear drive shaft. Worn-out U-joints or CV joints can cause the drive shaft to lose its balance, resulting in vibrations during acceleration. These vibrations may intensify as the vehicle’s speed increases. It is important to address this issue promptly, as continued use of a damaged rear drive shaft can lead to further damage to other drivetrain components.
4. Grease Leakage:
Grease leakage around the U-joints or CV joints of the rear drive shaft can be a sign of wear or damage. U-joints and CV joints are typically equipped with grease fittings to ensure proper lubrication. If the joints are damaged or worn, they may develop cracks or gaps that allow grease to escape. Grease leakage can lead to insufficient lubrication, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of the joints. If you notice signs of grease leakage around the rear drive shaft joints, it is recommended to have them inspected and replace the drive shaft if necessary.
5. Visible Cracks, Bends, or Dents:
Inspecting the physical condition of the rear drive shaft can reveal signs of wear or damage. Visual cues such as cracks, bends, or dents on the drive shaft indicate structural weakness and compromise its performance. These damages can occur due to impacts from road debris, rough driving conditions, or excessive torque loads. If any visible damage is present on the rear drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed by a qualified technician. Depending on the severity of the damage, the drive shaft may need to be replaced.
6. Excessive Play or Movement:
Excessive play or movement in the rear drive shaft is a clear indication of wear or damage. You can check for play by firmly gripping the drive shaft near the U-joints or CV joints and attempting to move it back and forth or rotate it. If there is noticeable play or excessive movement, it suggests that the joints are worn-out, the splines are damaged, or the slip yoke is loose. Excessive play can affect the drivetrain’s operation and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. In such cases, a rear drive shaft replacement may be necessary.
7. Maintenance History and Mileage:
Consider the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle when evaluating the need for rear drive shaft replacement. Rear drive shafts, like other components, have a finite lifespan and may require replacement after a certain mileage or duration of use. If the vehicle has reached a high mileage, or if there is a lack of maintenance records indicating regular inspection and lubrication of the drive shaft, it is advisable to have it assessed for wear or damage.
In summary, signs of wear or damage that indicate a need for rear drive shaft replacement include excessive vibrations and shaking, clunking or knocking noises, excessive vibration during acceleration, grease leakage, visible cracks, bends, or dents, and excessive play or movement in the drive shaft. Additionally, considering the maintenance history and mileage of the vehicle can provide valuable insights into the potential need for rear drive shaft replacement. If any of these signs are observed, it is recommended to have the rear drive shaft inspected by a qualified technician to determine the appropriate course of action, which may include replacement to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain system.
Can You Provide Real-World Examples of Vehicles Where Rear Drive Shafts Are Crucial?
Rear drive shafts play a crucial role in various types of vehicles, particularly those that utilize rear-wheel drive (RWD) or four-wheel drive (4WD) systems. Here are real-world examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial:
1. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Many sports cars and high-performance vehicles rely on rear-wheel drive configurations for their dynamic handling and performance characteristics. Rear drive shafts are crucial components in these vehicles as they transfer power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient acceleration and delivering torque for precise handling. Examples of sports cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Corvette, Porsche 911, Ford Mustang, and BMW M3.
2. Pickup Trucks and SUVs:
Pickup trucks and SUVs often employ rear-wheel drive or 4WD systems for their towing and off-road capabilities. Rear drive shafts are essential in these vehicles as they transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power distribution to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved traction and towing capacity. Examples of vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial in the pickup truck and SUV segment include the Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado, Toyota Tacoma, and Jeep Wrangler.
3. Commercial Vehicles and Vans:
Many commercial vehicles and vans utilize rear-wheel drive for their cargo-carrying capacity and towing capabilities. Rear drive shafts are critical in these vehicles as they transmit power from the engine to the rear wheels, enabling efficient propulsion and load-carrying capabilities. Examples of commercial vehicles and vans where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter, Ford Transit, Chevrolet Express, and Ram ProMaster.
4. Muscle Cars and Classic Cars:
Muscle cars and classic cars often feature rear-wheel drive configurations, and rear drive shafts are essential components in these vehicles. They transfer torque from the engine to the rear wheels, providing the iconic rear-wheel drive performance and driving experience typically associated with these vehicles. Examples of muscle cars and classic cars where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Chevrolet Camaro, Ford Mustang, Dodge Challenger, and Chevrolet Chevelle.
5. Off-Road and 4×4 Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles and 4×4 vehicles rely on rear drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These vehicles often have a transfer case that distributes power to both the front and rear axles. Rear drive shafts play a critical role in transmitting torque from the transfer case to the rear differential, enabling power delivery to the rear wheels. This configuration allows for improved off-road traction and maneuverability. Examples of off-road and 4×4 vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Jeep Wrangler, Land Rover Defender, Toyota Land Cruiser, and Ford Bronco.
6. Luxury and Executive Vehicles:
Many luxury and executive vehicles feature rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive configurations, where rear drive shafts are essential components. Rear drive shafts transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or rear axle, providing power distribution to the rear wheels. These vehicles prioritize comfort, performance, and refined driving experiences. Examples of luxury and executive vehicles where rear drive shafts are crucial include the Mercedes-Benz S-Class, BMW 7 Series, Audi A8, and Lexus LS.
In summary, rear drive shafts are crucial in a wide range of vehicles, including sports cars, pickup trucks, SUVs, commercial vehicles, muscle cars, off-road vehicles, and luxury vehicles. They play a vital role in power transmission, torque delivery, and overall performance, enabling efficient acceleration, traction, and handling. Rear drive shafts are integral components in these vehicles, contributing to their specific characteristics and capabilities.
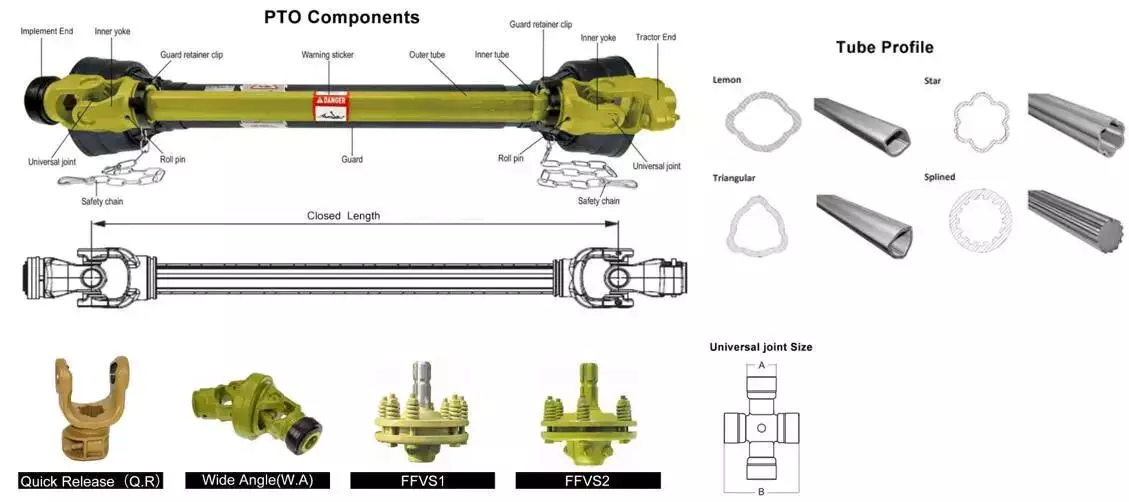
How Do Rear Drive Shafts Handle Variations in Torque, Speed, and Alignment?
Rear drive shafts are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or transmission to the rear wheels while accommodating the dynamic forces and movements encountered during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rear drive shafts handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment:
Variations in Torque:
Rear drive shafts are engineered to withstand and transmit varying levels of torque generated by the engine. Torque variations occur during acceleration, deceleration, and changes in load. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts are typically constructed with high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum to provide the necessary strength and rigidity. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure torque capacity and reliability. Additionally, universal joints (u-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints are incorporated into the drive shaft assembly to allow for rotational movement and accommodate changes in angles and torque loads.
Variations in Speed:
Rear drive shafts are designed to adapt to variations in rotational speed between the engine or transmission and the rear wheels. As the vehicle accelerates or decelerates, the rotational speed of the drive shaft changes. To handle these variations, the length and design of the rear drive shaft are carefully calculated to minimize vibrations and maintain smooth power delivery. The drive shaft may incorporate features such as balancing weights or dampers to reduce or eliminate vibrations caused by speed fluctuations. Additionally, the use of u-joints or CV joints allows for angular movement and accommodates speed differentials between the two ends of the drive shaft.
Variations in Alignment:
Rear drive shafts must also accommodate variations in alignment caused by suspension movement, chassis flex, and drivetrain articulation. As the suspension compresses or extends, the drivetrain components can shift in relation to each other, causing changes in the alignment of the rear drive shaft. To handle these variations, rear drive shafts incorporate flexible components such as u-joints or CV joints. These joints allow for angular movement and articulation, accommodating changes in the relative positions of the transmission, differential, and rear wheels. The use of flexible couplings or slip yokes at each end of the drive shaft also helps to compensate for alignment changes and prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft components.
Vibration and Harmonic Damping:
Vibrations and harmonic forces can be generated within the drivetrain, especially at higher speeds. Rear drive shafts are designed to mitigate these vibrations and dampen harmonic forces to ensure a smooth and balanced ride. Various techniques are employed to achieve this, including the use of properly balanced drive shafts, vibration-absorbing materials, and damping devices such as rubber or elastomer dampers. These measures help reduce the transmission of vibrations and harmonics throughout the drivetrain, enhancing the overall comfort, stability, and longevity of the rear drive shaft.
In summary, rear drive shafts are engineered to handle variations in torque, speed, and alignment within a vehicle’s drivetrain. They are constructed with high-strength materials, incorporate flexible joints, and employ techniques to dampen vibrations and harmonics. By accommodating these variations, rear drive shafts ensure efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reliable performance in various driving conditions.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China supplier OEM ODM Cardan Transmission Tractor Parts Pto Drive Shaft for Agriculture Machinery
Product Description
OEM ODM Cardan Transmission Tractor Parts Pto Drive Shaft for Agriculture Machinery
1. Tubes or Pipes
We’ve already got Triangular profile tube and Lemon profile tube for all the series we provide.
And we have some star tube, splined tube and other profile tubes required by our customers (for a certain series). (Please notice that our catalog doesnt contain all the items we produce)
If you want tubes other than triangular or lemon, please provide drawings or pictures.
2.End yokes
We’ve got several types of quick release yokes and plain bore yoke. I will suggest the usual type for your reference.
You can also send drawings or pictures to us if you cannot find your item in our catalog.
3. Safety devices or clutches
I will attach the details of safety devices for your reference. We’ve already have Free wheel (RA), Ratchet torque limiter(SA), Shear bolt torque limiter(SB), 3types of friction torque limiter (FF,FFS,FCS) and overrunning couplers(adapters) (FAS).
4.For any other more special requirements with plastic guard, connection method, color of painting, package, etc., please feel free to let me know.
Features:
1. We have been specialized in designing, manufacturing drive shaft, steering coupler shaft, universal joints, which have exported to the USA, Europe, Australia etc for years
2. Application to all kinds of general mechanical situation
3. Our products are of high intensity and rigidity.
4. Heat resistant & Acid resistant
5. OEM orders are welcomed
Our factory is a leading manufacturer of PTO shaft yoke and universal joint.
We manufacture high quality PTO yokes for various vehicles, construction machinery and equipment. All products are constructed with rotating lighter.
We are currently exporting our products throughout the world, especially to North America, South America, Europe, and Russia. If you are interested in any item, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are looking CZPT to becoming your suppliers in the near future.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Fork |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Power Source: | Pto Shaft Tube |
| Transport Package: | Standard Sea Worthy Package |
| Specification: | ISO |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-03-27